Pt For Tennis Elbow
Physical therapy (PT) plays a crucial role in the management and rehabilitation of tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis. This condition is characterized by pain and inflammation on the outer part of the elbow, where the muscles and tendons of the forearm attach to the lateral epicondyle. The primary goal of PT for tennis elbow is to reduce pain, promote healing, restore strength and flexibility, and improve overall function of the elbow and forearm.
Initial Assessment and Diagnosis
Before starting any PT program, a thorough assessment is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of tennis elbow and to rule out other potential causes of elbow pain. This assessment includes a review of the patient’s medical history, a physical examination to identify points of tenderness and assess range of motion and strength, and possibly imaging studies such as X-rays or MRI to evaluate for any structural damage.
Phase 1: Pain Reduction and Protection (Acute Phase)
In the initial phase of PT for tennis elbow, the focus is on reducing pain and inflammation, protecting the affected area from further injury, and promoting the initial stages of healing.
- Pain Management: Techniques such as ice, compression, and elevation may be recommended to reduce swelling and pain. Physical modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation may also be used to facilitate healing and reduce pain.
- Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition is crucial. This might include taking a break from tennis or other racquet sports, or modifying work activities that involve repetitive wrist and forearm motions.
- Stretching and Mobility Exercises: Gentle stretching of the wrist and forearm can help maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness.
Phase 2: Strengthening and Progression (Subacute Phase)
As pain and inflammation decrease, the focus shifts towards strengthening the muscles of the forearm and improving overall elbow function.
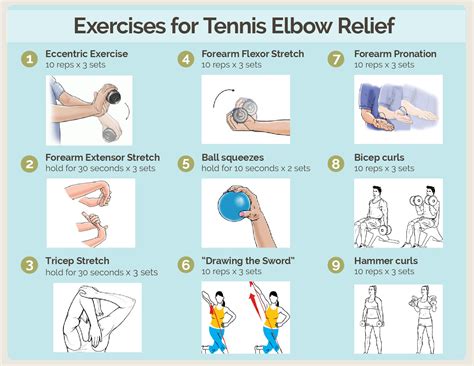
- Strengthening Exercises: Isometric, isotonic, and eccentric exercises are introduced to strengthen the extensor muscles of the forearm. Eccentric exercises, in particular, have been shown to be effective in the management of tennis elbow.
- Progressive Resistance Exercises: Using light weights, resistive bands, or grip strengtheners can help improve grip strength and forearm endurance.
- Plyometric and Functional Exercises: Once adequate strength has been achieved, plyometric exercises (like wrist flips) and functional activities (such as gripping, lifting, and throwing) can be introduced to mimic the demands of tennis and other sports.
Phase 3: Advanced Strengthening and Return to Sport (Chronic Phase)
In the final phase of rehabilitation, the focus is on advanced strengthening, improving athletic performance, and preventing future episodes of tennis elbow.
- Advanced Strengthening Techniques: Incorporating varying grip positions, wrist angles, and speeds can enhance the specificity of the strengthening program.
- Agility and Speed Drills: Exercises that mimic the quick changes of direction and speed encountered in tennis can be incorporated to enhance reaction time and agility.
- Sport-Specific Training: Gradually returning to tennis or other racquet sports involves starting with low-intensity, short sessions and progressively increasing duration, frequency, and intensity.
Manual Therapy andModalities
Throughout the rehabilitation process, manual therapy techniques such as massage, joint mobilization, and soft tissue mobilization can be beneficial in reducing pain, improving range of motion, and enhancing the healing process. Other modalities like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, shockwave therapy, and acupuncture may also be considered for patients who do not respond to traditional PT interventions.
Home Exercise Program
An essential component of PT for tennis elbow is a home exercise program. Patients are taught a series of exercises to perform at home, which helps in maintaining consistency with the rehabilitation program, promoting independence, and ensuring a quicker return to function and sport.
Prevention
Preventing tennis elbow involves a combination of proper training techniques, equipment selection, and physical conditioning. Strengthening the forearm muscles, improving flexibility, and using appropriate grip sizes and string tensions can reduce the risk of developing tennis elbow.
In conclusion, physical therapy for tennis elbow is a comprehensive and staged approach that aims to address the underlying causes of the condition, promote healing, restore function, and prevent recurrence. By combining pain management, strengthening exercises, functional training, and education on prevention strategies, individuals with tennis elbow can effectively manage their symptoms and return to their preferred activities and sports.
What are the primary causes of tennis elbow?
+Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is primarily caused by repetitive strain on the forearm extensors, leading to inflammation and micro-tears in the tendons. This can result from activities involving repetitive wrist and forearm motions, such as tennis, racquetball, and certain occupational tasks.
How long does it take to recover from tennis elbow with physical therapy?
+The recovery time for tennis elbow can vary significantly depending on the severity of the condition, the effectiveness of the treatment plan, and the individual’s adherence to the rehabilitation program. Generally, with proper physical therapy, most people can experience significant improvement within 6-12 weeks.
Can tennis elbow be prevented?
+While not all cases of tennis elbow can be prevented, the risk can be significantly reduced through proper training techniques, equipment selection, and physical conditioning. Strengthening the forearm muscles, improving flexibility, and using appropriate grip sizes and string tensions are among the preventive measures.