Strep Throat: Quick Diagnosis & Treatment
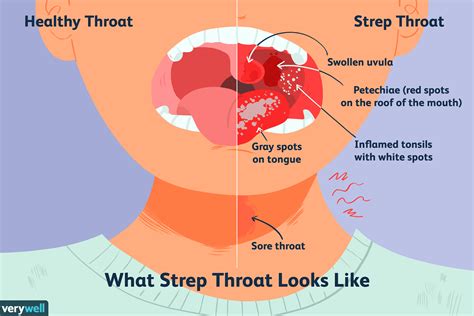
Strep throat, also known as streptococcal pharyngitis, is a bacterial infection caused by Group A Streptococcus (GAS) that affects the throat and tonsils. It is highly contagious and can spread through close contact with an infected person, such as sharing food or drinks, or by touching surfaces that have come into contact with the bacteria.
One of the primary challenges in diagnosing strep throat is distinguishing it from other types of sore throats, which can be caused by viral infections. The symptoms of strep throat can be similar to those of a viral sore throat, making it essential to visit a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. A healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination and take a thorough medical history to help determine the cause of the sore throat.
They may also perform a rapid strep test, which involves swabbing the throat to collect a sample of cells. This sample is then tested for the presence of GAS. If the results are positive, it confirms the diagnosis of strep throat. However, if the results are negative, the doctor may perform a throat culture, which involves sending the sample to a laboratory for further testing.
While awaiting the results, it is crucial to manage the symptoms of strep throat to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission to others. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate throat pain and reduce fever. It is also essential to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, such as water, tea, or soup.
In addition to these measures, there are several home remedies that can help soothe a sore throat. Gargling with warm salt water several times a day can help reduce swelling and kill bacteria. Honey has natural antibacterial properties and can be used to soothe a sore throat. Drinking warm liquids, such as tea or broth, can also help reduce throat pain.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will typically prescribe antibiotics to treat strep throat. The most common antibiotics used to treat strep throat are penicillin and amoxicillin. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if the symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Failure to complete the full course of antibiotics can lead to complications, such as kidney inflammation or rheumatic fever. It is also crucial to rest and avoid strenuous activities to help the body recover from the infection.
In some cases, strep throat can lead to complications, such as abscesses or sinus infections. If the infection spreads to other parts of the body, it can cause more severe complications, such as pneumonia or meningitis. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if the symptoms worsen or if there are signs of complications.
To prevent the spread of strep throat, it is crucial to practice good hygiene. Washing hands frequently, especially after blowing the nose, coughing or sneezing, can help prevent the transmission of the bacteria. Avoiding close contact with others, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding sharing food or drinks can also help reduce the risk of transmission.
What are the common symptoms of strep throat?
+The common symptoms of strep throat include a sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and white patches on the tonsils. In some cases, people may also experience a headache, stomachache, or nausea.
How is strep throat diagnosed?
+Strep throat is typically diagnosed using a rapid strep test or a throat culture. The doctor may also perform a physical examination and take a thorough medical history to help determine the cause of the sore throat.
What is the best way to treat strep throat?
+The best way to treat strep throat is with antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics and rest to help the body recover from the infection.
How can I prevent the spread of strep throat?
+To prevent the spread of strep throat, it is crucial to practice good hygiene. Washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact with others, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding sharing food or drinks can help reduce the risk of transmission.
What are the potential complications of strep throat?
+The potential complications of strep throat include abscesses, sinus infections, pneumonia, and meningitis. Failure to complete the full course of antibiotics can lead to these complications, making it essential to seek medical attention if the symptoms worsen or if there are signs of complications.
Can strep throat be treated without antibiotics?
+While some people may recover from strep throat without antibiotics, it is not recommended to treat the infection without them. Antibiotics are essential to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission to others.
In conclusion, strep throat is a bacterial infection that requires prompt medical attention to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission to others. By understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, individuals can take the necessary steps to manage the infection and prevent its spread. It is essential to practice good hygiene, complete the full course of antibiotics, and rest to help the body recover from the infection.
Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Strep Throat

- Visit a doctor for an accurate diagnosis
- Complete the full course of antibiotics
- Rest and avoid strenuous activities
- Practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of the infection
- Manage symptoms with over-the-counter pain relievers and home remedies
By following these steps and seeking medical attention if the symptoms worsen or if there are signs of complications, individuals can effectively manage strep throat and prevent its spread to others.
Key Takeaways

- Strep throat is a bacterial infection that requires prompt medical attention
- Antibiotics are essential to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission to others
- Practicing good hygiene and completing the full course of antibiotics can help manage the infection
- Seeking medical attention if the symptoms worsen or if there are signs of complications is crucial