Protein Total Blood Test
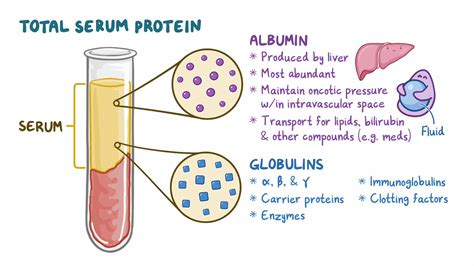
The protein total blood test, also known as the total protein test, is a diagnostic tool used to measure the total amount of protein in the blood. Proteins are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and maintaining fluid balance. The test is typically performed to evaluate liver and kidney function, as well as to diagnose and monitor various diseases and conditions that affect protein levels in the blood.
What is the Protein Total Blood Test?
The protein total blood test measures the total amount of protein in the blood, including albumin and globulin. Albumin is a type of protein produced by the liver that helps maintain fluid balance in the body and transports hormones, vitamins, and other substances throughout the body. Globulin is a type of protein that plays a crucial role in the immune system, helping to fight infections and diseases. The test is usually performed on a blood sample taken from a vein in the arm, and the results are typically available within a few hours.
Why is the Protein Total Blood Test Performed?
The protein total blood test is performed for various reasons, including:
- Liver disease diagnosis: The test can help diagnose liver diseases such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, and liver cancer, which can cause changes in protein levels in the blood.
- Kidney disease diagnosis: The test can help diagnose kidney diseases such as nephrotic syndrome and kidney failure, which can also affect protein levels in the blood.
- Nutrition and malnutrition assessment: The test can help evaluate a person’s nutritional status and diagnose malnutrition, which can cause changes in protein levels in the blood.
- Infection and inflammation diagnosis: The test can help diagnose infections and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, which can cause changes in protein levels in the blood.
- Cancer diagnosis: The test can help diagnose certain types of cancer, such as multiple myeloma, which can cause changes in protein levels in the blood.
How is the Protein Total Blood Test Performed?
The protein total blood test is typically performed in a clinical laboratory or hospital setting. The test involves the following steps:
- Blood sample collection: A blood sample is taken from a vein in the arm using a needle and syringe.
- Sample preparation: The blood sample is then prepared for testing by adding chemicals that help to separate the proteins from other substances in the blood.
- Protein measurement: The total protein level in the blood is then measured using a technique called spectroscopy, which involves measuring the amount of light absorbed by the proteins in the sample.
- Result interpretation: The results of the test are then interpreted by a healthcare professional, who will compare the total protein level in the blood to a normal range to determine if any abnormalities are present.
Understanding Protein Total Blood Test Results
The results of the protein total blood test are typically reported in grams per deciliter (g/dL) or grams per liter (g/L). The normal range for total protein in the blood varies depending on the laboratory and the individual, but it is typically between 6 and 8.3 g/dL. Abnormal results may indicate a range of conditions, including:
- Low protein levels: Low protein levels in the blood can indicate malnutrition, liver disease, or kidney disease.
- High protein levels: High protein levels in the blood can indicate dehydration, inflammation, or cancer.
- Abnormal protein ratios: Abnormal ratios of albumin to globulin can indicate liver or kidney disease.
What is the normal range for total protein in the blood?
+The normal range for total protein in the blood varies depending on the laboratory and the individual, but it is typically between 6 and 8.3 g/dL.
What can cause changes in protein levels in the blood?
+Changes in protein levels in the blood can be caused by a range of factors, including liver and kidney disease, malnutrition, infection, inflammation, and cancer.
How is the protein total blood test performed?
+The protein total blood test is typically performed in a clinical laboratory or hospital setting, and involves taking a blood sample from a vein in the arm, preparing the sample for testing, measuring the total protein level in the blood using spectroscopy, and interpreting the results.
Conclusion
The protein total blood test is a valuable diagnostic tool that can help evaluate liver and kidney function, as well as diagnose and monitor various diseases and conditions that affect protein levels in the blood. By understanding the test and its results, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care and treatment. Additionally, individuals can take steps to maintain healthy protein levels in the blood by eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions.
In the context of the protein total blood test, it is essential to consider the importance of liver and kidney function, as well as the role of nutrition and hydration in maintaining healthy protein levels. By taking a comprehensive approach to health and wellness, individuals can reduce their risk of developing conditions that affect protein levels in the blood, and maintain optimal overall health.
Furthermore, the protein total blood test can be used in conjunction with other diagnostic tools, such as imaging studies and physical examinations, to provide a complete picture of a patient’s health. By combining the results of the protein total blood test with other diagnostic information, healthcare professionals can develop effective treatment plans that address the underlying causes of abnormalities in protein levels.
Ultimately, the protein total blood test is a powerful tool that can help healthcare professionals diagnose and manage a range of conditions, and individuals can take steps to maintain healthy protein levels in the blood by adopting a balanced lifestyle and seeking regular medical care.
By exploring the protein total blood test in depth, we can gain a better understanding of the complex relationships between protein levels, liver and kidney function, and overall health. This knowledge can be used to develop innovative treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes, and can help individuals take a proactive approach to maintaining their health and wellness.
In conclusion, the protein total blood test is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide valuable insights into protein levels in the blood, and can be used to diagnose and manage a range of conditions. By understanding the test and its results, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care, and individuals can take steps to maintain healthy protein levels in the blood.
It is essential to note that the protein total blood test is just one diagnostic tool, and should be used in conjunction with other tests and examinations to provide a complete picture of a patient's health. By taking a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment, healthcare professionals can develop effective treatment plans that address the underlying causes of abnormalities in protein levels.
Steps to maintain healthy protein levels in the blood:
- Eat a balanced diet that includes a variety of protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, fish, and eggs.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and other fluids.
- Manage underlying medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, with the help of a healthcare professional.
- Get regular exercise to help maintain overall health and wellness.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, which can damage the liver and affect protein levels in the blood.
By following these steps, individuals can help maintain healthy protein levels in the blood, and reduce their risk of developing conditions that affect protein levels. Additionally, healthcare professionals can use the protein total blood test as a valuable diagnostic tool to diagnose and manage a range of conditions, and develop effective treatment plans that address the underlying causes of abnormalities in protein levels.



