Tetanus Shots: Quick And Painless Vaccination
Tetanus shots are a crucial part of maintaining your health and preventing a potentially life-threatening infection. The tetanus vaccine is designed to protect against tetanus, also known as lockjaw, which is a bacterial infection characterized by muscle stiffness, spasms, and rigidity. In this article, we will delve into the world of tetanus shots, exploring their importance, how they work, and what you can expect during the vaccination process.
Understanding Tetanus
To appreciate the significance of tetanus shots, it’s essential to understand the nature of the tetanus infection. Tetanus is caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani, which is commonly found in soil, dust, and the gastrointestinal tracts of animals. The bacteria can enter the body through wounds or cuts, and once inside, they produce toxins that affect the nervous system, leading to the characteristic symptoms of tetanus.
The Importance of Vaccination
Vaccination against tetanus is vital for several reasons. Firstly, tetanus infections can be severe and potentially fatal. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), tetanus is responsible for approximately 50,000 to 100,000 deaths worldwide each year. Secondly, the tetanus vaccine is highly effective in preventing the infection, with a success rate of over 90%. Finally, vaccination not only protects the individual but also contributes to herd immunity, reducing the risk of outbreaks and the spread of the infection within communities.
How Tetanus Shots Work
Tetanus shots contain inactivated toxins (toxoids) of the tetanus bacterium. When administered, these toxoids stimulate the body’s immune system to produce antibodies that can recognize and fight the tetanus toxin. This process provides long-term immunity against tetanus, significantly reducing the risk of infection. The vaccine is often combined with other vaccines, such as diphtheria and pertussis (DTaP vaccine), to protect against multiple infections simultaneously.
The Vaccination Process
Receiving a tetanus shot is a straightforward process. The vaccine is administered via an intramuscular injection, typically in the arm or leg. The injection might cause some minor discomfort, but this is usually temporary and subsides within a few days. Common side effects include redness, swelling, and soreness at the injection site, but these are generally mild and do not require medical attention.
Frequency of Vaccination
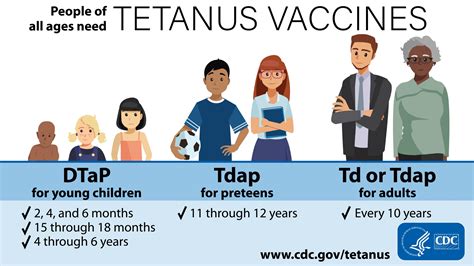
The tetanus vaccine is administered in a series of doses during childhood, with booster shots recommended every 10 years to maintain immunity. This frequency can vary depending on the individual’s health status, occupation, and travel history. For instance, individuals working in high-risk environments, such as construction or farming, may require more frequent booster shots. Additionally, travelers to areas with high rates of tetanus infection may need to update their vaccination status before traveling.
Special Considerations
There are certain situations where the tetanus vaccination schedule may need to be adjusted. For pregnant women, the tetanus vaccine is safe and recommended, especially during the third trimester, as it can provide protection to the newborn against neonatal tetanus. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, may require special consideration and potentially more frequent vaccinations to ensure adequate protection.
Myth vs. Reality: Addressing Common Misconceptions
Despite the tetanus vaccine’s proven safety and efficacy, several misconceptions surround its use. One common myth is that tetanus shots are only necessary for individuals who work with animals or in dirty environments. However, tetanus bacteria are ubiquitous, and anyone can be at risk of infection, regardless of their occupation or lifestyle. Another misconception is that the tetanus vaccine can cause serious side effects, such as neurological damage. While all vaccines carry some risk of adverse reactions, the tetanus vaccine has an excellent safety profile, with serious side effects being extremely rare.
Future Trends in Tetanus Vaccination
The field of vaccine development is continuously evolving, with researchers exploring new technologies and strategies to improve vaccine efficacy and accessibility. One area of focus is the development of vaccines that can provide longer-lasting immunity, potentially reducing the need for frequent booster shots. Additionally, there is a push towards creating combination vaccines that can protect against multiple infections simultaneously, simplifying vaccination schedules and improving compliance.
Practical Applications: Staying Protected
To stay protected against tetanus, it’s essential to follow the recommended vaccination schedule and maintain up-to-date records of your vaccinations. If you’re unsure about your tetanus vaccination status or have concerns about potential side effects, consult with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice and help you make informed decisions about your health.
How often do I need to get a tetanus shot?
+Generally, a booster shot is recommended every 10 years. However, this frequency may vary depending on your health status, occupation, and travel history. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Are tetanus shots safe during pregnancy?
+Yes, tetanus shots are safe and recommended during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, as they can provide protection to the newborn against neonatal tetanus.
What are the common side effects of tetanus shots?
+Common side effects include redness, swelling, and soreness at the injection site. These are generally mild and temporary, not requiring medical attention.
In conclusion, tetanus shots are a quick and painless way to protect yourself against a potentially life-threatening infection. By understanding the importance of vaccination, how tetanus shots work, and what to expect during the vaccination process, you can make informed decisions about your health. Remember, staying up-to-date with your tetanus vaccinations is a critical step in maintaining your health and contributing to the well-being of your community.