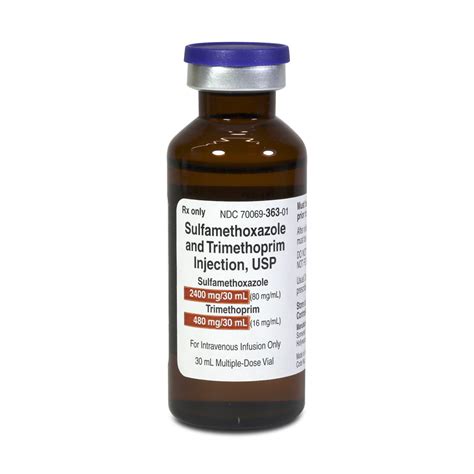
Sulfamethoxazoletmp Ds Tablet
Sulfamethoxazole, often prescribed in combination with trimethoprim (as in the case of the medication known as Bactrim, Septra, or Cotrim), is a type of antibiotic that belongs to the class of sulfonamides. When sulfamethoxazole is combined with trimethoprim, it forms a potent antibiotic duo known as co-trimoxazole. This combination is effective against a wide range of bacteria and is used to treat various infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and gastrointestinal infections, among others.
Uses of Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim
The combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria. This antibiotic treats only bacterial infections. It will not work for viral infections (such as common cold, flu). Using any antibiotic when it is not needed can cause it to not work for future infections.
Mechanism of Action
Sulfamethoxazole works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria, which is achieved by interfering with the production of folic acid in bacteria. Bacteria need folic acid to grow and multiply, and sulfamethoxazole blocks the production of dihydrofolic acid, which is necessary for the synthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid, a crucial component for bacterial growth and multiplication. Trimethoprim, on the other hand, inhibits the reduction of dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, further impeding the bacterial growth process. The combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is synergistic, providing a broader spectrum of activity than either drug alone.
Administration and Dosage
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is available in various dosage forms, including tablets and oral suspensions. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the type and severity of the infection being treated, as well as the patient’s age, weight, and kidney function. It is essential to follow the prescription instructions and complete the full treatment course, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to ensure the infection is fully cleared and to reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Side Effects
Like all medications, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim can cause side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. Severe side effects can include Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and blood disorders such as agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and thrombocytopenia. Patients should seek medical attention if they experience any signs of an allergic reaction or other severe side effects.
Interactions
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim can interact with various medications, including warfarin, phenytoin, and methotrexate, among others. These interactions can increase the risk of side effects or reduce the effectiveness of the medications. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking before starting sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim.
Precautions
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim should be used with caution in patients with certain medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease, and in those who are allergic to sulfonamides or have a history of drug allergies. It is also crucial to use this medication cautiously in pregnant women, as sulfonamides are known to cross the placental barrier, and in nursing mothers, as sulfonamides are excreted in breast milk.
Conclusion
Sulfamethoxazole, in combination with trimethoprim, is a widely used antibiotic effective against a broad spectrum of bacterial infections. Its mechanism of action, involving the inhibition of folic acid synthesis in bacteria, makes it a valuable treatment option. However, like all antibiotics, it should be used judiciously to minimize the risk of side effects and antibiotic resistance. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions and complete the full treatment course to ensure the best outcomes.
What is sulfamethoxazole used for?
+Sulfamethoxazole, often combined with trimethoprim, is used to treat various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and gastrointestinal infections.
How does sulfamethoxazole work?
+Sulfamethoxazole works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria by interfering with the production of folic acid, which is necessary for bacterial growth.
What are the common side effects of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim?
+Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. Severe side effects can include Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and blood disorders.
Sulfamethoxazole, in combination with trimethoprim, is an effective antibiotic against a wide range of bacterial infections. Its use should be guided by medical professionals, considering potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Pros and Cons of Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim
- Pros: Effective against a broad spectrum of bacterial infections, available in various dosage forms, and has a synergistic effect when combined with trimethoprim.
- Cons: Can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and allergic reactions, and may interact with other medications. It should be used cautiously in patients with certain medical conditions and in pregnant or nursing women.