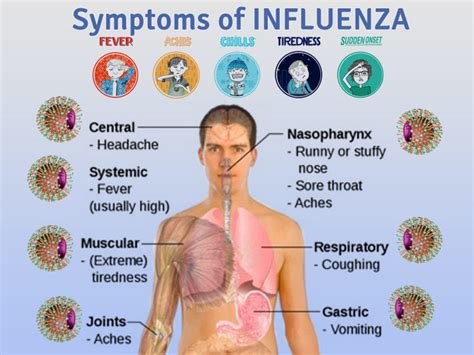
The recent flu virus, also known as influenza, has been causing widespread illness and concern globally. The symptoms of this viral infection can vary from person to person, but there are common signs that indicate its presence. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early detection, treatment, and prevention of complications.
Initial Symptoms The flu typically begins with a sudden onset of symptoms, which can include:
- High fever, usually above 102°F (39°C), which can last for 3-4 days
- Chills, which can range from mild to severe
- Cough, often dry and hacking, but can produce mucus
- Sore throat, which can be severe and painful
- Runny or stuffy nose, with clear or yellow discharge
- Headache, which can be mild or severe, and is often accompanied by fatigue
- Muscle or body aches, which can range from mild to severe
- Fatigue, which can be extreme and last for several days
Respiratory Symptoms As the flu progresses, respiratory symptoms can become more pronounced, including:
- Shortness of breath, which can be mild or severe
- Wheezing or chest tightness, which can be a sign of bronchitis or pneumonia
- Chest pain or discomfort, which can be a sign of pleurisy or pneumonia
- Coughing up mucus or phlegm, which can be yellow or green in color
Gastrointestinal Symptoms In some cases, the flu can cause gastrointestinal symptoms, including:
- Nausea and vomiting, which can be mild or severe
- Diarrhea, which can be watery or bloody
- Abdominal cramps or pain, which can be mild or severe
Other Symptoms Other symptoms that may occur with the flu include:
- Loss of appetite, which can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances
- Sweating, which can be profuse and lead to dehydration
- Confusion or disorientation, which can be a sign of severe illness or complications
- Severe headache or stiff neck, which can be a sign of meningitis or encephalitis
Complications In severe cases, the flu can lead to complications, such as:
- Pneumonia, which can be bacterial or viral
- Bronchitis, which can be acute or chronic
- Sinus infections, which can be acute or chronic
- Ear infections, which can be acute or chronic
- Dehydration, which can lead to electrolyte imbalances and organ failure
High-Risk Groups Certain groups are at higher risk for complications from the flu, including:
- Older adults, aged 65 and older
- Young children, under the age of 5
- Pregnant women, especially during the second and third trimesters
- People with underlying medical conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, or lung disease
- People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy
Diagnosis and Treatment Diagnosing the flu typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as:
- Rapid influenza diagnostic tests (RIDTs)
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests
- Culture tests
Treatment for the flu usually involves:
- Rest and hydration
- Over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to relieve symptoms
- Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir or zanamivir, to shorten the duration and severity of symptoms
- Hospitalization, in severe cases, to manage complications and provide supportive care
- Get vaccinated annually
- Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick
- Stay home from work or school if you're experiencing symptoms
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing
Conclusion The recent flu virus can cause severe illness and complications, especially in high-risk groups. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and prevention. By following preventive measures, such as vaccination and good hygiene, we can reduce the spread of the flu and protect ourselves and our loved ones.
What are the most common symptoms of the flu?
+The most common symptoms of the flu include high fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, headache, and muscle or body aches.
Who is at higher risk for complications from the flu?
+Certain groups are at higher risk for complications from the flu, including older adults, young children, pregnant women, people with underlying medical conditions, and people with weakened immune systems.
What are the best ways to prevent the spread of the flu?
+The best ways to prevent the spread of the flu include getting vaccinated annually, practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, staying home from work or school if you’re experiencing symptoms, and covering your mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing.