Type 1 Diabetes: Take Control Of Your Blood Sugar
Living with Type 1 Diabetes requires a deep understanding of the complex balance between insulin, diet, and lifestyle. It’s a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and managing it effectively is crucial to prevent complications and maintain a high quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of Type 1 Diabetes, exploring the latest research, expert advice, and practical tips to help you take control of your blood sugar levels.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. Without insulin, the body is unable to convert glucose into energy, leading to a buildup of sugar in the bloodstream. This can cause a range of symptoms, including increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
According to the American Diabetes Association, approximately 1.6 million Americans are living with Type 1 Diabetes, with around 64,000 new cases diagnosed each year.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Management
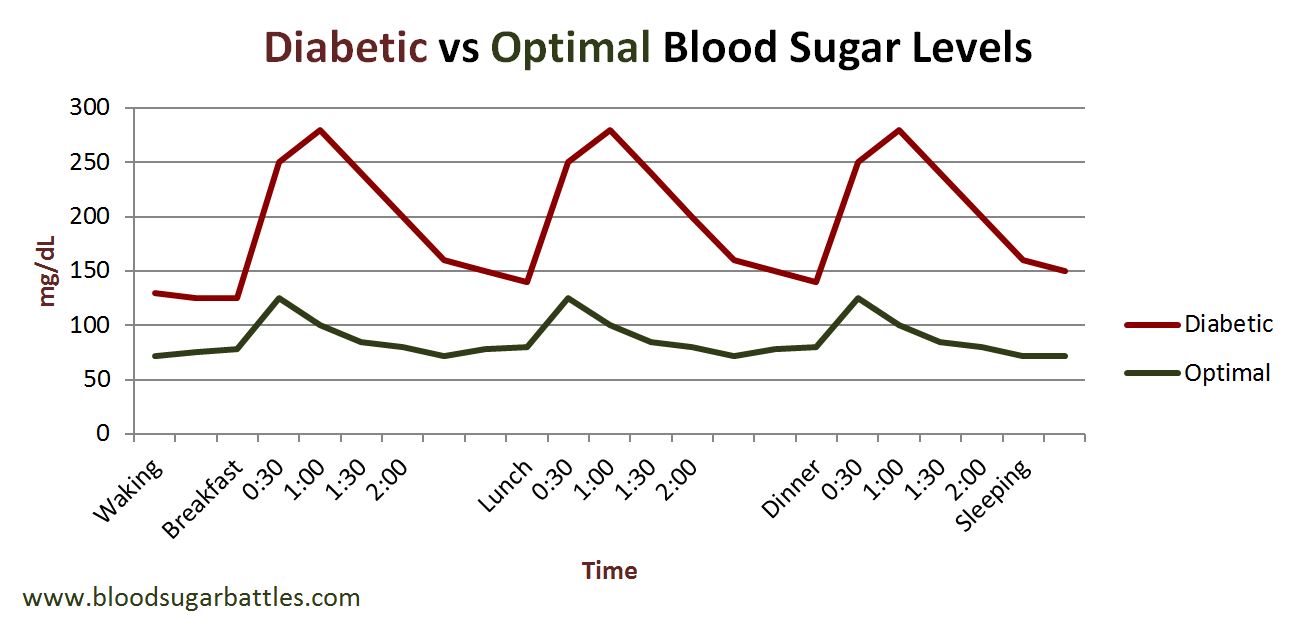
Managing blood sugar levels is critical for people with Type 1 Diabetes. High blood sugar levels can lead to short-term complications, such as diabetic ketoacidosis, while long-term complications can include heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Conversely, low blood sugar levels can cause shakiness, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness.
| Blood Sugar Level | Normal Range | Hyperglycemia | Hypoglycemia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before meals | 70-130 mg/dL | Above 180 mg/dL | Below 70 mg/dL |
| After meals | Less than 180 mg/dL | Above 200 mg/dL | Below 70 mg/dL |
Taking Control: A Holistic Approach
Taking control of your Type 1 Diabetes requires a holistic approach that incorporates diet, exercise, stress management, and insulin therapy. Here are some practical tips to get you started:
- Diet and Nutrition: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid sugary drinks and foods high in saturated and trans fats.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. Additionally, incorporate strength-training exercises, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and flexibility exercises into your routine.
- Stress Management: Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Therapy: Work closely with your healthcare provider to develop an insulin regimen that meets your individual needs. This may include multiple daily injections or the use of an insulin pump.
Step-by-Step Guide to Insulin Administration
- Choose the correct type and dose of insulin based on your healthcare provider's instructions.
- Prepare the injection site by washing your hands and cleaning the area with soap and water.
- Administer the insulin using a syringe, pen, or pump, following the manufacturer's instructions.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly to adjust your insulin doses as needed.
Advanced Technologies for Diabetes Management
Recent advancements in technology have revolutionized the way people with Type 1 Diabetes manage their condition. Some of these innovations include:
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: These small devices track blood sugar levels throughout the day, providing real-time data to help you make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and insulin therapy.
- Insulin Pumps: These small devices deliver a continuous flow of insulin, allowing for more precise control over blood sugar levels.
- Artificial Pancreas Systems: These systems use advanced algorithms to automate insulin delivery, mimicking the natural function of the pancreas.
Future Directions in Type 1 Diabetes Research
Researchers are working tirelessly to develop new treatments and potential cures for Type 1 Diabetes. Some of the most promising areas of research include:
- Stem Cell Therapies: Scientists are exploring the use of stem cells to regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Immunotherapy: Researchers are investigating ways to modulate the immune system to prevent or reverse the autoimmune response that causes Type 1 Diabetes.
- Gene Therapy: Scientists are working on developing gene therapies that can help restore normal insulin production in people with Type 1 Diabetes.
Conclusion
Living with Type 1 Diabetes requires a deep understanding of the condition, as well as a commitment to managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, stress management, and insulin therapy. By incorporating the latest research, expert advice, and practical tips into your daily routine, you can take control of your Type 1 Diabetes and live a long, healthy, and fulfilling life.
What are the symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes?
+The symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How can I manage my blood sugar levels?
+You can manage your blood sugar levels by following a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and taking your insulin as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
What are the potential complications of Type 1 Diabetes?
+The potential complications of Type 1 Diabetes include heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.