Test About Anxiety
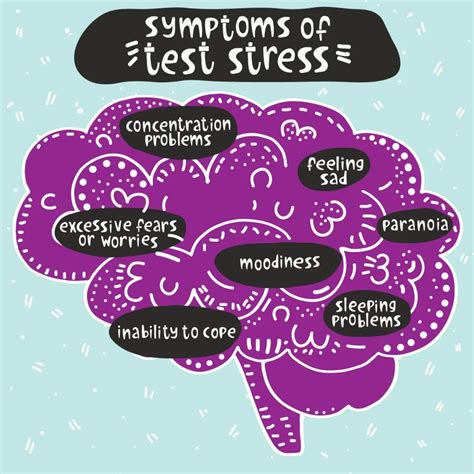
Anxiety is a pervasive and often debilitating mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by feelings of worry, nervousness, and fear that are persistent and overwhelming, interfering with an individual’s daily life and relationships. The experience of anxiety can vary widely from person to person, with some individuals experiencing mild symptoms that are manageable, while others may face severe anxiety that significantly impairs their ability to function.
At its core, anxiety is a natural response to stress, designed to alert the body to potential dangers and trigger the “fight or flight” response. However, when this response becomes excessive or is triggered by situations that are not actually threatening, it can lead to the development of an anxiety disorder. There are several types of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and phobias, each with its own set of symptoms and characteristics.
One of the most significant challenges in addressing anxiety is understanding its complex causes. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, research suggests that anxiety is the result of a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. For instance, individuals with a family history of anxiety are more likely to develop an anxiety disorder, indicating a potential genetic component. Additionally, traumatic life events, stress, and certain personality traits can also contribute to the development of anxiety.
Treatment for anxiety typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, medication. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective forms of psychotherapy for anxiety, helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to their anxiety. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and mindfulness practices, can also significantly reduce symptoms of anxiety by promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
Managing Anxiety: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify Your Triggers: Understanding what causes your anxiety is the first step to managing it. Keep a diary or journal to track when your anxiety symptoms occur and what might have triggered them.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation can help reduce anxiety symptoms by promoting relaxation.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Exercise is a natural anxiety reliever. It helps reduce stress and anxiety by releasing endorphins, also known as "feel-good" hormones.
- Seek Social Support: Talking to a trusted friend, family member, or mental health professional can provide valuable support and help you feel less isolated.
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: Often, anxiety is fueled by negative and unrealistic thoughts. Learning to challenge these thoughts through CBT can help you develop a more balanced and constructive way of thinking.
Despite the availability of effective treatments, many individuals with anxiety disorders do not receive the help they need. Barriers to treatment include lack of access to mental health services, stigma associated with mental illness, and misconceptions about the nature of anxiety and its treatment. It is essential to address these barriers by promoting awareness and understanding of anxiety, expanding access to mental health services, and supporting research into the causes and treatments of anxiety disorders.
Medication for Anxiety: Weighing the Pros and Cons

| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Can provide rapid relief from severe anxiety symptoms | May have side effects such as drowsiness, insomnia, or sexual dysfunction |
| Can be effective for individuals who have not responded to psychotherapy | May lead to dependence or withdrawal symptoms when discontinued |
| Can be used in conjunction with psychotherapy for enhanced effectiveness | Does not address the underlying causes of anxiety and may mask symptoms rather than resolving them |
In conclusion, anxiety is a complex and multifaceted mental health condition that requires a comprehensive approach to treatment. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and the various treatment options available, individuals can take the first steps towards managing their anxiety and improving their quality of life. It is crucial for society as a whole to support those affected by anxiety, promoting awareness, reducing stigma, and ensuring access to the care and resources needed to overcome this condition.
What are the most common symptoms of anxiety?
+The most common symptoms of anxiety include persistent and excessive worry, restlessness, feeling on edge, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances. These symptoms can vary in severity and impact daily life significantly.
How does anxiety affect daily life?
+Anxiety can significantly impair daily functioning, affecting relationships, work performance, and overall well-being. Individuals with anxiety may avoid certain situations or activities due to fear or worry, leading to social isolation and decreased quality of life.
What is the difference between normal anxiety and an anxiety disorder?
+Normal anxiety is a temporary and adaptive response to a perceived threat or stressor, whereas an anxiety disorder is characterized by excessive and persistent fear or anxiety that interferes with daily life. Anxiety disorders are more severe and can significantly impair functioning.



