Signs Of A Bladder Infection

Bladder infections, also known as urinary tract infections (UTIs), occur when bacteria invade the urinary system and multiply, causing inflammation and infection. The symptoms of a bladder infection can vary from person to person, but there are several common signs that may indicate the presence of an infection.
One of the most common signs of a bladder infection is a strong, persistent urge to urinate, even when the bladder is not full. This can be accompanied by a burning sensation or discomfort while urinating, which can range from mild to severe. In some cases, people may experience pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, lower back, or abdomen.
Another sign of a bladder infection is the presence of blood in the urine, which can appear as a pinkish or reddish tint. Cloudy or strong-smelling urine can also be a sign of an infection, as bacteria can cause the urine to become cloudy or develop a strong, unpleasant odor.
Frequency and urgency are also common symptoms of a bladder infection. People may find themselves urinating more frequently than usual, or feeling like they need to urinate immediately, even if their bladder is not full. In some cases, people may experience urinary incontinence, which can be embarrassing and disrupt daily activities.
Painful urination, also known as dysuria, is another common symptom of a bladder infection. This can be a sharp, stinging sensation or a dull ache, and can range from mild to severe. In some cases, people may experience pain or discomfort in the genital area, which can be tender to the touch.
For women, bladder infections can also cause symptoms such as pelvic pain, pressure, or discomfort, which can feel like menstrual cramps. Painful intercourse can also be a symptom of a bladder infection, as the infection can cause inflammation and discomfort in the vaginal area.
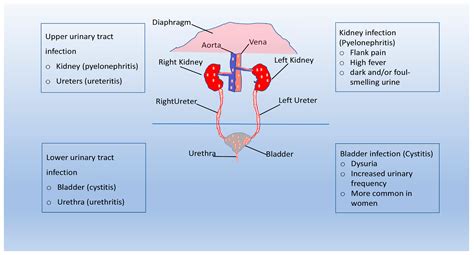
In older adults, bladder infections can cause different symptoms, such as confusion, agitation, or changes in mental status. This is because the infection can spread to the kidneys and cause a more serious condition called pyelonephritis, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
It’s essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. A healthcare provider can diagnose a bladder infection by analyzing a urine sample and performing a physical exam. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, which can help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
In addition to medical treatment, there are several home remedies that can help alleviate symptoms and prevent future infections. Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria and reduce the risk of infection. Urinating when the need arises, rather than holding it in, can also help prevent bacteria from multiplying. Wiping from front to back after using the bathroom can help prevent bacteria from entering the urethra.
Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands before and after using the bathroom, can also help prevent the spread of bacteria. Avoiding certain foods and beverages, such as spicy or acidic foods, can help reduce discomfort and prevent irritation.
What are the most common symptoms of a bladder infection?
+The most common symptoms of a bladder infection include a strong, persistent urge to urinate, burning sensation or discomfort while urinating, pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, lower back, or abdomen, and blood in the urine.
How is a bladder infection diagnosed?
+A bladder infection is typically diagnosed by analyzing a urine sample and performing a physical exam. The healthcare provider may also ask questions about symptoms and medical history.
What is the best way to prevent a bladder infection?
+The best way to prevent a bladder infection is to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands before and after using the bathroom, and drinking plenty of water to flush out bacteria. Urinating when the need arises, rather than holding it in, can also help prevent bacteria from multiplying.
Can a bladder infection be treated at home?
+While some home remedies, such as drinking plenty of water and practicing good hygiene, can help alleviate symptoms, a bladder infection typically requires medical treatment with antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
What are the complications of a bladder infection if left untreated?
+If left untreated, a bladder infection can lead to more serious complications, such as pyelonephritis, which can cause permanent damage to the kidneys and increase the risk of sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
Bladder infections can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can be treated with antibiotics. Practicing good hygiene and drinking plenty of water can help prevent future infections. If symptoms persist or worsen over time, it's essential to seek medical attention to prevent complications.
Step-by-Step Guide to Preventing Bladder Infections
- Drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria
- Urinate when the need arises, rather than holding it in
- Practice good hygiene, such as washing hands before and after using the bathroom
- Avoid certain foods and beverages, such as spicy or acidic foods
- Wipe from front to back after using the bathroom to prevent bacteria from entering the urethra
Pros and Cons of Antibiotic Treatment for Bladder Infections

Pros:
- Effective in eliminating bacteria causing the infection
- Can help alleviate symptoms quickly
- Can prevent complications, such as pyelonephritis
Cons:
- Can cause side effects, such as nausea and diarrhea
- Can contribute to antibiotic resistance
- May not address underlying causes of the infection



