Regular Blood Glucose Level
Maintaining a regular blood glucose level is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the amount of glucose present in the blood. It is an essential source of energy for the body’s cells, and its levels are tightly regulated by the body’s hormonal system.
The Importance of Regular Blood Glucose Levels
Regular blood glucose levels are vital for several reasons. Firstly, they help to prevent the complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Secondly, they enable individuals with diabetes to manage their condition effectively, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Finally, regular blood glucose levels help to maintain energy levels, supporting physical and mental performance.
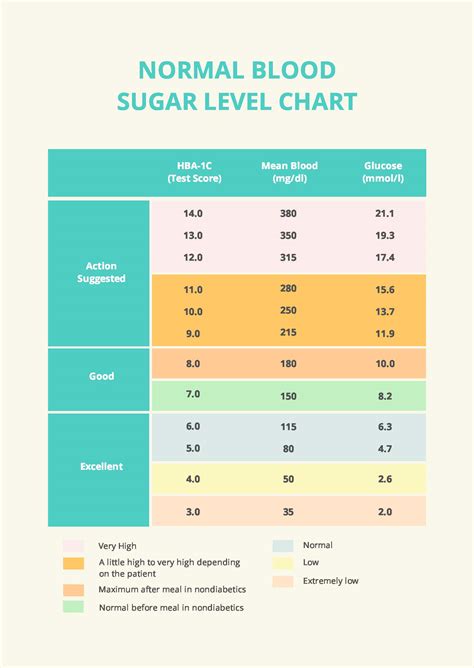
Normal Blood Glucose Levels
Normal blood glucose levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as food intake, physical activity, and sleep. The following are the typical ranges for blood glucose levels:
- Fasting blood glucose: 70-99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter)
- Postprandial blood glucose (after eating): Less than 140 mg/dL
- Random blood glucose: Less than 140 mg/dL
Factors That Affect Blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can influence blood glucose levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can cause blood glucose levels to rise.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise can help to lower blood glucose levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise blood glucose levels.
- Stress: Stress can cause blood glucose levels to increase.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality or duration can affect blood glucose regulation.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or puberty can impact blood glucose levels.
Strategies for Maintaining Regular Blood Glucose Levels
To maintain regular blood glucose levels, individuals can adopt the following strategies:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Monitor blood glucose levels: Regularly check blood glucose levels to identify patterns and make adjustments to diet and lifestyle as needed.
The Role of Technology in Blood Glucose Management
Technology has revolutionized blood glucose management, enabling individuals to track their levels more easily and make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle. Some examples of technology used in blood glucose management include:
- Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs): Small devices that track blood glucose levels throughout the day.
- Blood glucose meters: Portable devices that measure blood glucose levels using a small blood sample.
- Mobile apps: Apps that track blood glucose levels, provide personalized recommendations, and offer support and motivation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+Symptoms of high blood sugar include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, fatigue, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How often should I check my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on individual factors, such as the type of diabetes, medication regimen, and lifestyle. Generally, individuals with diabetes should check their blood glucose levels at least 4-6 times per day.
What are the risks of low blood sugar?
+Low blood sugar can cause confusion, dizziness, shakiness, and even loss of consciousness. If left untreated, it can lead to seizures, coma, and even death.
By following a comprehensive approach to blood glucose management, individuals can maintain optimal health, reduce their risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or lifestyle.



