Torn Meniscus Operation
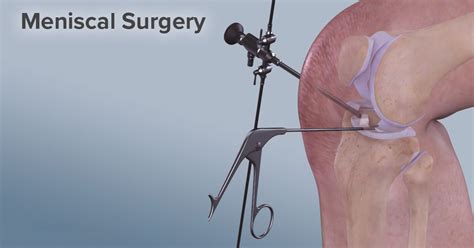
The meniscus, a crucial component of the knee joint, plays a pivotal role in absorbing shock, stabilizing the knee, and facilitating smooth movement. However, the meniscus is prone to tears, especially among athletes and individuals who engage in high-impact activities. A torn meniscus can cause significant pain, swelling, and limited mobility, necessitating surgical intervention in severe cases. The torn meniscus operation, also known as meniscectomy or meniscal repair, is a surgical procedure designed to alleviate symptoms and restore knee function.
Understanding the Meniscus and Meniscal Tears
The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure located between the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia) in the knee joint. There are two menisci in each knee, one on the inner (medial) aspect and one on the outer (lateral) aspect. Meniscal tears can occur due to traumatic injuries, such as a sudden twist or bend, or as a result of wear and tear over time. The severity of the tear can vary, ranging from small, asymptomatic tears to large, debilitating tears that require surgical attention.
Surgical Options for Torn Meniscus
The primary goal of torn meniscus surgery is to relieve symptoms, improve knee function, and prevent further damage to the joint. There are two main surgical options: meniscectomy and meniscal repair.
- Meniscectomy: This procedure involves the removal of the damaged meniscus tissue. It is typically performed for smaller tears or in cases where the meniscus is beyond repair. Meniscectomy can be done using arthroscopic techniques, which involve inserting a small camera and surgical instruments through tiny incisions.
- Meniscal Repair: This procedure involves repairing the torn meniscus by suturing or anchoring the damaged tissue. Meniscal repair is often preferred for larger tears, especially in younger patients or those with a high level of physical activity. The goal of meniscal repair is to preserve as much of the meniscus as possible, which can help maintain knee function and reduce the risk of future problems.
Torn Meniscus Operation Techniques
The torn meniscus operation is typically performed under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia, which numbs the lower part of the body. The surgery can be done using arthroscopic techniques or open surgery, depending on the severity of the tear and the surgeon’s preference.
- Arthroscopic Meniscectomy: This is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting an arthroscope (a small camera) and surgical instruments through tiny incisions. The surgeon uses the arthroscope to visualize the inside of the knee joint and remove the damaged meniscus tissue.
- Open Meniscectomy: This is a more traditional approach that involves making a larger incision to access the knee joint. Open meniscectomy may be necessary for more complex tears or in cases where arthroscopic techniques are not feasible.
- Meniscal Repair Techniques: Meniscal repair can be performed using various techniques, including inside-out repair, outside-in repair, and all-inside repair. The choice of technique depends on the location and severity of the tear, as well as the surgeon’s experience and preference.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery process after a torn meniscus operation can vary depending on the type of surgery, the severity of the tear, and the individual’s overall health. In general, patients can expect to follow a rehabilitation program that includes:
- Pain management: Controlling pain and discomfort with medication and other interventions.
- Swelling reduction: Applying ice, compression, and elevation to reduce swelling and promote healing.
- Range of motion exercises: Gentle exercises to maintain knee mobility and prevent stiffness.
- Strengthening exercises: Progressively strengthening the muscles around the knee to support the joint and improve function.
- Functional activities: Gradually returning to daily activities and sports, with a focus on proper technique and knee protection.
Potential Complications and Risks
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential complications and risks associated with torn meniscus surgery. These may include:
- Infection: Bacterial or other infections can occur after surgery, requiring antibiotic treatment or further surgical intervention.
- Nerve damage: The nerves surrounding the knee joint can be damaged during surgery, leading to numbness, tingling, or weakness.
- Blood clots: Blood clots can form in the leg or lung, requiring anticoagulant medication or other treatment.
- Knee stiffness: The knee joint can become stiff after surgery, requiring prolonged rehabilitation and physical therapy.
- Future knee problems: Torn meniscus surgery can increase the risk of future knee problems, such as osteoarthritis or ligament injuries.
Conclusion
Torn meniscus surgery is a common procedure designed to alleviate symptoms and restore knee function. While the surgery can be effective in relieving pain and improving mobility, it’s essential to understand the potential complications and risks involved. By working closely with an orthopedic surgeon and following a comprehensive rehabilitation program, individuals can optimize their recovery and reduce the risk of future knee problems.
What are the symptoms of a torn meniscus?
+The symptoms of a torn meniscus can include pain, swelling, limited mobility, and a feeling of instability in the knee joint. In some cases, a torn meniscus can cause a “catching” or “locking” sensation, where the knee joint feels like it’s getting stuck.
Can a torn meniscus be treated without surgery?
+In some cases, a torn meniscus can be treated without surgery, especially if the tear is small and asymptomatic. Conservative treatment options may include physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle modifications to reduce stress on the knee joint. However, more severe tears may require surgical intervention to relieve symptoms and restore knee function.
What is the recovery time for torn meniscus surgery?
+The recovery time for torn meniscus surgery can vary depending on the type of surgery, the severity of the tear, and the individual’s overall health. In general, patients can expect to follow a rehabilitation program that lasts several weeks to several months, with a gradual return to daily activities and sports.
Can I prevent a torn meniscus?
+While it’s not possible to completely prevent a torn meniscus, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of injury. These include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, and using proper technique when participating in sports or other activities.
What are the potential complications of torn meniscus surgery?
+Potential complications of torn meniscus surgery can include infection, nerve damage, blood clots, knee stiffness, and future knee problems. It’s essential to discuss these risks with an orthopedic surgeon and follow a comprehensive rehabilitation program to minimize the risk of complications.



