Polymyxin B Sulfate
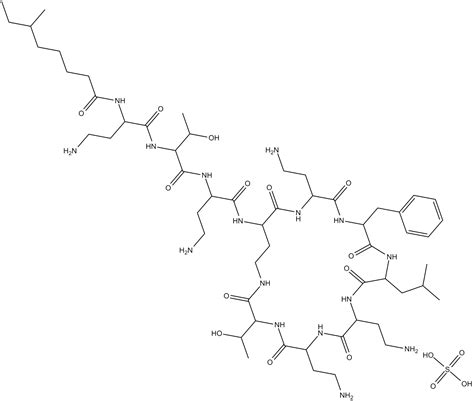
Polymyxin B sulfate is an antibiotic medication that belongs to the polymyxin class of drugs. It is used to treat various types of infections caused by gram-negative bacteria, which are a type of bacteria that have a unique outer membrane structure. Polymyxin B sulfate works by disrupting the outer membrane of the bacterial cell, ultimately leading to the death of the bacteria.
One of the key features of polymyxin B sulfate is its ability to target a wide range of gram-negative bacteria, including strains that are resistant to other types of antibiotics. This makes it a valuable treatment option for infections that are caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria. However, polymyxin B sulfate is not effective against gram-positive bacteria or fungal infections, and it is not typically used to treat infections caused by these types of microorganisms.
Polymyxin B sulfate is often used in combination with other antibiotics to treat complex infections. For example, it may be used in combination with a beta-lactam antibiotic, such as piperacillin or ticarcillin, to treat infections caused by bacteria that produce beta-lactamase enzymes. These enzymes can break down beta-lactam antibiotics, making them less effective against certain types of bacteria. By combining polymyxin B sulfate with a beta-lactam antibiotic, healthcare providers can create a treatment regimen that is more effective against a wider range of bacteria.
When using polymyxin B sulfate to treat infections, it is essential to monitor the patient's kidney function and adjust the dosage accordingly. This is because polymyxin B sulfate can be nephrotoxic, meaning that it can cause damage to the kidneys. By carefully monitoring the patient's kidney function and adjusting the dosage as needed, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of nephrotoxicity and ensure that the patient receives the most effective treatment possible.
In addition to its use as an antibiotic, polymyxin B sulfate has also been studied for its potential use in other medical applications. For example, researchers have investigated the use of polymyxin B sulfate as a treatment for sepsis, which is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to an infection becomes uncontrolled and causes widespread inflammation. Polymyxin B sulfate has also been studied as a potential treatment for cancer, as it has been shown to have anti-tumor activity in some laboratory studies.
History of Polymyxin B Sulfate

Polymyxin B sulfate was first discovered in the 1940s, when a team of researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, isolated the compound from a strain of bacteria called Bacillus polymyxa. The researchers found that the compound had potent antibacterial activity, and they began to study its potential use as an antibiotic. Over the next several decades, polymyxin B sulfate was developed and refined, and it became a widely used treatment for infections caused by gram-negative bacteria.
Comparative Analysis of Polymyxin B Sulfate with Other Antibiotics
Polymyxin B sulfate is often compared to other antibiotics that are used to treat infections caused by gram-negative bacteria. One of the key advantages of polymyxin B sulfate is its ability to target a wide range of bacteria, including strains that are resistant to other types of antibiotics. However, polymyxin B sulfate can also have some disadvantages, such as its potential to cause nephrotoxicity.
Advantages of Polymyxin B Sulfate:
- Effective against a wide range of gram-negative bacteria
- Can be used to treat infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria
- Can be used in combination with other antibiotics to create a synergistic effect
Disadvantages of Polymyxin B Sulfate:
- Can cause nephrotoxicity, particularly at high doses or with prolonged use
- May not be effective against gram-positive bacteria or fungal infections
- Can be more expensive than other antibiotics, particularly when used in combination with other medications
FAQs
What is polymyxin B sulfate used to treat?
+Polymyxin B sulfate is used to treat infections caused by gram-negative bacteria, including pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections.
How does polymyxin B sulfate work?
+Polymyxin B sulfate works by disrupting the outer membrane of the bacterial cell, ultimately leading to the death of the bacteria.
What are the potential side effects of polymyxin B sulfate?
+The potential side effects of polymyxin B sulfate include nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and neurotoxicity. Patients should be carefully monitored for these side effects, particularly when using high doses or prolonged treatment.
In conclusion, polymyxin B sulfate is a valuable antibiotic medication that is used to treat infections caused by gram-negative bacteria. Its ability to target a wide range of bacteria, including strains that are resistant to other types of antibiotics, makes it a valuable treatment option for complex infections. However, polymyxin B sulfate can also have some disadvantages, such as its potential to cause nephrotoxicity. By carefully monitoring patients and adjusting the dosage as needed, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of side effects and ensure that patients receive the most effective treatment possible.


