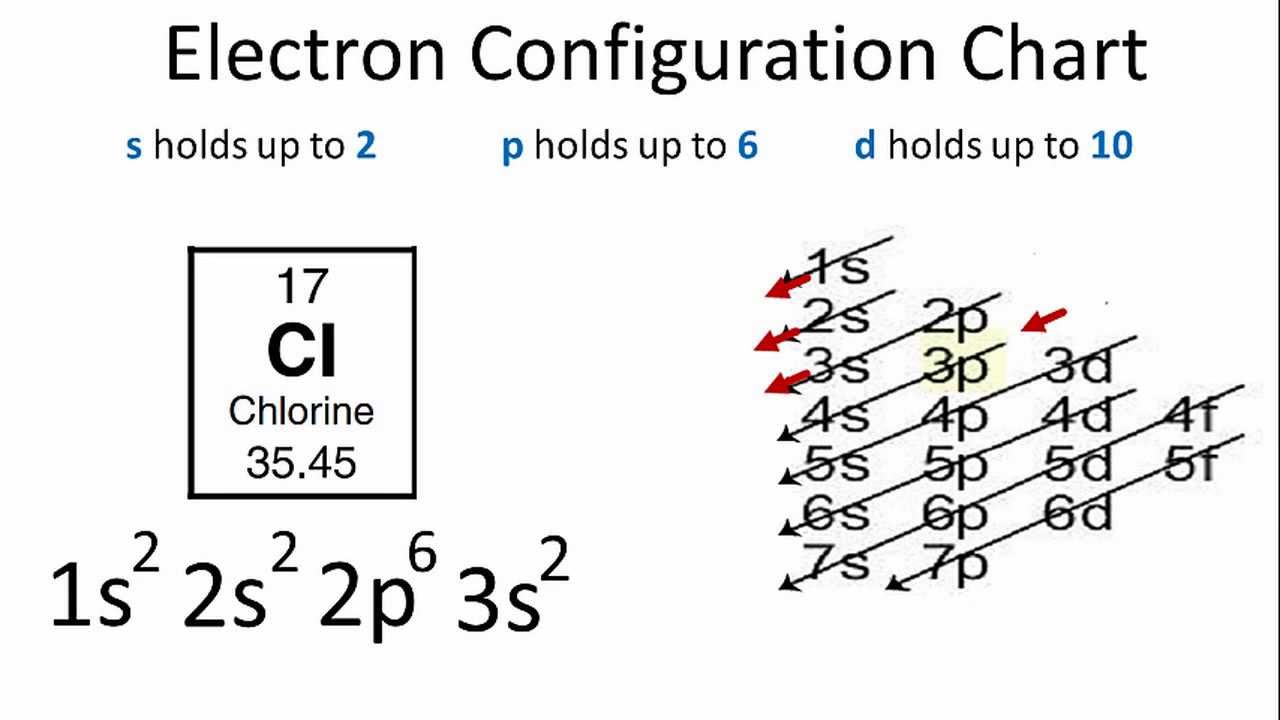
Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Chlorine
Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Chlorine - View the full answer step 2. Web electron configuration of nitrogen (n) [he] 2s 2 2p 3: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, and so on. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3:
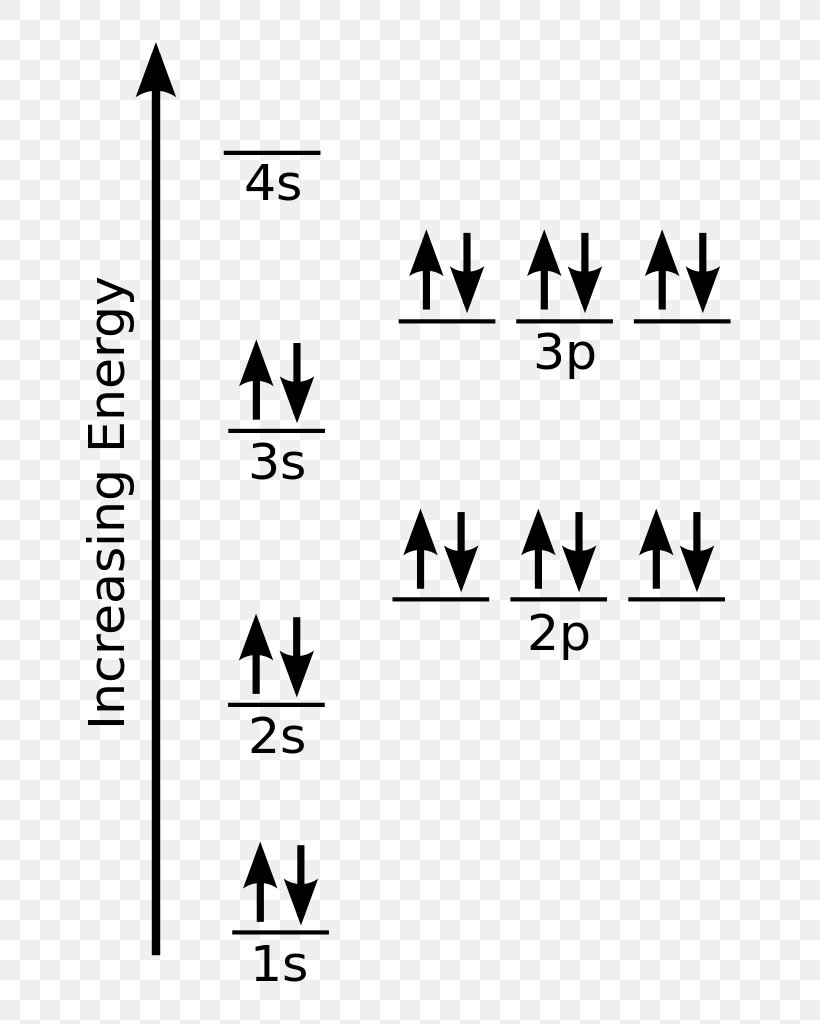
Of those 7 electrons, 2 can go into the 3s subshell, and the remaining 5 electrons can go into the 3p subshell. Two electrons can go into the 1s subshell, 2 can go into the 2s subshell, and 6 can go into the 2p subshell. Thus, the electron configuration for cl− should be. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5: The third electron goes into the second energy level, which can hold up to 8 electrons. Using figure \(\pageindex{2}\) as your guide, write the electron configuration of a neutral chlorine atom. Remove the outermost electrons in the cation, e.g.
Chlorine Cl (Element 17) of Periodic Table NewtonDesk
As per the aufbau rule, the electrons will be filled into 1s orbital first then 2s, then 2p…so on. Web the arrangement of electrons in chlorine in specific rules in different orbits and orbitals is.
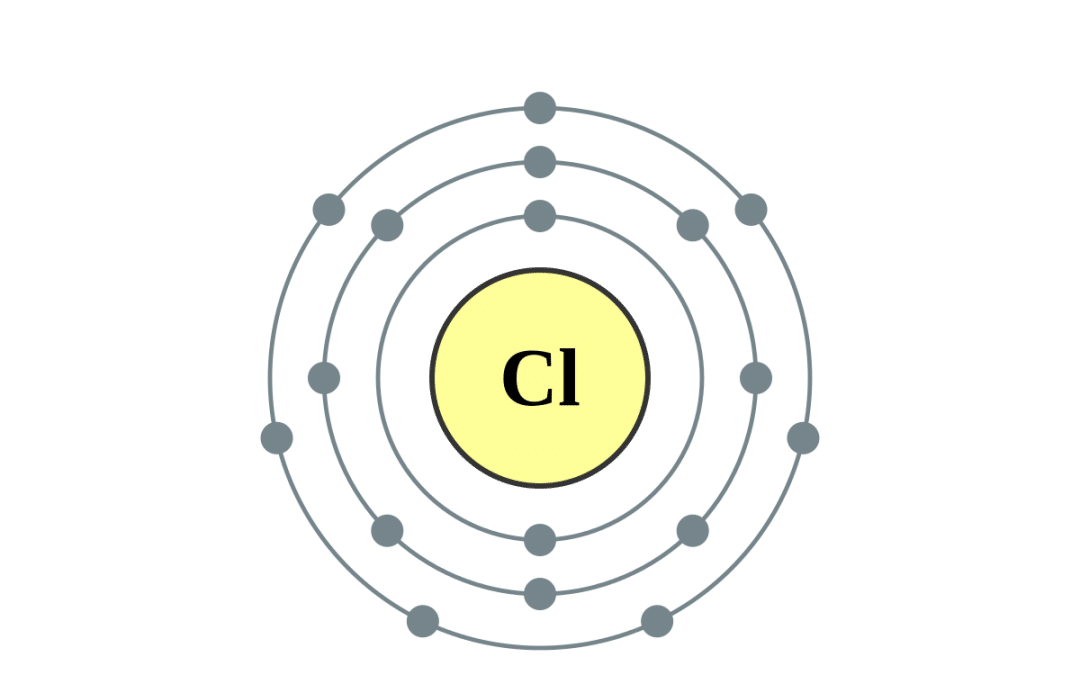
Draw a Bohr diagram of chlorine. Quizlet
Web first, we need to find the atomic number of chlorine. Web chemical engineering chemical engineering questions and answers draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of chlorine. Web the upper right side shows.
Atom Diagrams Electron Configurations of the Elements
Web full ground state electron configuration: The atomic number of cl is 17. Web a neutral chlorine atom has 17 electrons. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn.
draw atomic structure of chlorine Brainly.in
Web a chlorine atom is a neutral atom that has an atomic number of 17 which implies it has a total of 17 electrons. Web for nitrogen this would be 2.5 or 2,5 and for.
Electron Configuration For Chlorine
Thus, the electron configuration of neutral chlorine atoms. For cl −, it will be 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶. The atomic number of chlorine is 17, which means it has 17 electrons in its neutral state. The electron configuration.
Chlorine Electron Configuration (Cl) with Orbital Diagram
Web using figure \(\pageindex{2}\) as your guide, write the electron configuration of a neutral chlorine atom. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 = 18 electrons. The first two electrons are in the first energy level, which.
Chlorine Electron Configuration YouTube
Write the electron configuration for a neutral atom of chlorine. Web the neutral atom chlorine (z=17), for instance has 17 electrons. Therefore, the first energy level is filled with 2 electrons. Web the electron configurations.
Chlorine Protons Neutrons Electrons Electron Configuration
This problem has been solved! Using figure \(\pageindex{2}\) as your guide, write the electron configuration of a neutral chlorine atom. Web electron configuration for chlorine. The atomic number of cl is 17. 1s 2 2s.
Chlorine Periodic Table Electron Configuration Elcho Table
It is also 17, since the number of protons (which is also 17) is equal to the. Using figure \(\pageindex{2}\) as your guide, write the electron configuration of a neutral chlorine atom. This problem has.
15 Interesting Facts About Chlorine
Find the atomic number of chlorine from the periodic table. Using figure \(\pageindex{2}\) as your guide, write the electron configuration of a neutral chlorine atom. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert.
Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Chlorine Web the electron configurations of silicon (14 electrons), phosphorus (15 electrons), sulfur (16 electrons), chlorine (17 electrons), and argon (18 electrons) are analogous in the electron configurations of their outer shells to their corresponding family members carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon, respectively, except that the principal. Therefore, its ground state electronic configuration can be written as 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 5. Therefore, the first energy level is filled with 2 electrons. Remove the outermost electrons in the cation, e.g. We'll need to know how many sublevel is present in each energy level, and in turn, how many electrons each sublevel can.


