Uti Symptoms: Get Accurate Diagnosis
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are a common health issue affecting millions of people worldwide, with symptoms that can range from mildly irritating to severely debilitating. Despite their prevalence, UTIs are often misunderstood or misdiagnosed, leading to delayed or inappropriate treatment. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the world of UTI symptoms, exploring the complexities of diagnosis, the importance of accurate identification, and the latest approaches to managing these infections.
Understanding UTI Symptoms
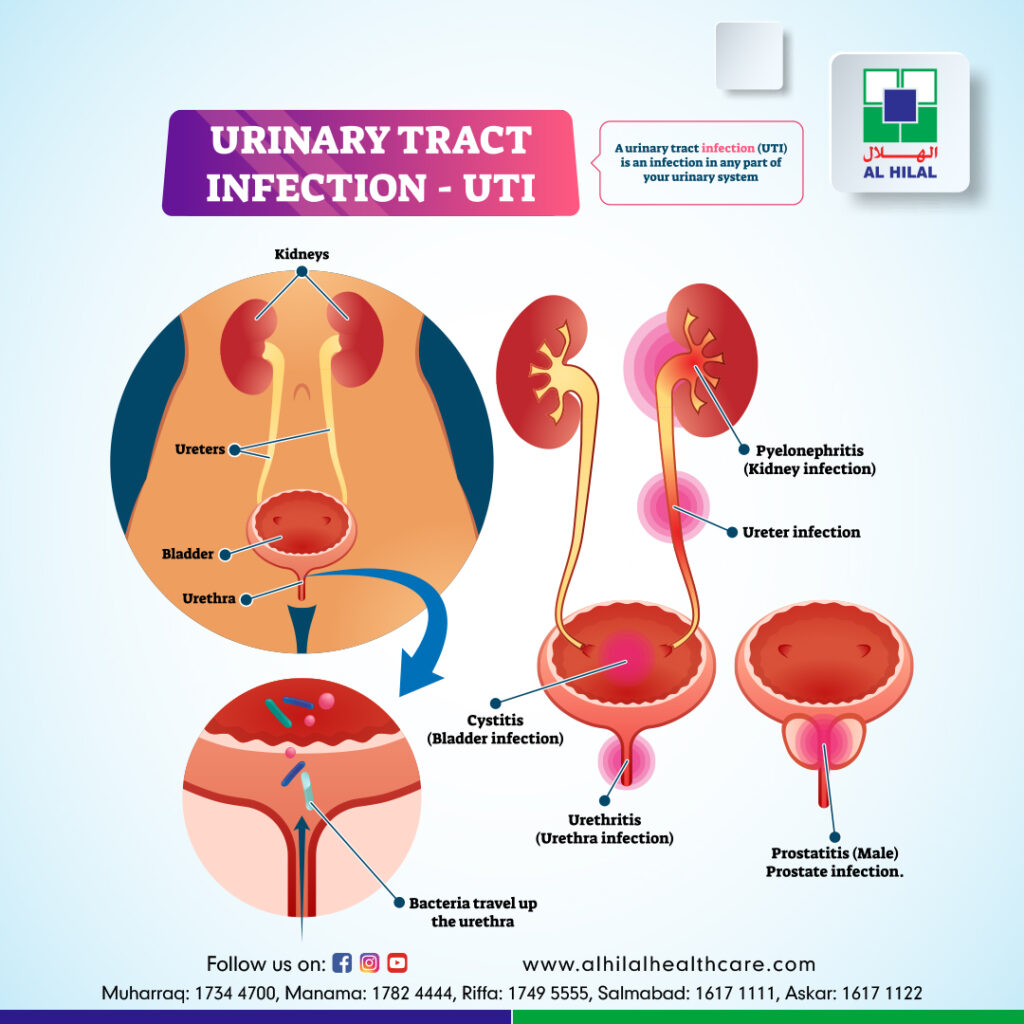
UTI symptoms can vary significantly from person to person and may depend on the specific part of the urinary tract that is infected. The urinary tract includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Infections can occur in any part of this system, with the lower urinary tract (bladder and urethra) being the most common site.
Lower Urinary Tract Infections: Symptoms often include a strong, persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation while urinating, passing frequent, small amounts of urine, and urine that appears cloudy, dark, or has an unusual odor. In women, pelvic pain and, in men, rectal pain may also be present.
