Ppo Vs Hmo: Compare Plans
When navigating the complex world of health insurance, two terms that frequently come up are PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) and HMO (Health Maintenance Organization). Both types of plans have their own set of benefits and drawbacks, and understanding the differences between them is crucial for making an informed decision about your healthcare coverage. In this article, we’ll delve into the specifics of PPO and HMO plans, comparing their structures, advantages, and disadvantages to help you make the best choice for your needs.
Introduction to PPO Plans
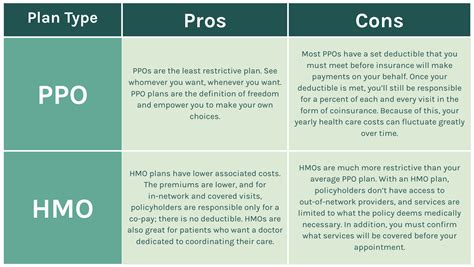
PPO plans are a type of health insurance that offers a balance between freedom of choice and cost savings. With a PPO, you have the option to visit any healthcare provider you wish, both in-network and out-of-network, though seeing an in-network provider will generally save you money. PPOs are known for their flexibility; they do not require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) or obtain referrals to see specialists.
How PPO Plans Work
- Network: PPOs have a network of healthcare providers who have agreed to offer discounted services to plan members.
- Out-of-Network Coverage: One of the defining features of PPOs is their ability to cover services from out-of-network providers, albeit at a higher cost to the patient.
- Cost: The cost of a PPO plan can vary widely based on factors like the network size, deductible, copays, and coinsurance rates.
Introduction to HMO Plans
HMOs, on the other hand, are designed to provide comprehensive healthcare at a lower cost, with an emphasis on preventive care. To achieve this, HMOs operate within a more structured framework. You’re required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) from the plan’s network, and this PCP acts as a gatekeeper for your healthcare needs. Generally, to see a specialist, you’ll need a referral from your PCP.
How HMO Plans Work
- Network: Similar to PPOs, HMOs have a network of providers, but the network is typically smaller and more localized.
- Primary Care Physician (PCP): Your PCP is central to your care, managing your health and referring you to specialists when necessary.
- Referrals and Out-of-Network Care: HMOs usually do not cover out-of-network care except in emergency situations, and referrals from your PCP are necessary to see specialists.
Comparative Analysis: PPO vs. HMO
Flexibility and Freedom of Choice
- PPO: Offers more flexibility with the option to see any healthcare provider, in-network or out-of-network, without the need for a referral.
- HMO: Less flexible, requiring a PCP and often needing referrals to see specialists, with limited to no out-of-network coverage.
Cost Considerations
- PPO: Generally more expensive than HMOs, with higher premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs, especially for out-of-network care.
- HMO: Typically less expensive, with lower premiums and out-of-pocket expenses, thanks to the restricted network and emphasis on preventive care.
Access to Specialists
- PPO: Easier access to specialists without needing referrals, though seeing an in-network specialist will be more cost-effective.
- HMO: Requires a referral from your PCP to see a specialist, which can sometimes delay access but is designed to ensure that specialist care is truly necessary.
Decision Framework
When deciding between a PPO and an HMO, consider the following factors:
- Healthcare Needs: If you have ongoing health issues that require frequent visits to specialists, a PPO might offer the flexibility you need. For preventive care and less complex health needs, an HMO could be more cost-effective.
- Budget: Evaluate your budget against the plan’s premiums, deductibles, copays, and coinsurance rates. If cost is a significant concern, HMOs are often the more affordable option.
- Provider Network: Consider whether your current healthcare providers are part of the plan’s network. If you have a preferred doctor or hospital, ensure they are included in the network to minimize out-of-pocket costs.
- Lifestyle and Preferences: If you value the freedom to choose your healthcare providers and don’t mind potentially higher costs, a PPO might suit you better. If you’re open to working within a more structured system for cost savings, an HMO could be preferable.
FAQ Section
What does PPO stand for in health insurance?
+PPO stands for Preferred Provider Organization. It's a type of health plan that offers a network of healthcare providers who have agreed to offer discounted services to plan members.
Do HMO plans cover out-of-network care?
+HMO plans typically do not cover out-of-network care except in emergency situations. For non-emergency care, you're usually required to stay within the plan's network to receive coverage.
How do I choose between a PPO and an HMO?
+To choose between a PPO and an HMO, consider your healthcare needs, budget, the provider network, and your personal preferences regarding flexibility and cost. Evaluate which plan aligns better with your current situation and priorities.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the decision between a PPO and an HMO depends on your individual health needs, financial situation, and personal preferences. By understanding the core differences and considerations outlined in this comparison, you can make an informed decision that best suits your health insurance requirements. Whether you prioritize flexibility and access to a broader range of providers or prefer a more cost-effective, structured approach to healthcare, there’s a plan out there designed to meet your needs.