Sed Rate High: Understand Your Test Results
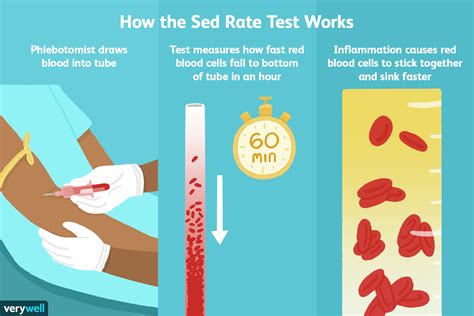
Elevated sed rates can be a cause for concern, and understanding what this test measures and what the results imply is crucial for managing your health. The sed rate, short for erythrocyte sedimentation rate, is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body.
The sed rate is used to detect inflammation in the body, which can be caused by a variety of conditions, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancers. A high sed rate indicates that there is inflammation present, but it does not specify the cause or location of the inflammation. The test is often used in conjunction with other tests, such as the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, to help diagnose and monitor conditions.
What Does a High Sed Rate Indicate?
A sed rate that is higher than normal can indicate the presence of inflammation in the body. The normal range for the sed rate varies depending on the laboratory and the individual’s age and sex. Generally, a sed rate of 0-20 mm/h is considered normal for adults, while a rate above 20 mm/h may indicate inflammation.
There are several conditions that can cause a high sed rate, including:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can cause inflammation and lead to a high sed rate.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and scleroderma can cause chronic inflammation and a high sed rate.
- Cancer: Some types of cancer, such as lymphoma and leukemia, can cause inflammation and a high sed rate.
- Chronic diseases: Conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can cause chronic inflammation and a high sed rate.
Understanding Your Test Results
When interpreting your sed rate test results, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Age and sex: The normal range for the sed rate varies depending on age and sex. For example, older adults and women tend to have higher sed rates than younger adults and men.
- Other test results: The sed rate should be considered in conjunction with other test results, such as the CRP test, to get a comprehensive understanding of inflammation in the body.
- Medical history: Your medical history, including any underlying conditions or medications, can affect the sed rate.
What to Do If You Have a High Sed Rate
If you have a high sed rate, your doctor may order additional tests to determine the cause of the inflammation. These tests may include:
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to visualize the affected area.
- Blood tests: Additional blood tests to check for infections, autoimmune diseases, or cancer.
- Biopsy: A biopsy to examine tissue or cells for signs of inflammation or disease.
Treatment for a high sed rate depends on the underlying cause of the inflammation. Your doctor may prescribe medications to reduce inflammation, such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In some cases, lifestyle changes, such as exercise, diet, and stress reduction, may be recommended to help manage inflammation.
Taking Control of Your Health
While a high sed rate can be concerning, there are steps you can take to manage inflammation and reduce your sed rate. These include:
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
- Eat an anti-inflammatory diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce inflammation.
- Manage stress: Stress can exacerbate inflammation; practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help.
- Get enough sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for reducing inflammation and promoting overall health.
A high sed rate indicates inflammation in the body, which can be caused by a variety of conditions. Understanding your test results and working with your doctor to determine the underlying cause of the inflammation is crucial for managing your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a normal sed rate range?
+A normal sed rate range varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and sex. Generally, a sed rate of 0-20 mm/h is considered normal for adults.
What causes a high sed rate?
+A high sed rate can be caused by a variety of conditions, including infections, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and chronic diseases.
How is a high sed rate treated?
+Treatment for a high sed rate depends on the underlying cause of the inflammation. Medications, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both may be recommended to reduce inflammation and manage the underlying condition.
In conclusion, a high sed rate can be a cause for concern, but understanding what the test measures and what the results imply is crucial for managing your health. By working with your doctor to determine the underlying cause of the inflammation and taking steps to manage inflammation, you can reduce your sed rate and improve your overall health.



