Premature Labor Signs: Know The Symptoms
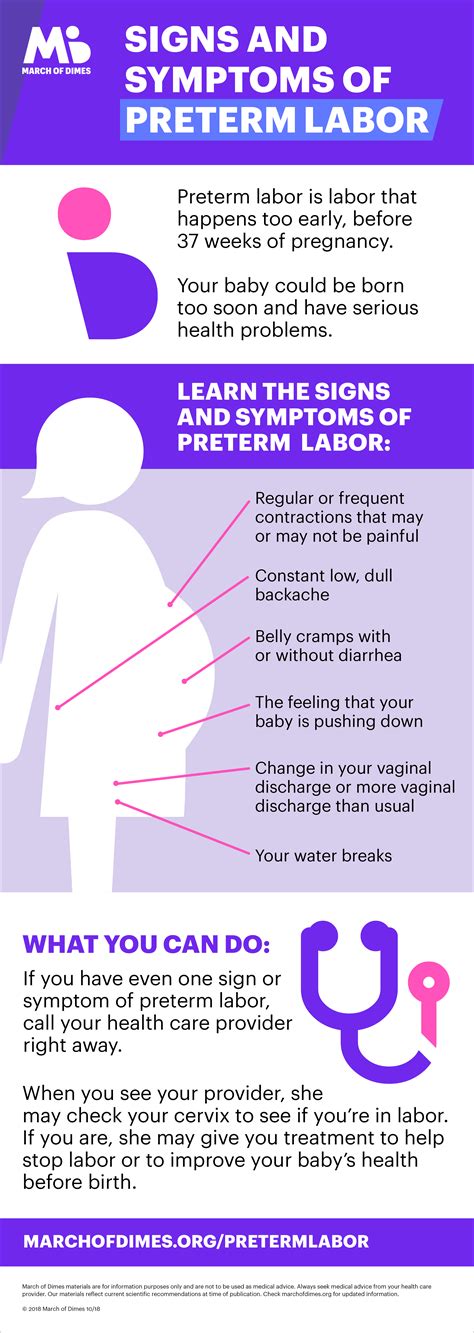
Premature labor, also known as preterm labor, is a serious health concern that can have significant consequences for both the mother and the baby. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of premature labor to seek medical attention promptly. Premature labor is labor that begins before 37 weeks of gestation, and it can be a life-threatening condition if not treated promptly.
Understanding the symptoms of premature labor can help expectant mothers take proactive steps to ensure a healthy pregnancy. The symptoms of premature labor can be subtle, and they may resemble other conditions, making it crucial to be aware of the warning signs. Some of the common symptoms of premature labor include:
- Contractions: Contractions that are regular, persistent, and intensifying can be a sign of premature labor. These contractions may feel like menstrual cramps or a tight band around the abdomen.
- Back pain: Back pain that is persistent, severe, and radiates to the abdomen can be a symptom of premature labor.
- Vaginal bleeding: Vaginal bleeding or spotting can be a sign of premature labor, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms.
- Abdominal cramping: Abdominal cramping that is severe, persistent, and accompanied by other symptoms can be a sign of premature labor.
- Pressure in the pelvis: A feeling of pressure in the pelvis or a sensation that the baby is pushing down can be a symptom of premature labor.
Risk Factors for Premature Labor
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of premature labor. These risk factors include:
- Previous preterm birth: Women who have had a previous preterm birth are at a higher risk of experiencing premature labor.
- Multiple pregnancies: Women carrying twins, triplets, or other multiples are at a higher risk of premature labor.
- Cervical insufficiency: Women with a history of cervical insufficiency or cervical surgery are at a higher risk of premature labor.
- Uterine abnormalities: Women with uterine abnormalities, such as a uterus that is abnormally shaped, are at a higher risk of premature labor.
- Infections: Women with infections, such as urinary tract infections or vaginal infections, are at a higher risk of premature labor.
Prevention and Management
While it is not possible to prevent all cases of premature labor, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk. These steps include:
- Regular prenatal care: Regular prenatal check-ups can help identify potential risks and prevent complications.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can help reduce the risk of premature labor.
- Avoiding smoking and substance abuse: Smoking and substance abuse can increase the risk of premature labor, and avoiding these behaviors can help reduce the risk.
- Managing chronic conditions: Managing chronic conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, can help reduce the risk of premature labor.
Conclusion
Premature labor is a serious health concern that requires prompt medical attention. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of premature labor can help expectant mothers take proactive steps to ensure a healthy pregnancy. By understanding the risk factors and taking steps to reduce the risk, women can help prevent premature labor and ensure a healthy outcome for both themselves and their babies.
FAQ Section

What are the most common symptoms of premature labor?
+The most common symptoms of premature labor include regular contractions, back pain, vaginal bleeding, abdominal cramping, and pressure in the pelvis.
What are the risk factors for premature labor?
+Risk factors for premature labor include previous preterm birth, multiple pregnancies, cervical insufficiency, uterine abnormalities, and infections.
How can I reduce the risk of premature labor?
+To reduce the risk of premature labor, schedule regular prenatal check-ups, maintain a healthy lifestyle, avoid smoking and substance abuse, manage chronic conditions, and stay informed about the signs and symptoms of premature labor.
What should I do if I experience symptoms of premature labor?
+If you experience symptoms of premature labor, seek medical attention promptly. Contact your healthcare provider or go to the emergency room if you are experiencing severe symptoms or if your water breaks.
Can premature labor be treated?
+Yes, premature labor can be treated. Treatment options may include medication to stop contractions, bed rest, and hospitalization. In some cases, premature labor may require immediate delivery.



