Triglycerides Normal Range: Know Your Levels
Understanding triglycerides and their role in your overall health is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Triglycerides are a type of fat found in your blood, and when their levels become too high, it can increase your risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. In this article, we will delve into the importance of triglycerides, the normal range for triglyceride levels, and how you can manage them to ensure your heart health remains optimal.
What Are Triglycerides?
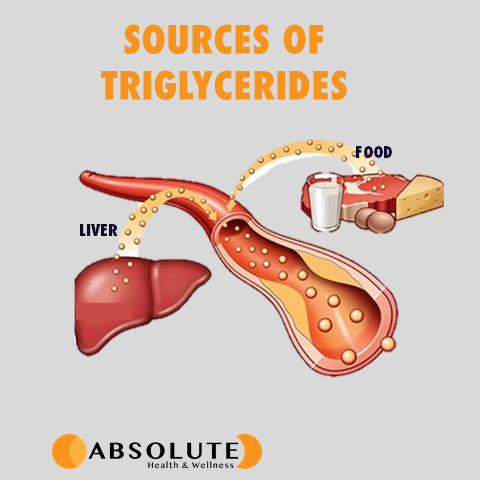
Triglycerides are the most common type of fat in the body and are composed of three fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol molecule. They are an important source of energy, but high levels can be harmful. Triglycerides come from the food we eat, particularly from fats and oils, and are also produced in the liver. When you eat, your body converts any calories it doesn’t need immediately into triglycerides, which are stored in your fat cells. Later, hormones such as insulin and epinephrine release triglycerides for energy between meals.
Importance of Triglycerides
While high levels of triglycerides can be detrimental to health, they also play a crucial role in the body’s energy system. They serve as the main form of energy storage in the body, and their regulation is vital for maintaining health. However, when triglyceride levels become elevated, it can signal an increased risk of developing conditions such as pancreatitis, fatty liver disease, and most notably, cardiovascular disease. High triglyceride levels can contribute to the hardening or thickening of the artery walls, which increases the risk of stroke, heart attack, and other heart diseases.
Normal Range for Triglyceride Levels
The normal range for triglyceride levels can vary slightly depending on the laboratory conducting the test, but generally, the following levels are considered: - Normal: Less than 150 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) - Borderline High: 150 to 199 mg/dL - High: 200 to 499 mg/dL - Very High: 500 mg/dL or above
It’s essential to understand that these levels should be considered in the context of other lipid profiles, including LDL (bad cholesterol), HDL (good cholesterol), and total cholesterol levels. A healthcare provider can offer personalized advice based on your overall lipid profile and other risk factors for heart disease.
Factors Affecting Triglyceride Levels
Several factors can influence your triglyceride levels, including: - Diet: Consuming high amounts of sugar, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates can increase triglyceride levels. - Weight: Being overweight or obese can significantly raise triglyceride levels. - Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can help lower triglyceride levels. - Genetics: Family history can play a role in triglyceride levels. - Certain Medications: Such as beta-blockers, estrogen, and corticosteroids. - Medical Conditions: Including diabetes, kidney disease, and hypothyroidism.
Managing Triglyceride Levels
Fortunately, high triglyceride levels can often be managed through lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Here are some strategies to help you lower your triglyceride levels: - Dietary Changes: Focus on a heart-healthy diet that is low in sugar and saturated fats. Include more soluble fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats found in foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. - Weight Loss: If you are overweight, losing weight can help lower triglyceride levels. - Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. - Limit Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol can raise triglyceride levels. - Quit Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease and can also affect triglyceride levels.
Medications for High Triglycerides
If lifestyle changes are not enough to lower your triglyceride levels, your doctor may prescribe medication. Common medications for high triglycerides include: - Fibrates: These drugs, such as fenofibrate and gemfibrozil, can help lower triglyceride levels and raise HDL cholesterol. - Niacin: Niacin can help raise HDL cholesterol and lower both LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. - Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish oil supplements, these can help lower triglyceride levels. - Statins: While primarily used to lower LDL cholesterol, statins can also lower triglyceride levels.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy triglyceride levels is crucial for reducing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions. By understanding what triglycerides are, their normal range, and how to manage them, you can take proactive steps towards a healthier heart. Always consult with a healthcare provider to interpret your triglyceride levels in the context of your overall health and to develop a personalized plan for managing your lipid profiles.
What are normal triglyceride levels?
+Normal triglyceride levels are generally considered to be less than 150 mg/dL. However, it’s essential to consider these levels in conjunction with other lipid profiles and health factors.
How can I lower my triglyceride levels?
+Lifestyle changes such as a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, weight loss if needed, limiting alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking can help lower triglyceride levels. In some cases, medication may be necessary.
What medications are used to treat high triglycerides?
+Medications for high triglycerides include fibrates, niacin, omega-3 fatty acids, and statins. The choice of medication depends on the individual’s overall health profile and the severity of their high triglyceride levels.
Related Terms:
- Triglycerides normal range by age
- What causes high triglycerides
- Low triglycerides symptoms
- How to reduce triglycerides
- Triglycerides level chart
- Triglycerides diet