Ppo And Hmo
When it comes to health insurance, two of the most common types of plans are Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) and Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs). Both types of plans have their own unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, which can make it challenging for individuals to decide which one is best for their needs.
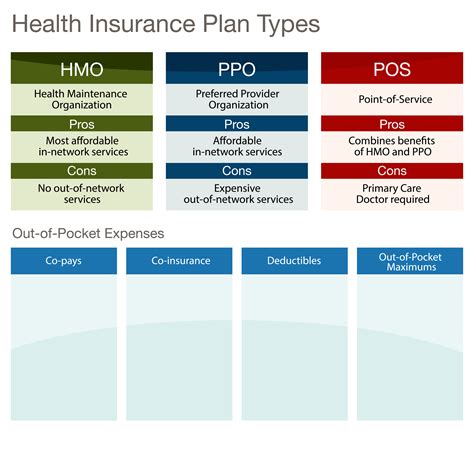
To begin with, let’s take a closer look at PPOs. A PPO is a type of health insurance plan that allows policyholders to receive medical care from any healthcare provider, both in-network and out-of-network. In-network providers are those who have a contract with the insurance company to provide services at a discounted rate, while out-of-network providers do not have such a contract. Policyholders who choose to see an out-of-network provider will typically have to pay a higher deductible and copayment.
One of the primary advantages of PPOs is the flexibility they offer. Policyholders are not required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) or obtain a referral to see a specialist. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who have existing relationships with healthcare providers or who require specialized care. Additionally, PPOs often provide more comprehensive coverage, including services such as preventive care, hospital stays, and prescription medications.
However, PPOs can also be more expensive than other types of health insurance plans. Policyholders typically pay higher premiums, deductibles, and copayments, especially if they choose to see out-of-network providers. Furthermore, PPOs often have higher out-of-pocket maximums, which can leave policyholders with significant medical bills if they require extensive care.
On the other hand, HMOs are a type of health insurance plan that provides coverage for medical services from a specific network of healthcare providers. HMOs require policyholders to choose a PCP, who coordinates their medical care and provides referrals to specialists as needed. HMOs often have lower premiums, deductibles, and copayments compared to PPOs, making them a more affordable option for many individuals.
One of the primary advantages of HMOs is their focus on preventive care. HMOs often provide coverage for routine check-ups, screenings, and health education programs, which can help policyholders stay healthy and avoid costly medical procedures. Additionally, HMOs typically have lower out-of-pocket maximums, which can provide policyholders with greater financial protection in the event of a medical emergency.
However, HMOs can also be more restrictive than PPOs. Policyholders are typically required to see healthcare providers within the HMO’s network, and may need to obtain a referral from their PCP to see a specialist. This can limit policyholders’ access to specialized care or second opinions, and may require them to switch healthcare providers if they move or their provider leaves the network.
In terms of cost, HMOs are often less expensive than PPOs, especially for individuals who do not require extensive medical care. However, HMOs can also have higher costs for policyholders who require specialized care or out-of-network services. Additionally, HMOs may have limited provider networks, which can make it difficult for policyholders to find healthcare providers who meet their needs.
PPO Pros and Cons
- Flexibility to see any healthcare provider, both in-network and out-of-network
- No requirement to choose a primary care physician or obtain a referral to see a specialist
- Comprehensive coverage, including preventive care, hospital stays, and prescription medications
- Higher premiums, deductibles, and copayments, especially for out-of-network services
- Higher out-of-pocket maximums, which can leave policyholders with significant medical bills
HMO Pros and Cons
- Lower premiums, deductibles, and copayments compared to PPOs
- Focus on preventive care, including routine check-ups, screenings, and health education programs
- Lower out-of-pocket maximums, which can provide policyholders with greater financial protection
- Restrictive network of healthcare providers, which can limit access to specialized care or second opinions
- Requirement to choose a primary care physician and obtain referrals to see specialists
In conclusion, both PPOs and HMOs have their own strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice for an individual will depend on their unique needs and circumstances. By carefully considering the pros and cons of each type of plan, individuals can make informed decisions about their health insurance coverage and ensure that they receive the care they need at a price they can afford.
What is the primary difference between a PPO and an HMO?
+The primary difference between a PPO and an HMO is the flexibility to see healthcare providers. PPOs allow policyholders to see any healthcare provider, both in-network and out-of-network, while HMOs require policyholders to see healthcare providers within the HMO's network.
Which type of plan is more expensive, a PPO or an HMO?
+PPOs are often more expensive than HMOs, especially for individuals who require extensive medical care or out-of-network services. However, HMOs can also have higher costs for policyholders who require specialized care or out-of-network services.
What is the advantage of choosing an HMO over a PPO?
+The advantage of choosing an HMO over a PPO is the focus on preventive care and the lower premiums, deductibles, and copayments. HMOs often provide coverage for routine check-ups, screenings, and health education programs, which can help policyholders stay healthy and avoid costly medical procedures.
Ultimately, the decision between a PPO and an HMO will depend on an individual’s unique needs and circumstances. By carefully considering the pros and cons of each type of plan, individuals can make informed decisions about their health insurance coverage and ensure that they receive the care they need at a price they can afford.


