Sodium Benefits Uncovered: Boost Health
The importance of sodium in our diets is a topic of ongoing debate. While excessive sodium consumption is linked to various health issues, such as high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease, it is also essential for maintaining proper bodily functions. Sodium plays a crucial role in regulating the amount of water in our bodies, transmitting nerve impulses, and facilitating muscle contractions. In this article, we will delve into the benefits of sodium, explore its functions, and discuss how to maintain a healthy balance of this vital mineral in our diets.
Sodium’s Role in the Body
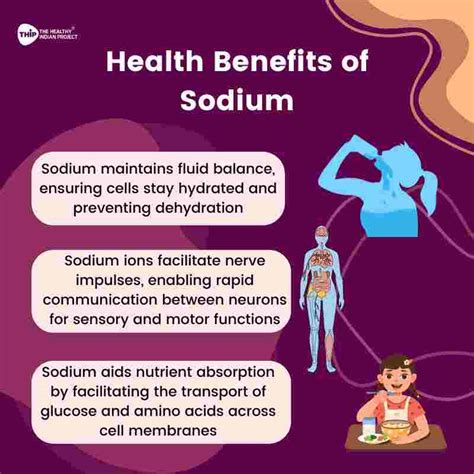
Sodium is an electrolyte that helps regulate the balance of fluids within our cells. It also enables the transmission of nerve impulses, which are crucial for muscle contractions and relaxations. Furthermore, sodium helps maintain proper blood pressure and supports the functioning of our adrenal glands. The adrenal glands produce hormones that regulate various bodily functions, such as metabolism, blood pressure, and electrolyte balance.
Benefits of Sodium
While it is well-known that excessive sodium consumption can lead to health problems, a moderate intake of sodium can have several benefits. Some of these benefits include:
- Regulation of Fluid Balance: Sodium helps regulate the amount of water in our bodies, which is essential for maintaining proper blood pressure and ensuring that our cells function correctly.
- Transmission of Nerve Impulses: Sodium enables the transmission of nerve impulses, which are crucial for muscle contractions and relaxations.
- Muscle Function: Sodium helps regulate muscle contractions and relaxations, which is essential for maintaining proper muscle function.
- Adrenal Function: Sodium supports the functioning of our adrenal glands, which produce hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
Foods Rich in Sodium
While it is possible to get too much sodium from processed and packaged foods, there are also many whole foods that are naturally rich in sodium. Some examples include:
- Celery: Celery is a good source of sodium, with one large stalk containing about 50 milligrams.
- Beets: Beets are a rich source of sodium, with one cup of cooked beets containing about 200 milligrams.
- Milk: Milk is a good source of sodium, with one cup containing about 100 milligrams.
- Sea Salt: Sea salt is a natural source of sodium and can be used as a healthier alternative to table salt.
Health Risks of Sodium Deficiency
While excessive sodium consumption is a well-known health risk, a deficiency in sodium can also have serious health consequences. Some of the health risks associated with sodium deficiency include:
- Hyponatremia: Hyponatremia is a condition characterized by low sodium levels in the blood. It can cause symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, and muscle cramps.
- Muscle Weakness: Sodium deficiency can cause muscle weakness and cramps, as sodium is essential for muscle function.
- Fatigue: Sodium deficiency can cause fatigue, as sodium is necessary for the transmission of nerve impulses.
Maintaining a Healthy Balance
To maintain a healthy balance of sodium in our diets, it is essential to consume moderate amounts from whole foods and avoid excessive consumption from processed and packaged foods. The American Heart Association recommends consuming no more than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day, with an ideal limit of 1,500 milligrams per day for most adults.
Tips for Reducing Sodium Intake
If you are concerned about your sodium intake, there are several steps you can take to reduce your consumption. Some tips include:
- Read Labels: Read food labels to check the sodium content of packaged foods.
- Choose Low-Sodium Options: Choose low-sodium options when available, such as low-sodium soups and sauces.
- Cook from Scratch: Cook meals from scratch using whole ingredients to control the amount of sodium that goes into your food.
- Use Herbs and Spices: Use herbs and spices to add flavor to your food instead of salt.
Practical Applications of Sodium
Sodium has several practical applications beyond its role in human health. Some examples include:
- Manufacturing: Sodium is used in the manufacture of various products, such as paper, dyes, and textiles.
- Water Softening: Sodium is used in water softening systems to remove minerals such as calcium and magnesium.
- Road Salt: Sodium is used as a road salt to melt ice and snow on roads and highways.
Future Trends in Sodium Research
Research on sodium is ongoing, and there are several future trends that are worth noting. Some of these trends include:
- Personalized Sodium Recommendations: Research is being conducted to develop personalized sodium recommendations based on an individual’s health status, lifestyle, and other factors.
- Sodium Reduction Technologies: New technologies are being developed to reduce sodium content in foods, such as sodium-reducing ingredients and processing technologies.
- Sodium and Gut Health: Research is being conducted to explore the relationship between sodium and gut health, including the impact of sodium on the gut microbiome.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sodium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining proper bodily functions. While excessive sodium consumption can lead to health problems, a moderate intake of sodium can have several benefits. By consuming moderate amounts of sodium from whole foods and avoiding excessive consumption from processed and packaged foods, we can maintain a healthy balance of this vital mineral in our diets.
FAQ Section
What is the recommended daily intake of sodium?
+The American Heart Association recommends consuming no more than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day, with an ideal limit of 1,500 milligrams per day for most adults.
What are the health risks of sodium deficiency?
+Sodium deficiency can cause symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, and muscle cramps. It can also lead to more serious health problems, such as hyponatremia and muscle weakness.
How can I reduce my sodium intake?
+To reduce your sodium intake, read food labels, choose low-sodium options, cook meals from scratch using whole ingredients, and use herbs and spices to add flavor to your food instead of salt.
What are the practical applications of sodium beyond its role in human health?
+Sodium has several practical applications beyond its role in human health, including manufacturing, water softening, and road salt.
What are the future trends in sodium research?
+Future trends in sodium research include personalized sodium recommendations, sodium reduction technologies, and the relationship between sodium and gut health.
How can I maintain a healthy balance of sodium in my diet?
+To maintain a healthy balance of sodium in your diet, consume moderate amounts from whole foods and avoid excessive consumption from processed and packaged foods.