Symptoms Of Uti
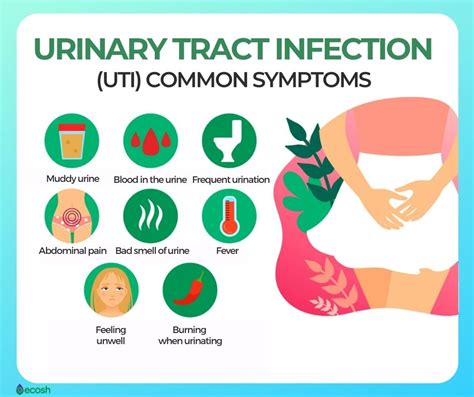
Understanding the symptoms of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is crucial for early detection and treatment. UTIs can affect any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The symptoms can vary depending on the location of the infection.
Common Symptoms:
- Painful Urination: One of the most common symptoms of a UTI is dysuria, which is a burning sensation while urinating. This discomfort can range from mild to severe.
- Frequent Urination: People with UTIs often feel the need to urinate more frequently than usual. This can be accompanied by the sensation of needing to urinate immediately.
- Urgency: The urgent need to urinate is a hallmark symptom of UTIs. This sensation is hard to ignore and can be very distressing.
- Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine: Urine that is cloudy, dark, or has a strong, unpleasant odor can be a sign of a UTI. Healthy urine is typically clear and does not have a strong smell.
- Blood in the Urine: In some cases, UTIs can cause hematuria, which is the presence of blood in the urine. This can make the urine appear pink, red, or brown.
- Pain in the Lower Abdomen: Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen, which can feel like cramping, is common in UTIs.
- Fever: A low-grade fever can accompany a UTI, especially if the infection has moved up the urinary tract to the kidneys.
- Chills: Some people may experience chills alongside a fever when they have a UTI.
- Pelvic Pain: In women, UTIs can cause pelvic pain, which is a broad term that refers to pain in the lowest part of the torso, in the area below the waist and between the hipbones.
- Discomfort in the Genital Area: Both men and women can experience discomfort or pain in the genital area due to a UTI.
Less Common Symptoms:
- Back Pain: If the UTI has reached the kidneys, it can cause back pain, which is often felt in the upper back or flank area.
- Nausea and Vomiting: In some cases, especially when the infection is severe or has spread to the kidneys, nausea and vomiting can occur.
- Mental Changes: Elderly individuals with UTIs might experience confusion, agitation, or other changes in mental status, especially if the infection is severe or they have underlying health conditions.
Symptoms in Men, Women, and Children:
- Women: Women are more likely to experience UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. Symptoms are generally the same as those listed above.
- Men: While less common, men can also get UTIs. Symptoms are similar, but men are more likely to experience discomfort or pain in the genital area.
- Children: In children, UTI symptoms can be less specific. Infants and toddlers might show signs such as fever, irritability, or wetting their diaper more often than usual. Older children may exhibit more typical UTI symptoms, such as pain while urinating or urinary frequency.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
It’s essential to seek medical attention if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a UTI, especially if:
- Symptoms are severe or persistent
- There is blood in the urine
- Fever is high (over 103°F) or lasts for more than 2 days
- Back pain is severe
- Symptoms return after treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment of UTIs are crucial to prevent complications, such as the spread of the infection to the kidneys or the development of sepsis, a potentially life-threatening condition.
In addition to recognizing symptoms, it’s also beneficial to understand how UTIs are diagnosed and treated. The diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, urinalysis (a urine test), and sometimes imaging studies like ultrasound. Treatment usually involves a course of antibiotics and, in some cases, medications to alleviate symptoms.
For those looking to prevent future UTIs, maintaining good urinary hygiene, staying hydrated, and avoiding certain foods or drinks that can irritate the bladder can be beneficial. However, it’s crucial to follow specific advice from a healthcare provider, as prevention strategies can vary depending on individual health needs.
What are the most common symptoms of a UTI?
+The most common symptoms include painful urination, frequent urination, urgent need to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and in some cases, blood in the urine. Fever, chills, and lower abdomen pain are also possible.
How are UTIs diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, reviewing the patient's medical history, a urinalysis (urine test), and sometimes imaging studies like an ultrasound. The urinalysis can detect the presence of bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities in the urine.
What is the standard treatment for UTIs?
+The standard treatment for most UTIs involves a course of antibiotics. The specific type and duration of antibiotic treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria causing it. In some cases, medications to alleviate symptoms such as pain or discomfort may also be prescribed.
Can UTIs be prevented?
+While not all UTIs can be prevented, there are steps that can reduce the risk. These include practicing good hygiene, staying well-hydrated, avoiding certain foods or drinks that can irritate the bladder, and urinating when the need arises rather than delaying. Following specific preventive advice from a healthcare provider is also recommended.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of a UTI and seeking medical attention promptly is vital for effective treatment and preventing complications. Understanding the nuances of UTI diagnosis, treatment, and prevention can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their urinary health.