Sugar Level Range
Maintaining an optimal blood sugar level is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. The human body regulating blood sugar levels is a delicate process, involving various hormones and organs, notably insulin and glucagon produced by the pancreas. Understanding the normal sugar level range and how it fluctuates throughout the day can help in managing diet, exercise, and medication effectively.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, influenced by factors such as meal times, the type of food consumed, physical activity, and sleep patterns. Here’s a general outline of what is considered within the normal range for blood glucose levels:
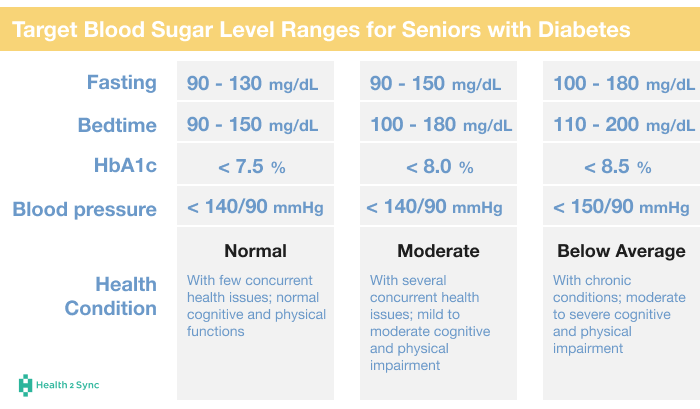
Fasting Blood Sugar (Before Eating): For individuals without diabetes, a normal fasting blood sugar level is typically between 70 to 99 mg/dL. For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association suggests aiming for a fasting blood sugar level between 80 to 130 mg/dL.
After Meals: Postprandial or after-meal blood sugar levels should ideally be less than 140 mg/dL for people without diabetes. For individuals with diabetes, it’s recommended to keep after-meal blood sugar levels below 180 mg/dL to minimize the risk of complications.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, stress levels, certain medications, and sleep quality. Understanding how these factors impact blood glucose can help individuals manage their levels more effectively:
Diet: Consuming foods high on the glycemic index (GI) can cause a spike in blood sugar levels, whereas foods low on the GI, such as whole grains, vegetables, and most fruits, are digested more slowly and have a more gradual effect on blood sugar.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body to more efficiently use insulin and lower blood sugar levels. However, intense exercise can initially cause blood sugar to rise due to the release of stress hormones like adrenaline.
Stress: Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Effective stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help mitigate this effect.
Medications: Certain medications, including some used to treat depression, high blood pressure, and corticosteroids, can affect blood sugar levels. It’s essential for individuals taking these medications to monitor their blood sugar closely and discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Effective management of blood sugar levels involves a multifaceted approach, including dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, monitoring of blood glucose, and, if prescribed, medication. For individuals with diabetes, creating a personalized meal plan with the help of a dietitian can be particularly beneficial. This plan typically focuses on portion control, balancing carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and selecting foods that are rich in nutrients and fiber but low in added sugars and unhealthy fats.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes to understand how different factors affect their blood glucose. This involves using a glucose meter and test strips to measure blood sugar levels at various times of the day, such as upon waking, before meals, and after eating. Keeping a log of these readings, along with notes on diet, exercise, and any symptoms experienced, can help identify patterns and make informed decisions about managing blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range is essential for preventing complications associated with diabetes and ensuring overall well-being. By understanding the factors that influence blood sugar, making informed dietary choices, staying physically active, and managing stress, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels. For those with diabetes, working closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized management plan is key to achieving and maintaining good blood sugar control.
Additional Resources
For individuals looking to learn more about managing blood sugar levels, several resources are available:
- The American Diabetes Association (ADA) offers comprehensive guidelines, recipes, and tools for managing diabetes and preventing its complications.
- The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics provides advice on healthy eating, including meal planning tips and strategies for blood sugar management.
- Local healthcare providers and diabetes support groups can also offer valuable information, support, and guidance tailored to individual needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is considered a normal blood sugar level for someone with diabetes after eating?
+For individuals with diabetes, it’s recommended to keep after-meal blood sugar levels below 180 mg/dL to minimize the risk of complications.
How does physical activity affect blood sugar levels?
+Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body to more efficiently use insulin and lower blood sugar levels. However, intense exercise can initially cause blood sugar to rise due to the release of stress hormones.
What role does diet play in managing blood sugar levels?
+Diet plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. Consuming foods low on the glycemic index, such as whole grains, vegetables, and most fruits, can help maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
By understanding and managing blood sugar levels effectively, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, improve their quality of life, and maintain their overall health and well-being.


