Stevens Johnson Syndrome
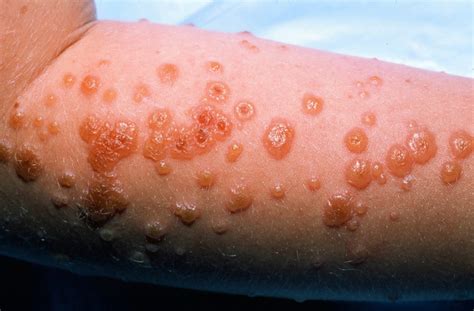
Stevens Johnson Syndrome (SJS) is a rare and potentially life-threatening condition that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is considered a medical emergency that requires immediate attention and treatment. SJS is often triggered by an adverse reaction to medication, infection, or other factors, and it can cause widespread skin lesions, blisters, and peeling, as well as damage to the eyes, mouth, and genital areas.
Understanding the Condition
SJS is a type of severe skin reaction that is characterized by a combination of skin and mucous membrane lesions, as well as systemic symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and muscle pain. The condition is often associated with the use of certain medications, such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, and anticonvulsants. In some cases, SJS can be triggered by an infection, such as a viral or bacterial infection, or by other factors, such as radiation therapy or Vaccinations.
The exact cause of SJS is not always clear, but it is thought to involve an abnormal immune response to a triggering factor, such as a medication or infection. This abnormal response leads to the activation of immune cells, which release chemical mediators that cause inflammation and damage to the skin and mucous membranes.
Symptoms of Stevens Johnson Syndrome
The symptoms of SJS can vary in severity and scope, but they often include:
- Skin lesions: Widespread skin lesions, blisters, and peeling, which can be painful and tender to the touch.
- Mucous membrane lesions: Lesions and blisters on the mucous membranes, including the eyes, mouth, and genital areas.
- Systemic symptoms: Fever, fatigue, muscle pain, and other systemic symptoms, which can be severe and debilitating.
- Eye symptoms: Conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers, and other eye symptoms, which can lead to vision loss if left untreated.
- Mouth and throat symptoms: Mouth ulcers, throat pain, and difficulty swallowing, which can make eating and drinking challenging.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing SJS can be challenging, as the condition can resemble other skin and mucous membrane disorders. A diagnosis is typically made based on a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and medical history.
Treatment for SJS usually involves a combination of supportive care and medication. The goals of treatment are to:
- Manage symptoms: Relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing of skin and mucous membrane lesions.
- Prevent complications: Prevent infection, vision loss, and other complications, such as sepsis and organ failure.
- Withdraw triggering factors: Discontinue the use of any medications or other factors that may be triggering the condition.
Supportive care may include:
- Wound care: Dressing and caring for skin lesions to promote healing and prevent infection.
- Pain management: Using pain medications and other therapies to relieve pain and discomfort.
- Fluid replacement: Replacing fluids and electrolytes to prevent dehydration and promote healing.
- Nutritional support: Providing nutritional support to promote healing and prevent malnutrition.
Medications may include:
- Corticosteroids: Reducing inflammation and promoting healing with corticosteroids.
- Antibiotics: Preventing infection and promoting healing with antibiotics.
- Immunosuppressants: Reducing the immune response and promoting healing with immunosuppressants.
Complications and Prognosis
SJS can lead to serious complications, including:
- Infection: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, which can be life-threatening.
- Vision loss: Permanent vision loss due to eye involvement.
- Organ failure: Failure of organs, such as the kidneys or liver, due to severe inflammation and damage.
- Death: SJS can be fatal if left untreated or if treatment is delayed.
The prognosis for SJS varies depending on the severity of the condition, the promptness and effectiveness of treatment, and the presence of underlying medical conditions. With prompt and effective treatment, most people with SJS can recover, but some may experience long-term complications, such as vision loss or scarring.
Prevention and Future Directions
Preventing SJS involves avoiding triggering factors, such as certain medications, and being aware of the signs and symptoms of the condition. Research is ongoing to better understand the causes and mechanisms of SJS, as well as to develop new treatments and therapies.
In the future, it is hoped that advances in genetics, immunology, and pharmacology will lead to the development of more effective and targeted treatments for SJS, as well as improved diagnostic tools and preventive strategies.
What are the common triggers of Stevens Johnson Syndrome?
+The common triggers of Stevens Johnson Syndrome include medications, such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, and anticonvulsants, as well as infections, such as viral or bacterial infections, and other factors, such as radiation therapy or vaccinations.
What are the symptoms of Stevens Johnson Syndrome?
+The symptoms of Stevens Johnson Syndrome include skin lesions, mucous membrane lesions, systemic symptoms, such as fever and fatigue, and eye symptoms, such as conjunctivitis and corneal ulcers.
How is Stevens Johnson Syndrome diagnosed?
+Diagnosing Stevens Johnson Syndrome involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and medical history, as well as ruling out other skin and mucous membrane disorders.
What is the treatment for Stevens Johnson Syndrome?
+Treatment for Stevens Johnson Syndrome typically involves a combination of supportive care and medication, including wound care, pain management, fluid replacement, and nutritional support, as well as medications, such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, and immunosuppressants.
What are the complications of Stevens Johnson Syndrome?
+The complications of Stevens Johnson Syndrome include infection, vision loss, organ failure, and death, as well as long-term complications, such as scarring and vision loss.
Can Stevens Johnson Syndrome be prevented?
+Preventing Stevens Johnson Syndrome involves avoiding triggering factors, such as certain medications, and being aware of the signs and symptoms of the condition, as well as researching and developing new treatments and therapies.
In conclusion, Stevens Johnson Syndrome is a rare and potentially life-threatening condition that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is characterized by a combination of skin and mucous membrane lesions, as well as systemic symptoms, and can be triggered by an adverse reaction to medication, infection, or other factors. With prompt and effective treatment, most people with SJS can recover, but some may experience long-term complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and complications of SJS is essential for providing effective care and promoting recovery.