Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy
Tubal ectopic pregnancy is a life-threatening condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. This type of pregnancy is also known as ectopic pregnancy or tubal pregnancy. The fallopian tubes are not designed to support a growing embryo, and as the pregnancy progresses, the tube can rupture, causing severe internal bleeding and potentially life-threatening complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
Tubal ectopic pregnancy is often caused by damage to the fallopian tubes, which can be due to various factors such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, or previous surgery. Other risk factors include:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): A bacterial infection that can cause inflammation and scarring in the fallopian tubes.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, leading to inflammation and scarring.
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: Women who have had a previous ectopic pregnancy are at increased risk of having another ectopic pregnancy.
- Fertility Treatments: Women who undergo fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), may be at increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Symptoms
The symptoms of tubal ectopic pregnancy can vary, but common signs include:
- Abdominal Pain: Severe, sharp, or crampy pain in the lower abdomen.
- Vaginal Bleeding: Light to heavy bleeding or spotting.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Similar to morning sickness, but can be more severe.
- Shoulder Pain: Pain in the shoulder or upper abdomen due to internal bleeding.
- Fainting or Dizziness: Due to blood loss or shock.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing tubal ectopic pregnancy can be challenging, as the symptoms are often similar to those of a normal pregnancy or other conditions. A combination of the following tests and examinations may be used to diagnose ectopic pregnancy:
- Pelvic Exam: A physical exam to check for tenderness and abnormalities in the reproductive organs.
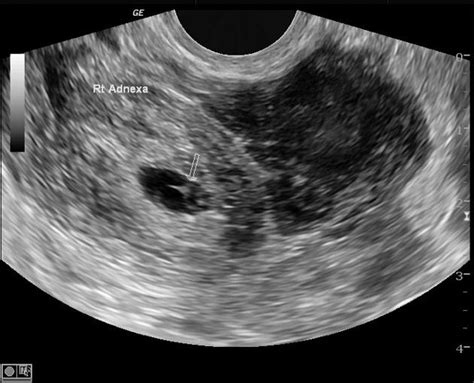
- Ultrasound: An imaging test to visualize the reproductive organs and detect any abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: To measure hormone levels, including human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and progesterone.
- Laparoscopy: A surgical procedure to visually examine the reproductive organs.
Treatment
Treatment for tubal ectopic pregnancy depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health. Options include:
- Expectant Management: Close monitoring of the patient’s condition, with the hope that the body will absorb the pregnancy tissue.
- Medical Management: Medications, such as methotrexate, to stop the growth of the embryo and allows the body to absorb the pregnancy tissue.
- Surgery: Laparoscopic or open surgery to remove the ectopic pregnancy and repair any damage to the fallopian tube.
Complications
Tubal ectopic pregnancy can lead to serious complications, including:
- Rupture of the Fallopian Tube: Leading to severe internal bleeding and potentially life-threatening shock.
- Infertility: Damage to the fallopian tube can increase the risk of infertility.
- Hysterectomy: In severe cases, removal of the uterus may be necessary to control bleeding.
Prevention
While it is not possible to completely prevent tubal ectopic pregnancy, women can reduce their risk by:
- Practicing Safe Sex: To reduce the risk of PID and other infections.
- Getting Regular Check-Ups: To monitor reproductive health and detect any potential issues early.
- Avoiding Smoking: To reduce the risk of ectopic pregnancy and other health complications.
What are the chances of having a successful pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy?
+The chances of having a successful pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy depend on various factors, including the extent of damage to the fallopian tube and the overall health of the woman. Women who have had an ectopic pregnancy are at increased risk of having another ectopic pregnancy, but many women are still able to have successful pregnancies.
Can ectopic pregnancy be prevented?
+While it is not possible to completely prevent ectopic pregnancy, women can reduce their risk by practicing safe sex, getting regular check-ups, and avoiding smoking. Women who have had a previous ectopic pregnancy should discuss their individual risk factors and prevention strategies with their healthcare provider.
What are the symptoms of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy?
+The symptoms of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy can include severe abdominal pain, heavy vaginal bleeding, fainting or dizziness, and shoulder pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
In conclusion, tubal ectopic pregnancy is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt medical attention. Women who are at risk of ectopic pregnancy should be aware of the symptoms and seek medical help immediately if they experience any unusual symptoms. By understanding the causes, risk factors, and treatment options, women can reduce their risk of ectopic pregnancy and ensure the best possible outcome.