Upper Urinary Tract Infections: These are typically more severe and can involve the kidneys. Symptoms may include flank pain, high fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. In severe cases, upper UTIs can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
The Challenge of Diagnosing UTIs
Diagnosing UTIs can be complex due to the overlap of symptoms with other conditions and the potential for asymptomatic infections, especially in older adults. A accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and to prevent complications such as kidney damage or the spread of infection.
Clinical Evaluation: Healthcare providers will typically start with a physical exam and a medical history to identify risk factors and symptoms suggestive of a UTI.
Urinalysis: This involves analyzing a urine sample for the presence of red and white blood cells, bacteria, and the presence of nitrites, which many UTI-causing bacteria produce. While useful, urinalysis can sometimes yield false-negative results, especially in patients who have recently urinated or are using certain types of birth control.
Urine Culture: Considered the gold standard for diagnosing UTIs, urine culture involves growing bacteria from a urine sample in a laboratory. This not only confirms the presence of bacteria but also helps identify the specific type of bacteria and its antibiotic sensitivity profile.
Accurate Diagnosis: Why It Matters
An accurate diagnosis is not just about confirming the presence of an infection; it’s also about identifying the right treatment approach. UTIs are caused by a variety of bacteria, and the choice of antibiotic depends on the type of bacteria and local resistance patterns.
Antibiotic Resistance: The misuse and overuse of antibiotics have led to increasing rates of antibiotic resistance among UTI-causing bacteria. Accurate diagnosis helps in selecting the most appropriate antibiotic, thereby reducing the risk of contributing to antibiotic resistance.
Complications Prevention: Prompt and accurate treatment can prevent complications such as pyelonephritis (a kidney infection), sepsis, and in pregnant women, premature labor and low birth weight babies.
Future Directions in UTI Diagnosis
The field of UTI diagnosis is evolving, with research focused on developing more rapid, accurate, and less invasive diagnostic tools. Point-of-care tests that can quickly identify the presence and type of bacteria are being developed, which could significantly reduce the time to appropriate treatment.
Biomarkers and Genomic Testing: There is a growing interest in identifying biomarkers for UTIs that could allow for quicker diagnosis and potentially more targeted treatments. Genomic testing may also play a role in the future, helping to identify genetic factors that predispose individuals to UTIs.
Emerging Therapies: Beyond diagnostics, new therapies are being explored, including vaccines against common UTI pathogens and non-antibiotic treatments to reduce the reliance on antibiotics.
Living with UTIs: Prevention and Management
While UTIs can be effectively treated, prevention is a crucial aspect of managing these infections, especially for individuals who experience recurrent UTIs.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps to dilute the urine and increase urination, which can help to flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
Urination After Intercourse: For women, urinating after sexual intercourse may help to flush out bacteria that may have entered the urethra.
Cranberry Juice: Although the evidence is mixed, some studies suggest that cranberry juice may prevent UTIs by preventing bacteria from adhering to the bladder and urinary tract walls.
Good Hygiene Practices: Wiping from front to back after using the toilet and avoiding the use of scented soaps or douches can reduce the risk of introducing bacteria into the urinary tract.
Conclusion
UTI symptoms can be subtle and misleading, and accurate diagnosis is key to effective management and prevention of complications. As our understanding of UTIs evolves, so too do the approaches to diagnosis and treatment. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can better navigate the challenges of UTIs and work towards maintaining urinary tract health.
What are the primary symptoms of a lower urinary tract infection?
+The primary symptoms include a strong urge to urinate, a burning sensation while urinating, frequent urination, and cloudy or dark urine. Additionally, there may be pelvic pain in women and rectal pain in men.
How is a urinary tract infection diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, urinalysis, and urine culture. The urine culture is the most definitive test, as it can identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection and its antibiotic susceptibility.
What can I do to prevent UTIs?
+Prevention strategies include staying well-hydrated, urinating after sexual intercourse, considering cranberry juice (though evidence is mixed), practicing good hygiene, and avoiding scented soaps or douches.
Why is accurate diagnosis of UTIs important?
+Accurate diagnosis is crucial for selecting the appropriate antibiotic, thereby reducing the risk of contributing to antibiotic resistance and ensuring effective treatment to prevent complications such as kidney damage or sepsis.
What are some future directions in UTI diagnosis and treatment?
+Future directions include the development of rapid point-of-care tests, biomarkers, and genomic testing for quicker and more targeted treatments. Additionally, there is research into new therapies such as vaccines and non-antibiotic treatments to combat UTIs.



