Type 2 Diabetes Glucose Levels: Manage With Ease
Maintaining optimal glucose levels is crucial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. It’s a delicate balance that, when achieved, can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve overall quality of life. The journey to managing type 2 diabetes glucose levels effectively begins with understanding the condition, its impact on the body, and the strategies available for its management.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
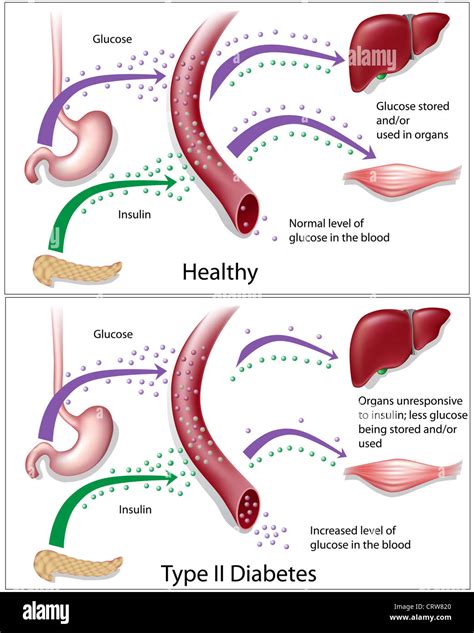
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by the body’s inability to use insulin properly, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. Over time, the body becomes resistant to insulin, and the pancreas may also produce less insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. This condition can lead to a variety of complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage, if not properly managed.
The Importance of Glucose Monitoring
Glucose monitoring is a critical component of type 2 diabetes management. It involves regularly checking blood glucose levels to understand how different factors such as food, physical activity, and medications affect these levels. By doing so, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication to keep their glucose levels within a target range.
Strategies for Managing Glucose Levels
1. Dietary Changes
Adopting a healthy diet is one of the most effective ways to manage type 2 diabetes. This includes focusing on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It’s also important to limit intake of sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats. Working with a dietitian or a healthcare provider to develop a personalized meal plan can be incredibly beneficial.
2. Physical Activity
Regular physical activity not only helps lower blood glucose levels but also improves insulin sensitivity, making the body more responsive to insulin. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent options, and it’s recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Strength training exercises can also be beneficial, as they help build muscle mass, which further improves insulin sensitivity.
3. Medication Adherence
For many individuals with type 2 diabetes, medication is a necessary part of their management plan. This can include metformin, sulfonylureas, or other glucose-lowering medications, depending on the individual’s specific needs and health status. It’s crucial to take medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider and to discuss any concerns or side effects.
4. Stress Management
Stress can raise blood glucose levels and make it more challenging to manage diabetes. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help mitigate this effect. Getting enough sleep and maintaining a consistent daily routine are also important for managing stress and supporting overall diabetes management.
Advanced Management Techniques
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM involves wearing a small device that tracks glucose levels throughout the day and night. This provides valuable insights into daily patterns and can help identify factors that cause glucose levels to rise or fall, allowing for more precise management.
2. Insulin Therapy
For some individuals with type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy may be necessary, especially if other treatments are not effective in controlling glucose levels. This involves injecting insulin, which helps the body regulate blood sugar levels. The type and regimen of insulin can vary based on individual needs.
Future Perspectives in Type 2 Diabetes Management
The landscape of type 2 diabetes management is continually evolving, with new technologies, medications, and lifestyle interventions being developed. Advances in CGM, insulin pumps, and automated insulin delivery systems are making it easier for individuals to manage their condition. Additionally, research into the potential of bariatric surgery and newer medications that target different pathways in glucose metabolism is offering hope for more effective management strategies.
FAQs
What are normal blood glucose levels for someone with type 2 diabetes?
+For individuals with type 2 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following target blood glucose levels: before meals, less than 130 mg/dL, and less than 180 mg/dL after eating.
How often should I check my blood glucose levels if I have type 2 diabetes?
+The frequency of checking blood glucose levels can vary depending on your treatment plan and how well your diabetes is controlled. Generally, it's recommended to check levels at least once a day, but this can increase to several times a day, especially if you're taking insulin or noticing significant fluctuations in your levels.
Can type 2 diabetes be reversed through lifestyle changes alone?
+While type 2 diabetes cannot be "cured" in the classical sense, significant lifestyle changes, including weight loss, a healthy diet, and regular physical activity, can lead to remission, where blood glucose levels return to a normal range without the need for diabetes medications. This is most effective in the early stages of the disease.
Conclusion
Managing type 2 diabetes requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates dietary changes, physical activity, medication adherence, and stress management. By adopting these strategies and staying informed about the latest advances in diabetes care, individuals with type 2 diabetes can effectively manage their glucose levels, reduce the risk of complications, and lead a healthy, fulfilling life. Regular communication with healthcare providers and ongoing education are key to navigating the complexities of diabetes management and achieving the best possible outcomes.