Strep Throat In Adults: Comprehensive Care Guide
Strep throat, caused by the Group A Streptococcus bacterium, is a common and highly contagious infection that affects millions of people worldwide every year. While it is often associated with children, adults can also contract strep throat, and the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment may differ slightly from those experienced by younger patients. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of strep throat in adults, discussing its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Understanding Strep Throat
Strep throat is a bacterial infection that occurs when the Group A Streptococcus bacterium infects the throat and tonsils. The bacteria can spread through airborne droplets, close contact with an infected person, or by sharing food and drinks. Adults can contract strep throat from their children, coworkers, or even by touching contaminated surfaces.
Symptoms of Strep Throat in Adults
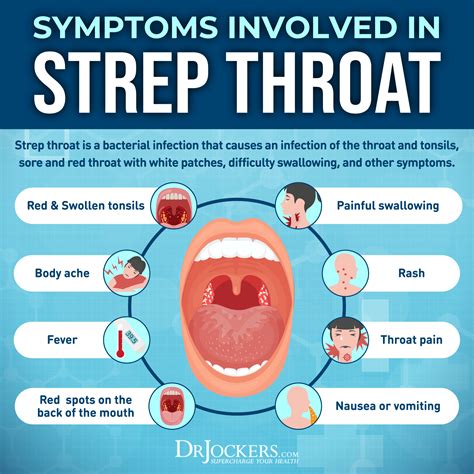
The symptoms of strep throat in adults can vary in severity and may resemble those of a common cold or flu. Common symptoms include:
- Sore throat, which can range from mild to severe
- White or yellowish patches on the tonsils
- Swollen, tender lymph nodes in the neck
- Fever, which can range from 101°F to 104°F (38.3°C to 40°C)
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
In some cases, adults may experience additional symptoms, such as a rash, joint pain, or a feeling of being generally unwell.
Diagnosis of Strep Throat in Adults
Diagnosing strep throat in adults can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other illnesses. A healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination, take a thorough medical history, and conduct one or more of the following tests:
- Rapid strep test: A quick and simple test that involves swabbing the throat to collect a sample, which is then tested for the presence of Group A Streptococcus bacteria.
- Throat culture: A more comprehensive test that involves swabbing the throat and sending the sample to a laboratory for analysis.
- Blood tests: To rule out other infections or illnesses that may be causing the symptoms.
Treatment Options for Strep Throat in Adults
If diagnosed with strep throat, adults can expect to receive antibiotic treatment to help eliminate the bacteria and reduce the risk of complications. The most commonly prescribed antibiotics for strep throat are:
- Penicillin: A natural antibiotic that is effective against a wide range of bacteria, including Group A Streptococcus.
- Amoxicillin: A broad-spectrum antibiotic that is often prescribed for adults with strep throat.
- Azithromycin: A macrolide antibiotic that is effective against a variety of bacterial infections, including strep throat.
In addition to antibiotics, adults with strep throat may also benefit from over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to help manage symptoms like sore throat, headache, and fever.
Complications of Strep Throat in Adults
If left untreated, strep throat can lead to complications, such as:
- Rheumatic fever: A rare but serious condition that can cause inflammation in the joints, skin, and heart.
- Kidney inflammation: A condition that can cause damage to the kidneys and lead to chronic kidney disease.
- Abscesses: Pus-filled pockets that can form in the throat, tonsils, or lymph nodes.
- Sinusitis: An infection of the sinuses that can cause facial pain, congestion, and discharge.
Prevention Strategies for Strep Throat in Adults
While it is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of contracting strep throat, adults can take steps to reduce their chances of getting infected:
- Practice good hygiene: Wash hands frequently, especially after coming into contact with someone who is sick.
- Avoid close contact: Try to maintain a distance from people who are sick, and avoid sharing food, drinks, or personal items.
- Get enough rest: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help keep the immune system strong.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, tea, and soup, to help soothe a sore throat and keep the body hydrated.
- Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, to help keep the immune system strong.
Strep throat is a highly contagious infection that can spread quickly through close contact with an infected person. Adults can take steps to reduce their risk of getting infected by practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact, and getting enough rest.
FAQs About Strep Throat in Adults
How long does it take to recover from strep throat?
+Most adults can expect to recover from strep throat within 7-10 days, although some people may take longer to fully recover. It's essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare provider to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
Can strep throat be treated without antibiotics?
+No, strep throat cannot be treated without antibiotics. While some cases may resolve on their own, antibiotics are necessary to eliminate the bacteria and reduce the risk of complications. Without antibiotics, the infection can spread and lead to more severe complications.
How can I prevent spreading strep throat to others?
+To prevent spreading strep throat to others, it's essential to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact, and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing. Adults with strep throat should also stay home from work or school until they have completed at least 24 hours of antibiotic treatment.
In conclusion, strep throat is a common and highly contagious infection that can affect adults of all ages. While the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment may differ slightly from those experienced by children, it’s essential for adults to seek medical attention if they suspect they have strep throat. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, adults can take steps to reduce their risk of getting infected and prevent the spread of the bacteria to others.