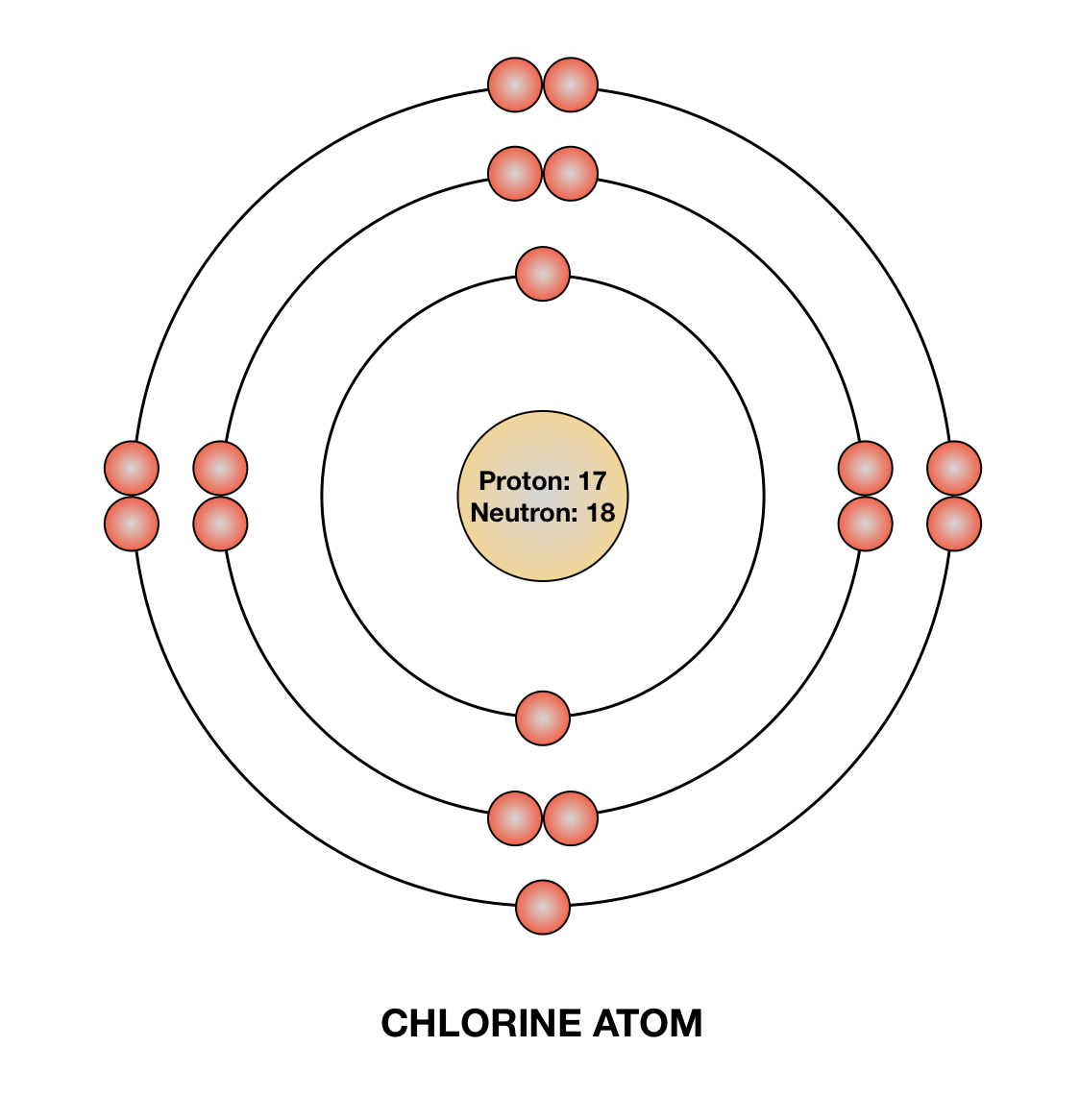
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chlorineatom-58b602515f9b5860464c5c02.jpg)