Skin Picking Disorder: Break Free From Compulsive Habits
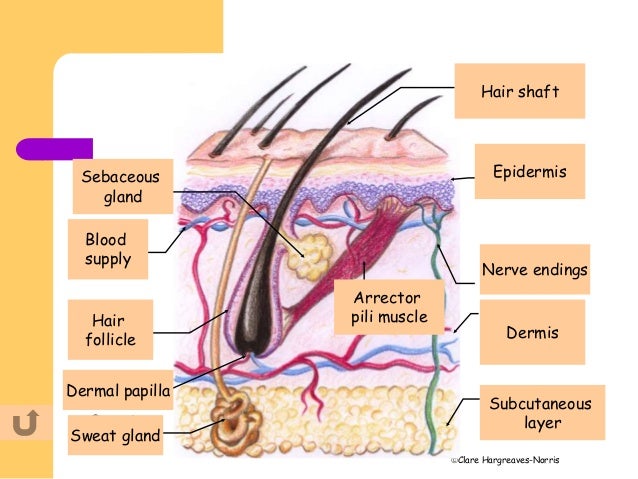
The struggle with skin picking disorder, also known as dermatillomania or excoriation disorder, is a deeply personal and often secretive battle that many individuals face. Characterized by the recurring and irresistible urge to pick at one’s own skin, this condition can lead to significant distress, impairment in social and occupational functioning, and a profound impact on one’s quality of life. The compulsive behavior associated with skin picking disorder can result in skin lesions, scarring, and infection, further exacerbating the emotional turmoil experienced by those affected.
Understanding the Complexity of Skin Picking Disorder
Skin picking disorder is classified as a body-focused repetitive behavior (BFRB), a category of conditions that also includes hair pulling disorder (trichotillomania) and nail biting, among others. These behaviors are not just habits but complex psychological and neurobiological disorders that require comprehensive understanding and treatment. Research suggests that individuals with skin picking disorder often experience heightened stress, anxiety, and emotional regulation difficulties, which can trigger the compulsive skin picking as a maladaptive coping mechanism.
The Vicious Cycle of Skin Picking
- Trigger: Many individuals report that their skin picking is triggered by stress, anxiety, or other emotional states. For some, the trigger might be more sensory, such as the feeling of certain textures on the skin or the sight of minor skin imperfections.
- Behavior: Once triggered, the individual feels an overwhelming urge to pick at their skin. This act might provide temporary relief or satisfaction but ultimately leads to feelings of guilt, shame, and frustration.
- Consequence: The consequences of skin picking, such as skin damage, infection, and scarring, can worsen the individual’s emotional state, creating a vicious cycle where the emotional distress exacerbates the urge to engage in the very behavior that worsens their condition.
Strategies for Overcoming Skin Picking Disorder
Breaking free from the compulsive habits associated with skin picking disorder requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses the psychological, emotional, and physical aspects of the condition.
Seek Professional Help: Consulting with a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, is crucial. They can provide a diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan, which may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT, particularly the module known as habit reversal training (HRT), has been shown to be effective in treating skin picking disorder. This form of therapy helps individuals become more aware of their behaviors and the situations that trigger them, teaching them how to replace the harmful behavior with a less harmful one.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress and anxiety, thereby decreasing the urge to engage in skin picking.
Support Groups: Joining a support group, either in-person or online, can provide a sense of community and understanding, helping individuals feel less isolated in their struggle with skin picking disorder.
Self-Care and Stress Management: Engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, ensuring sufficient sleep, and practicing good skin care can help manage stress and improve overall well-being, reducing the likelihood of triggering skin picking episodes.
Conclusion
Overcoming skin picking disorder is a journey that requires patience, understanding, and support. By acknowledging the complexity of this condition and seeking out the right tools and resources, individuals can work towards breaking free from the compulsive habits that have held them back for so long. It’s a path that involves not just treating the symptoms but addressing the underlying causes, fostering a deeper understanding of oneself, and cultivating a more compassionate and supportive relationship with one’s own body and mind.
FAQ Section
What are the signs and symptoms of skin picking disorder?
+Signs and symptoms of skin picking disorder include recurrent skin picking resulting in skin lesions, repeated attempts to stop or reduce the behavior, and significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. Individuals may also experience feelings of anxiety, stress, or boredom that trigger the skin picking.
How is skin picking disorder diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of skin picking disorder is typically made by a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, through a comprehensive clinical interview and assessment. They will evaluate the individual’s behavior patterns, emotional state, and the impact of the skin picking on their daily life to determine if the criteria for skin picking disorder are met.
Can skin picking disorder be treated?
+Yes, skin picking disorder can be treated. Effective treatments include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), particularly habit reversal training (HRT), and in some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of anxiety, depression, or other related conditions. A comprehensive treatment plan, tailored to the individual’s specific needs and circumstances, offers the best chance of overcoming the disorder.