Tb Test Side Effects
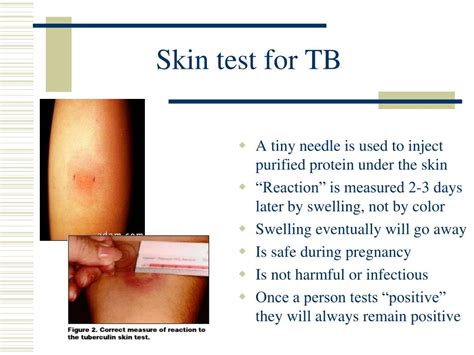
The tuberculosis (TB) test, also known as the Mantoux test or tuberculin skin test, is a widely used diagnostic tool to detect the presence of TB infection. While the test is generally safe and effective, it can cause some side effects in certain individuals. Understanding these side effects and their implications is crucial for both healthcare providers and individuals undergoing the test.
Common Side Effects of the TB Test
The most common side effects of the TB test are related to the skin reaction at the injection site. These can include:
- Redness and swelling: The skin at the injection site may become red, swollen, and inflamed, which can be uncomfortable and itchy.
- Induration: A firm, raised area (induration) may develop at the injection site, which can be tender to the touch.
- Itching and burning: Some individuals may experience itching, burning, or stinging sensations at the injection site.
- Blisters or ulcers: In rare cases, the skin reaction can lead to the formation of blisters or ulcers, which can be painful and may take longer to heal.
Less Common Side Effects of the TB Test
While less common, some individuals may experience more severe side effects, including:
- Allergic reactions: In rare cases, individuals may be allergic to the tuberculin used in the test, which can cause more severe reactions, such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing.
- Infection: As with any injection, there is a small risk of infection at the injection site, which can cause symptoms such as increased redness, swelling, and pus.
- Systemic reactions: In rare cases, the TB test can cause systemic reactions, such as fever, headache, and muscle pain, which can be uncomfortable and may require medical attention.
Rare but Serious Side Effects of the TB Test
While extremely rare, the TB test can cause serious side effects, including:
- Anaphylaxis: A life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention.
- Serum sickness: A rare immune system reaction that can cause symptoms such as fever, rash, and joint pain.
- Hypersensitivity vasculitis: A rare condition characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can cause symptoms such as skin lesions, fever, and joint pain.
Who is at Risk for TB Test Side Effects?
Certain individuals may be at a higher risk for experiencing side effects from the TB test, including:
- Individuals with a history of allergies or allergic reactions
- Those with weakened immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS patients or individuals taking immunosuppressive medications
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Individuals with a history of skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis
What to Expect After the TB Test
After the TB test, it is essential to monitor the injection site for any signs of reaction or infection. Individuals should:
- Keep the injection site clean and dry
- Avoid scratching or rubbing the injection site
- Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and itching
- Seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or if there are signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus
Conclusion
While the TB test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it can cause side effects in certain individuals. Understanding these side effects and their implications is crucial for both healthcare providers and individuals undergoing the test. By being aware of the potential risks and taking steps to minimize them, individuals can ensure a safe and effective testing experience.
What are the most common side effects of the TB test?
+The most common side effects of the TB test are related to the skin reaction at the injection site, including redness, swelling, induration, itching, and burning.
Who is at risk for TB test side effects?
+Certain individuals may be at a higher risk for experiencing side effects from the TB test, including those with a history of allergies, weakened immune systems, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and individuals with a history of skin conditions.
What should I do if I experience side effects after the TB test?
+If you experience side effects after the TB test, it is essential to monitor the injection site for any signs of reaction or infection and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or if there are signs of infection.