Draw A Free-Body Diagram Of The System Skydiver-Parachute
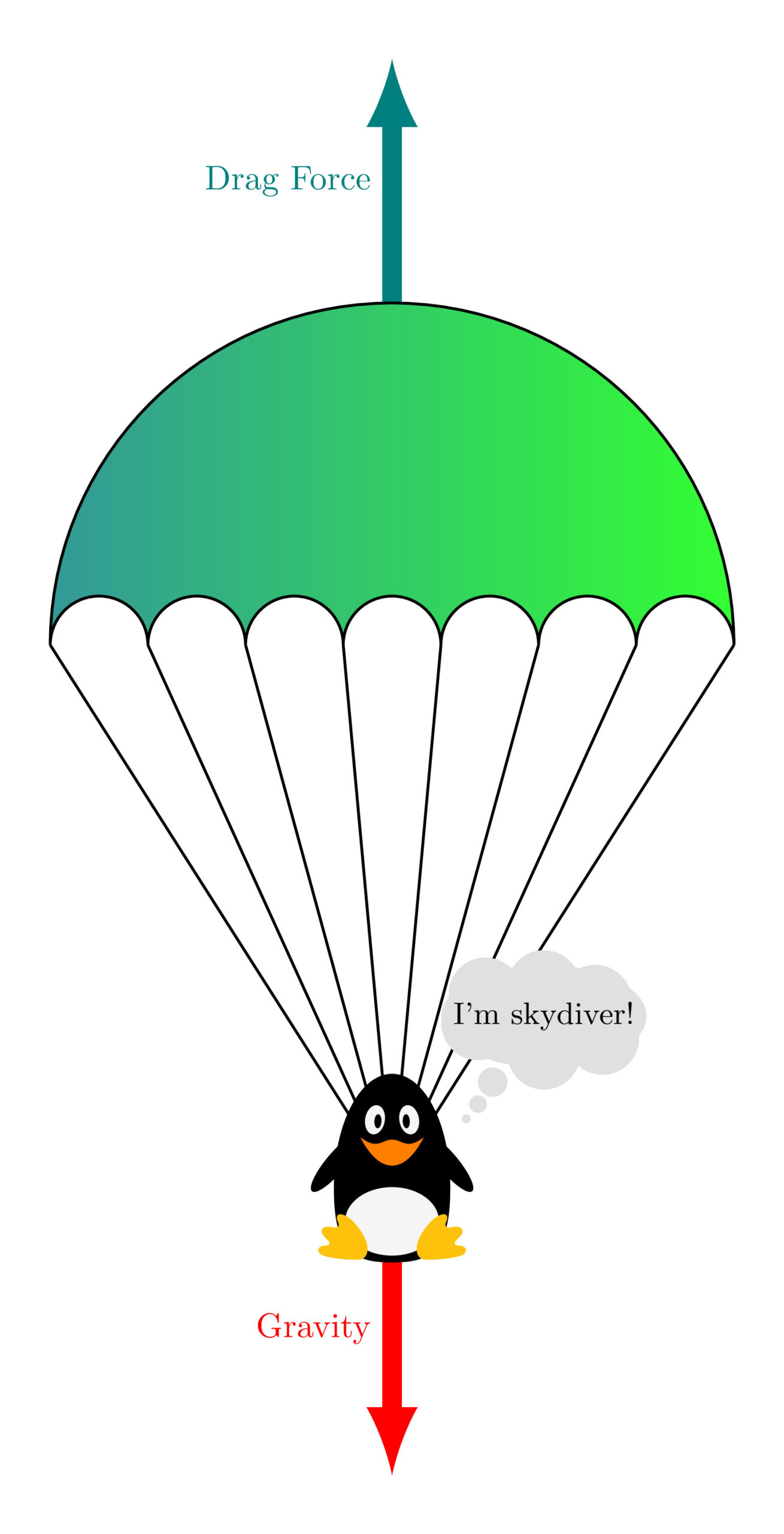
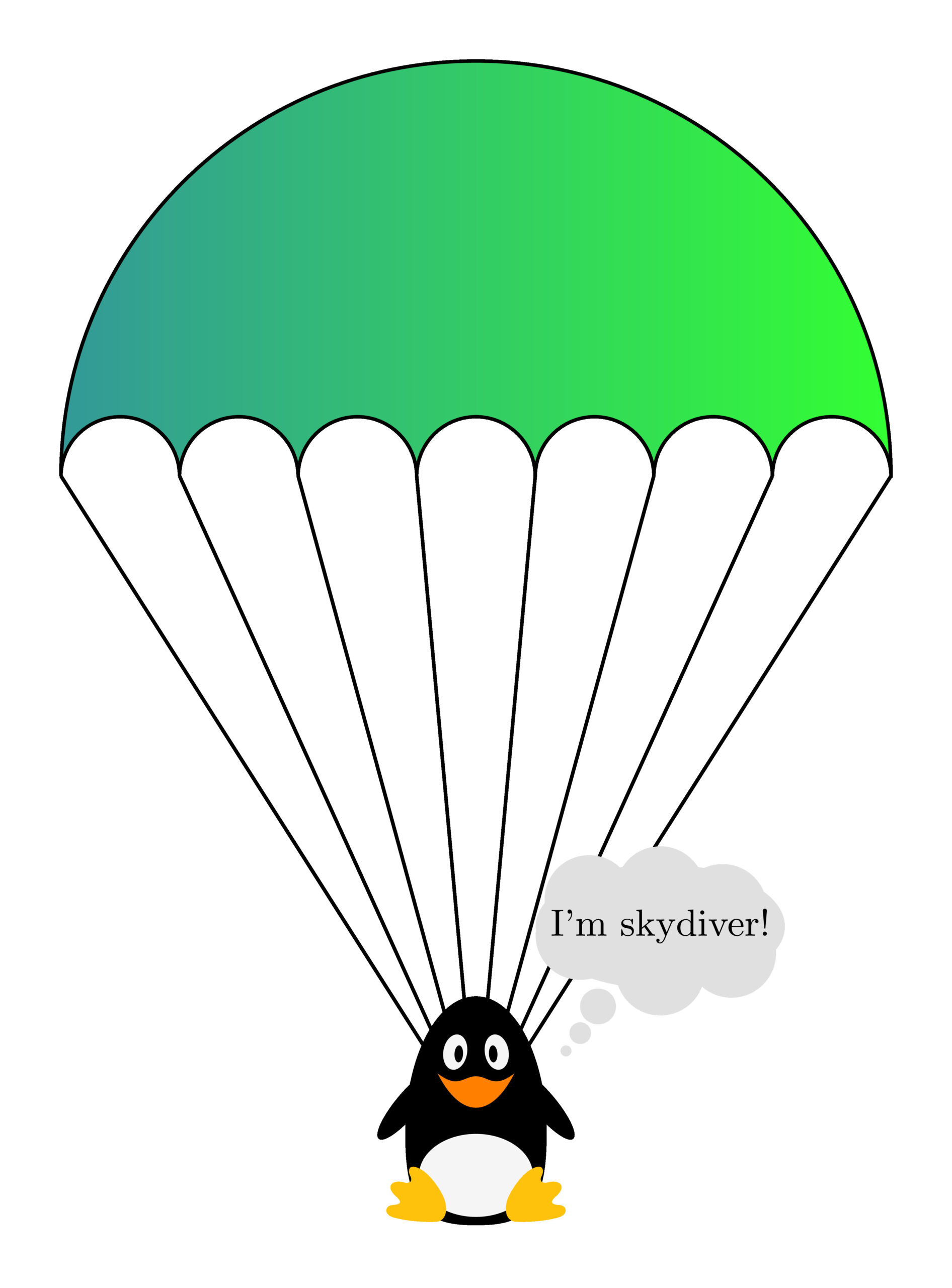
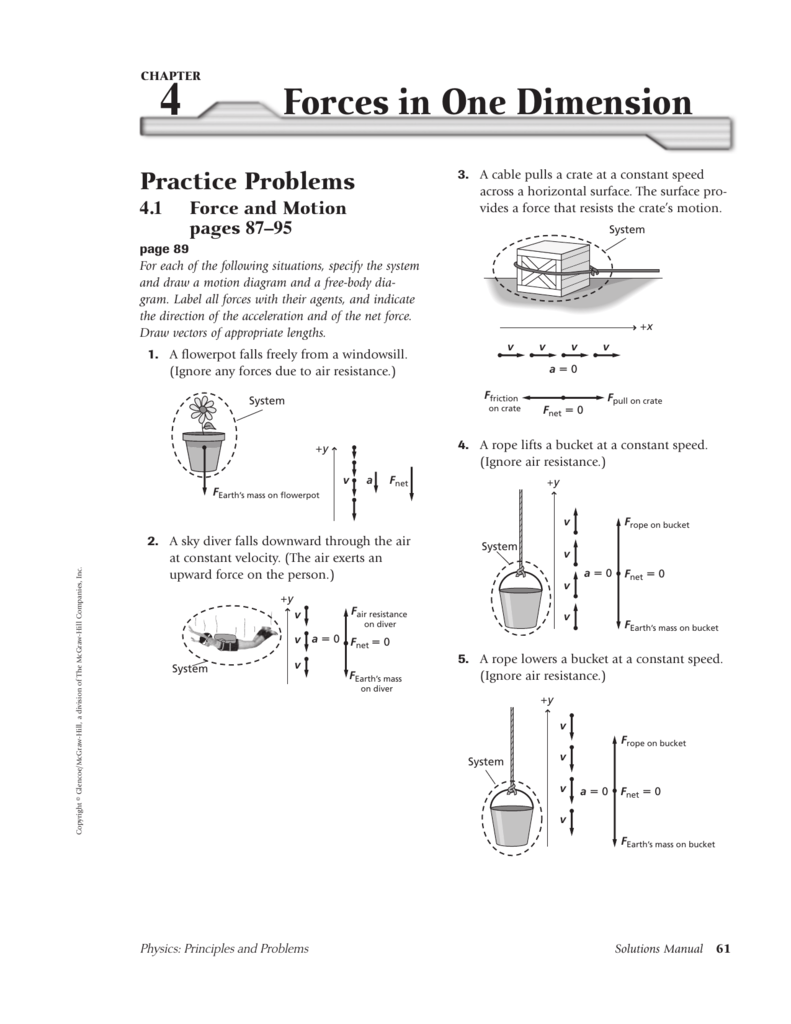
Draw A Free-Body Diagram Of The System Skydiver-Parachute - The parachute pulls upward on the skydiver with a force of 620 n. Web construct a free body diagram showing the forces on a skydiver who has just opened their parachute. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. That is, fnet = 0 f net = 0) or newton’s second law if the body is accelerating (unbalanced force; Web consider the apparatus that connects the parachute to the skydiver to be part of the parachute.
After pulling the parachute, they descend 46 meters in 4 seconds. Web draw a free body diagram of the following: Web construct a free body diagram showing the forces on a skydiver who has just opened their parachute. (i put below the steps [1st pic] that were given on mastering physics) can you also write a small description like in the second picture for the skydiving. Learners view the size of the two individual forces, the velocity, and the height over the course of the falling motion. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. What is the force of air resistance on the diver?
Draw A Free Body Diagram Of The System Skydiver Parachute Wiring Site
A skydiver still riding in the plane a skydiver has jumped from the plane and is in free fall a skydiver jumped from the plane and has reached terminal velocity (max speed) a skydiver initially.
Draw A Free Body Diagram Of The System Skydiver Parachute
In this case, there are two forces acting on the skydiver: Post any question and get expert help quickly. Provide each group with materials to make parachutes (plastic or tissue paper, ruler, scissors, twine, and.
Draw A Free Body Diagram Of The System Skydiver Parachute Free
Web the skydiving interactive simulates the motion of a falling skydiver. Draw a free body diagram labelling all the forces on the skydiver. Mainly, we will learn how to: The parachute pulls upward on the.
How Do Skydivers Know Where to Land?
This question hasn't been solved yet ask an expertask an expert not the exact question you're looking for? Draw the vectors starting at the black dot. The relative magnitudes of all forces should be drawn.
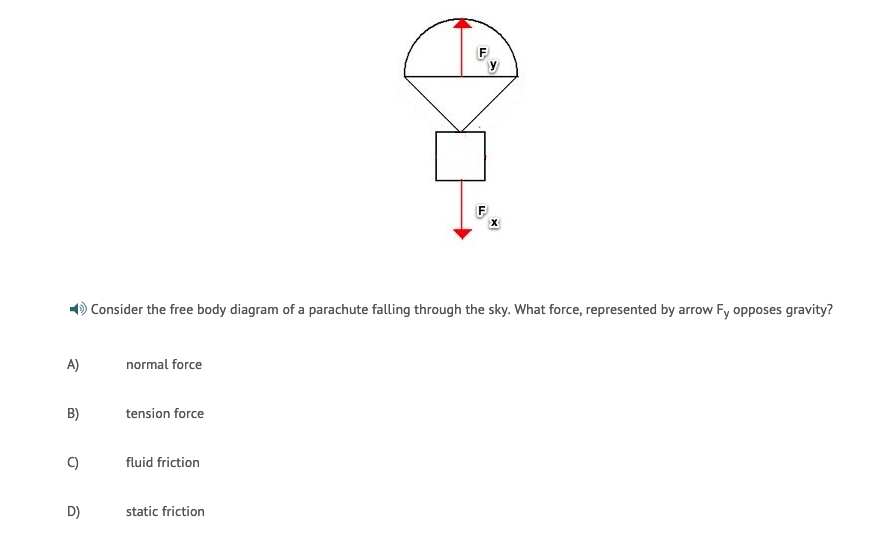
Solved Consider the free body diagram of a parachute falling
Web this tikz tutorial is about drawing a free body diagram of a skydiver with parachute. 1) draw an arc in latex using tikz, 2) use foreach loop for repetitive objects, 3) draw animals using.
Draw A Free Body Diagram Of The System Skydiver Parachute Wiring
After pulling the parachute, they descend 46 meters in 4 seconds. That is, fnet ≠ 0 f net ≠ 0 ). In this case, there are two forces acting on the skydiver: Web draw a.
Forces when Skydiving physics lesson diagram including skydiver
Draw your ideas on the worksheet. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded. The location and orientation of the vectors.
TikZ Free Body Diagram Skydiver with Parachute TikZBlog
Draw the vectors starting at the black dot. Here is the latex code: Web this tikz tutorial is about drawing a free body diagram of a skydiver with parachute. Web study with quizlet and memorize.
Draw A Free Body Diagram Of The System Skydiver Parachute Wiring
G is the acceleration due to gravity, which is 9.8 m/s 2 m is his mass d is the drag force acting upwards w is the force of gravity pulling him down v is the.
TikZ Free Body Diagram Skydiver with Parachute TikZBlog
1) draw an arc in latex using tikz, 2) use foreach loop for repetitive objects, 3) draw animals using the package tikzlings, and much more! Drawing the object & surface because we’re moving through space,.
Draw A Free-Body Diagram Of The System Skydiver-Parachute The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. After pulling the parachute, they descend 46 meters in 4 seconds. (i put below the steps [1st pic] that were given on mastering physics) can you also write a small description like in the second picture for the skydiving. G is the acceleration due to gravity, which is 9.8 m/s 2 m is his mass d is the drag force acting upwards w is the force of gravity pulling him down v is the speed at which he falls vt is the constant (terminal) speed he reaches when d = w Web discuss with your partner how and why you think a parachute allows a skydiver to softly land.