Vaginal Bleeding Not Menstrual
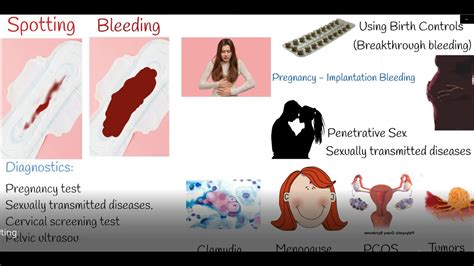
Vaginal bleeding that is not associated with the menstrual cycle can be a concerning and potentially serious issue for women. This type of bleeding is medically referred to as abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) and can have various causes, ranging from mild to severe. Understanding the potential causes, recognizing the signs, and seeking appropriate medical attention are crucial for addressing and managing vaginal bleeding not related to menstruation.
Causes of Non-Menstrual Vaginal Bleeding
The causes of abnormal vaginal bleeding can be broadly categorized into several groups, including hormonal changes, anatomical issues, and systemic diseases.
Hormonal Imbalance: Changes in hormone levels, particularly fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone, can lead to irregular bleeding. This is common in puberty, perimenopause, and menopause. Birth control methods, especially when first started or stopped, can also cause hormonal imbalances leading to bleeding.
Pregnancy Complications: Bleeding during pregnancy can be a sign of a miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or placental issues like placenta previa. It’s essential to seek immediate medical attention if bleeding occurs during pregnancy.
Infections and Inflammations: Infections of the reproductive tract, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), can cause bleeding. Inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis) or endometrium (endometritis) can also lead to abnormal bleeding.
Polyps and Fibroids: Uterine polyps and fibroids are growths in the uterus that can cause irregular bleeding. While often benign, they can lead to significant bleeding and discomfort.
Cancer: Although less common, vaginal bleeding can be a symptom of cervical, uterine, or ovarian cancer. Any unusual bleeding, especially in postmenopausal women, warrants a thorough medical evaluation.
Injury or Trauma: Physical trauma to the genital area can result in bleeding.
Medications: Certain medications, including anticoagulants (blood thinners), can increase the risk of vaginal bleeding.
Systemic Diseases: Bleeding disorders, such as von Willebrand disease, and diseases affecting the liver or kidney can also lead to abnormal vaginal bleeding due to their impact on blood clotting and hormone regulation.
Signs and Symptoms
While the primary symptom is vaginal bleeding that occurs outside of the normal menstrual cycle, other signs may accompany it, depending on the underlying cause. These can include:
- Heavy or Prolonged Bleeding: Soaking more than one pad or tampon per hour.
- Pelvic Pain: Cramping or a dull ache in the lower abdomen.
- Abnormal Vaginal Discharge: Changes in the amount, color, or odor of discharge.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature, indicating a possible infection.
- Weakness or Dizziness: Due to significant blood loss.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing the cause of non-menstrual vaginal bleeding involves a combination of:
- Medical History: Discussing menstrual history, sexual history, and any previous surgeries or conditions.
- Physical Exam: Including a pelvic exam to check for any abnormalities.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or MRI to visualize the uterus and ovaries.
- Endometrial Biopsy: A sample of the uterine lining is taken to check for cancer or abnormal cell changes.
- Blood Tests: To check for pregnancy, hormonal levels, and signs of infection.
Treatment depends on the cause and may include:
- Hormonal Therapies: To regulate hormonal imbalances.
- Surgery: To remove polyps, fibroids, or in cases of cancer.
- Antibiotics: For infections.
- Blood Transfusions: In cases of severe blood loss.
- Pain Management: For discomfort and pain.
Prevention and Management
While not all causes of non-menstrual vaginal bleeding can be prevented, maintaining good reproductive health can reduce the risk. This includes:
- Regular Health Check-ups: Annual gynecological exams can help identify issues early.
- Practicing Safe Sex: Reducing the risk of STDs and unwanted pregnancies.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress.
Conclusion
Vaginal bleeding that is not part of the regular menstrual cycle is a symptom that requires medical evaluation to determine its cause. By understanding the potential causes, recognizing the signs, and seeking medical care when necessary, women can ensure their reproductive health and address any issues promptly and effectively.
FAQ Section
What are the most common causes of non-menstrual vaginal bleeding in women of reproductive age?
+Hormonal imbalances, pregnancy complications, and infections are among the most common causes. Hormonal birth control methods can also lead to irregular bleeding, especially when first initiated or after cessation.
How is non-menstrual vaginal bleeding diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical exam, imaging tests like ultrasound, endometrial biopsy, and blood tests to check for pregnancy, infections, or hormonal imbalances.
What are the signs that non-menstrual vaginal bleeding might be a sign of a serious condition?
+Signs of a potentially serious condition include heavy or prolonged bleeding, severe pelvic pain, fever, or bleeding after sexual intercourse. Any vaginal bleeding during pregnancy or in postmenopausal women should be evaluated promptly.
Can non-menstrual vaginal bleeding be prevented?
+While not all causes can be prevented, practicing safe sex, maintaining a healthy weight, and not smoking can reduce the risk of certain conditions that may lead to abnormal bleeding. Regular health check-ups are also crucial for early detection and management of potential issues.
How is non-menstrual vaginal bleeding treated?
+Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include hormonal therapies, antibiotics for infections, surgery for removal of growths like polyps or fibroids, and in some cases, blood transfusions for significant blood loss.