Tizanidine 4 Mg Tablet: Effective Pain Relief Solution
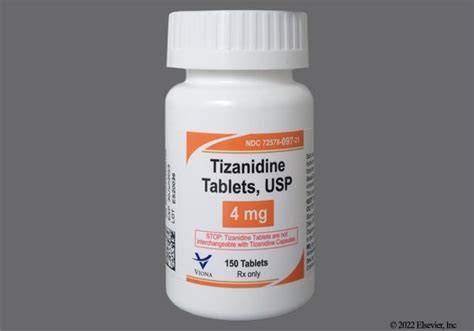
The quest for effective pain management has led to the development of various medications, each with its unique characteristics and benefits. Among these, tizanidine hydrochloride has emerged as a significant player, particularly in the form of a 4 mg tablet. This article delves into the intricacies of tizanidine, its mechanism of action, benefits, potential side effects, and the significance of the 4 mg dosage, providing a comprehensive overview for both healthcare professionals and individuals seeking relief from muscle spasms and pain.
Introduction to Tizanidine

Tizanidine is a muscle relaxant used to treat muscle spasms caused by conditions such as multiple sclerosis or spinal injury. It works by blocking nerve impulses (pain sensations) that are sent to the brain. The drug is an α2 adrenergic agonist, which means it acts on the central nervous system to produce its effects. This distinguishes it from other types of muscle relaxants, which might work through different mechanisms, such as acting directly on muscles or on the neuromuscular junction.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of tizanidine involves its ability to bind to α2-adrenergic receptors in the brain and spinal cord. This binding action inhibits the release of excitatory amino acids, which play a role in transmitting pain and spasm signals. By reducing the release of these neurotransmitters, tizanidine decreases the muscle tone, which in turn reduces muscle spasms and the associated pain.
Benefits of Tizanidine 4 Mg Tablets
The 4 mg tablet of tizanidine offers a convenient and effective dosage for managing muscle spasms. Its benefits can be summarized as follows:
- Rapid Onset of Action: Tizanidine starts working within a short time frame, providing quick relief from spasms and pain.
- Effective Muscle Relaxation: By acting centrally, it helps in reducing muscle tone, thereby alleviating spasms and discomfort.
- Flexibility in Dosage: The 4 mg dosage can be adjusted based on the patient’s response, though it’s typically taken as needed, up to a maximum recommended dose.
- Relatively Short Duration of Action: This means that the drug’s effects are shorter-lived, which can be beneficial for managing acute spasms without prolonged sedation or muscle weakness.
Potential Side Effects
Like all medications, tizanidine can cause side effects. Common ones include drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and dry mouth. More serious but less common side effects can include hypotension (low blood pressure), bradycardia (slow heart rate), and in rare cases, liver damage or allergic reactions. It’s crucial for patients to discuss their medical history, including any liver or kidney conditions, with their healthcare provider before starting tizanidine.
Interactions and Precautions
Tizanidine can interact with a variety of medications, including fluvoxamine, ciprofloxacin, and other drugs that are potent inhibitors of CYP1A2, an enzyme involved in its metabolism. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal products they are taking. Additionally, because tizanidine can cause drowsiness and affect coordination, patients should avoid driving or operating heavy machinery until they know how the drug affects them.
Practical Application of Tizanidine 4 Mg Tablets
For individuals suffering from muscle spasms, incorporating tizanidine 4 mg tablets into their treatment plan under the guidance of a healthcare provider can offer significant relief. Here are some practical considerations:
- Dosage and Frequency: Typically, the dose is titrated up based on the patient’s response. The maximum recommended dose is usually not to exceed 36 mg in 24 hours, with most patients not requiring more than 16 to 24 mg.
- Monitoring Side Effects: Patients should be regularly monitored for side effects, especially in the initial phase of treatment or when adjusting the dose.
- Combination Therapy: Sometimes, tizanidine may be used in combination with other muscle relaxants or drugs. Close monitoring is necessary to avoid adverse effects.
Comparison with Other Muscle Relaxants
The landscape of muscle relaxants is diverse, with options ranging from baclofen and cyclobenzaprine to metaxalone and methocarbamol. Each has its specific uses, side effect profiles, and mechanisms of action. For instance:
- Baclofen acts on GABA receptors and is particularly useful for treating spasticity related to multiple sclerosis.
- Cyclobenzaprine works similarly to antidepressants by affecting serotonin and norepinephrine levels, and it’s often prescribed for acute musculoskeletal conditions.
- Metaxalone directly affects the central nervous system to suppress pain and discomfort but is less commonly associated with sedation compared to some other muscle relaxants.
Historical Evolution of Muscle Relaxants
The development of muscle relaxants like tizanidine reflects an evolving understanding of pain and muscle physiology. Early muscle relaxants were often derived from plants or involved the use of general anesthetics. The discovery of neurotransmitters like GABA and the role of adrenergic receptors have paved the way for more targeted therapies. Today, there’s a push towards drugs with fewer side effects, better efficacy, and a more nuanced understanding of their mechanisms, signaling a promising future for the management of muscle spasms and pain.
Future Trends in Pain Management
As research continues, the future of pain management, including the use of muscle relaxants like tizanidine, looks promising. Emerging trends include the development of more selective receptor agonists, drugs that can modulate the immune response to reduce chronic pain, and innovative drug delivery systems that minimize side effects. Additionally, there’s a growing interest in non-pharmacological interventions, such as physical therapy, acupuncture, and psychological therapies, which can complement or even replace medication in some cases.
Conclusion
Tizanidine 4 mg tablets represent a valuable option for managing muscle spasms and associated pain. With its unique mechanism of action, flexibility in dosage, and relatively fast onset of action, it offers relief to many individuals. However, as with any medication, a comprehensive understanding of its benefits, potential side effects, and interactions is crucial for maximizing its therapeutic potential. As the medical field continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest advancements and considering a multifaceted approach to pain management will be key to improving patient outcomes.
What is the primary use of tizanidine 4 mg tablets?
+Tizanidine 4 mg tablets are primarily used to treat muscle spasms caused by conditions such as multiple sclerosis or spinal injury.
How does tizanidine work?
+Tizanidine acts as an α2 adrenergic agonist, blocking nerve impulses (pain sensations) that are sent to the brain, thereby reducing muscle spasms and associated pain.
What are the common side effects of tizanidine?
+Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and dry mouth. It's essential to discuss any concerns or pre-existing conditions with a healthcare provider before taking tizanidine.
Can tizanidine interact with other medications?
+Yes, tizanidine can interact with several medications, including fluvoxamine and ciprofloxacin, which are potent inhibitors of CYP1A2. Patients should provide their healthcare provider with a list of all medications they are taking.
What is the recommended dosage of tizanidine 4 mg tablets?
+The dosage of tizanidine is typically titrated based on patient response, with the maximum recommended dose not exceeding 36 mg in 24 hours. However, the dosage should be determined by a healthcare provider based on individual patient needs.
In conclusion, while tizanidine 4 mg tablets are a valuable tool in managing muscle spasms, it’s critical for patients to be well-informed about their use, ensuring they maximize the benefits while minimizing risks. By combining medication with lifestyle adjustments and possibly other therapies, individuals can better manage their condition and improve their quality of life.