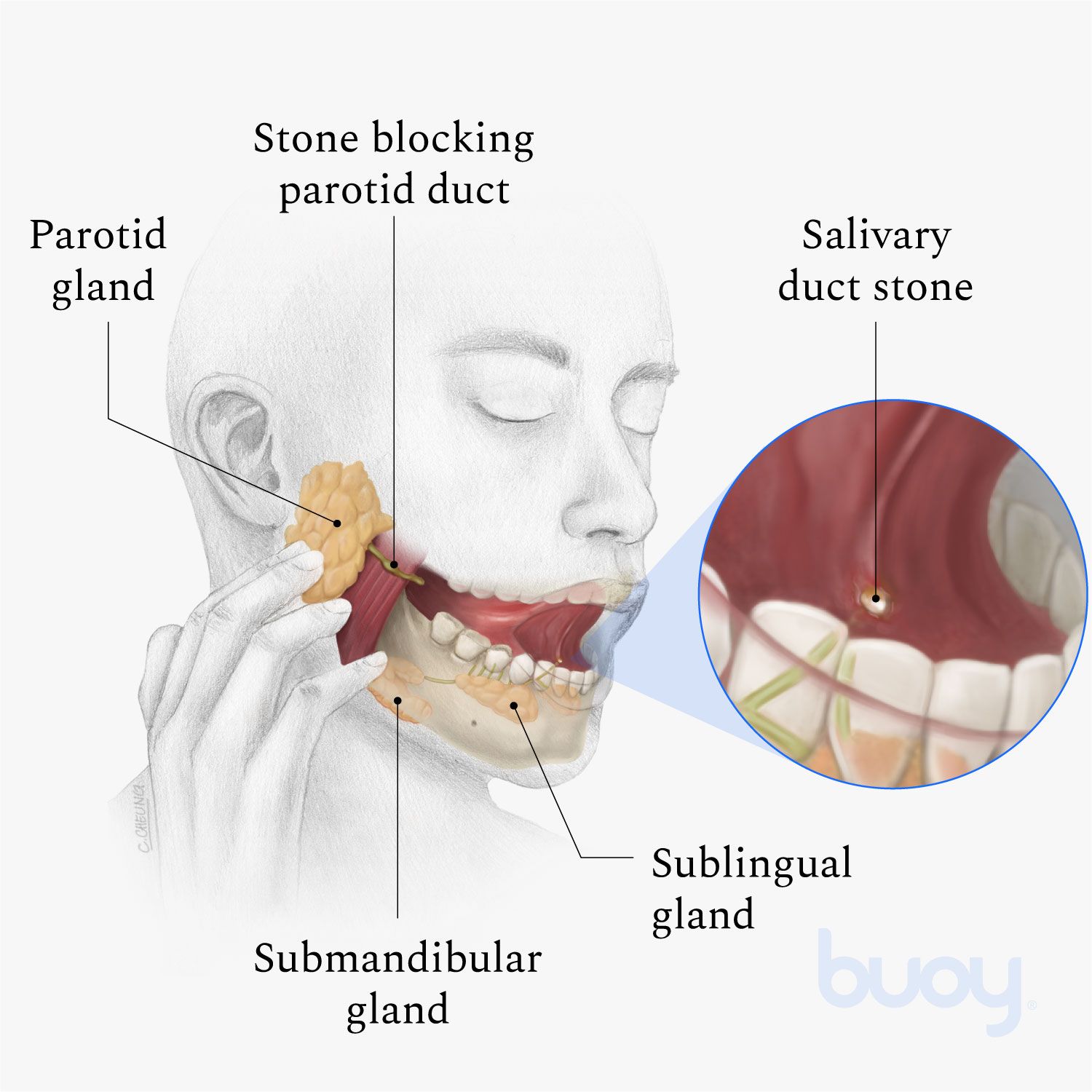
The spit gland stone, also known as a sialolithiasis, is a condition where a small, hard mineral deposit forms within the salivary glands or ducts. This can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain and swelling. In this article, we will delve into the world of spit gland stones, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Causes of Spit Gland Stones
Spit gland stones are typically caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can lead to a decrease in saliva production, which can cause the glands to become congested and increase the risk of stone formation.
- Poor diet: A diet high in processed foods and sugar can lead to an increased risk of stone formation.
- Genetics: Some people may be more prone to developing spit gland stones due to their genetic makeup.
- Age: Spit gland stones are more common in older adults.
Symptoms of Spit Gland Stones
The symptoms of spit gland stones can vary in severity and may include:
- Pain: A dull ache or sharp pain in the gland or duct, which can radiate to the ear, jaw, or face.
- Swelling: The gland or duct may become swollen and tender to the touch.
- Inflammation: The gland or duct may become inflamed, leading to redness and warmth in the affected area.
- Difficulty swallowing: In some cases, the stone may cause difficulty swallowing or a feeling of something being stuck in the throat.
Diagnosis of Spit Gland Stones
Diagnosing spit gland stones typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests. A doctor may use:
- Ultrasound: To visualize the gland or duct and detect any stones.
- CT scan: To provide more detailed images of the gland or duct and surrounding tissues.
- Sialography: A procedure where a dye is injected into the gland or duct to visualize any blockages.
Treatment Options for Spit Gland Stones
Treatment for spit gland stones depends on the size and location of the stone, as well as the severity of symptoms. Options may include:
- Surgical removal: In some cases, the stone may need to be surgically removed.
- Endoscopy: A procedure where a small camera is inserted into the gland or duct to visualize and remove the stone.
- Pain management: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medication to manage symptoms.
- Antibiotics: If the stone has caused an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection.
Prevention of Spit Gland Stones
While it may not be possible to completely prevent spit gland stones, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your saliva production flowing.
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Brush and floss your teeth regularly to reduce the risk of infection.
- Eat a healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to reduce the risk of stone formation.
What are the symptoms of a spit gland stone?
+The symptoms of a spit gland stone can include pain, swelling, inflammation, and difficulty swallowing. In some cases, the stone may cause a feeling of something being stuck in the throat.
How are spit gland stones diagnosed?
+Diagnosing spit gland stones typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or sialography.
Can spit gland stones be prevented?
+While it may not be possible to completely prevent spit gland stones, staying hydrated, maintaining good oral hygiene, and eating a healthy diet can help to reduce the risk of stone formation.
In conclusion, spit gland stones are a common condition that can cause a range of symptoms. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, you can take steps to reduce your risk and seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms. Remember to stay hydrated, maintain good oral hygiene, and eat a healthy diet to keep your salivary glands functioning properly.