Thyroid Antibody Test Results Decoded
Understanding thyroid antibody test results can be a complex task, especially for those without a medical background. However, grasping the basics of these tests and what their results imply is crucial for managing thyroid health. The thyroid gland, located in the neck, plays a pivotal role in regulating metabolism, energy generation, and overall hormonal balance. When the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, it can lead to autoimmune thyroid diseases, with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease being the most common forms. The thyroid antibody test is a blood test used to diagnose and monitor these conditions by detecting the presence of specific antibodies.
Introduction to Thyroid Antibodies
Thyroid antibodies are proteins made by the immune system that can mistakenly attack the thyroid gland. The two main types of thyroid antibodies tested for are:
- Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPOAb): These antibodies are associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition that leads to hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid).
- Thyroglobulin Antibodies (TgAb): Also linked to Hashimoto’s, these antibodies can sometimes be present in other thyroid conditions.
- Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin (TSI) or Thyrotropin Receptor Antibodies (TRAb): These are associated with Graves’ disease, an autoimmune condition that leads to hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
Decoding Test Results
Interpreting thyroid antibody test results requires understanding the context of the test, including the reason for testing and any symptoms the patient is experiencing. Here are some general guidelines:
Negative Results: If the test results show that thyroid antibody levels are within the normal range, it suggests that there is no significant autoimmune activity against the thyroid gland. However, it’s essential to remember that some individuals with autoimmune thyroid disease may not always have positive antibody tests, especially in the early stages or if the disease is not active.
Positive Results: Elevated levels of thyroid antibodies indicate an autoimmune response against the thyroid gland. A positive result for TPOAb or TgAb suggests Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, while a positive result for TSI or TRAb suggests Graves’ disease. It’s crucial to note that having these antibodies does not necessarily mean the disease is active or causing symptoms; some people can have positive antibody tests without thyroid dysfunction.
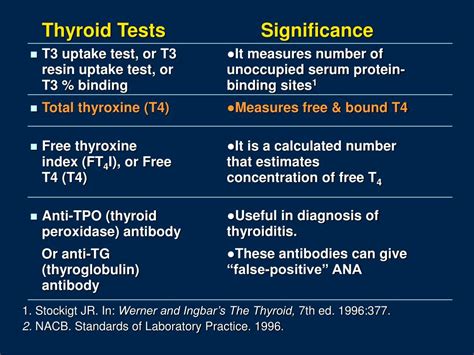
Understanding the Numbers
The reference ranges for thyroid antibody tests can vary between laboratories, so it’s essential to consult the laboratory report for specific reference ranges. Generally, results are considered:
- Negative if the antibody level is below the reference range.
- Equivocal or Borderline if the level is near the threshold, suggesting a possible but not definite presence of antibodies. In such cases, the test might need to be repeated for confirmation.
- Positive if the antibody level exceeds the reference range, indicating the presence of autoimmune antibodies against the thyroid.
What to Do Next
If thyroid antibody tests are positive, the next steps depend on the clinical context, including symptoms, physical examination findings, and other laboratory tests such as thyroid function tests (TFTs) that measure thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
For Those Without Symptoms: Regular monitoring of thyroid function and antibody levels might be recommended to observe any changes over time.
For Those With Symptoms: Treatment will depend on the specific condition diagnosed. For Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, treatment usually involves thyroid hormone replacement medication to normalize thyroid hormone levels. For Graves’ disease, treatment options include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine ablation, or surgery to reduce thyroid hormone production.
Lifestyle and Management
While medical treatment is crucial for managing autoimmune thyroid diseases, lifestyle modifications can also play a significant role in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. This includes maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and ensuring adequate sleep. Some individuals may also find benefit in avoiding certain foods or substances that can exacerbate thyroid problems, although the evidence for dietary influences is still evolving.
Conclusion
Thyroid antibody tests are a vital tool in the diagnosis and management of autoimmune thyroid diseases. Understanding the results of these tests and their implications can empower individuals to take an active role in their health care. It’s crucial to work closely with healthcare providers to interpret test results within the context of overall health and symptoms, and to develop a personalized plan for managing thyroid health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do positive thyroid antibody test results mean?
+Positive thyroid antibody test results indicate the presence of autoimmune antibodies against the thyroid gland, which can be associated with conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease. However, having these antibodies does not always mean the disease is active or causing symptoms.
How are thyroid antibody tests used in diagnosis?
+Thyroid antibody tests are used alongside clinical evaluation and other laboratory tests like thyroid function tests to diagnose autoimmune thyroid diseases. They help in distinguishing between different thyroid conditions and guiding appropriate treatment.
Can thyroid antibody levels change over time?
+Yes, thyroid antibody levels can fluctuate over time. Regular monitoring may be necessary to track changes in antibody levels and adjust treatment plans accordingly. Lifestyle changes and certain treatments can influence these levels.
What lifestyle changes can help manage thyroid health?
+Maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active, managing stress, and ensuring adequate sleep can help in managing thyroid health. Some individuals may also benefit from avoiding specific foods or substances, although it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes.