What Affects Blood Sugar Readings? Expert Advice
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, especially for individuals with diabetes. Blood sugar readings can fluctuate due to various factors, making it essential to understand what affects these readings to manage them effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the factors that influence blood sugar levels, providing expert advice on how to navigate these complexities.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Before exploring the factors that affect blood sugar readings, it’s crucial to understand what blood sugar levels are and why they’re important. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary energy source for the body’s cells. The body regulates blood sugar levels through a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Readings
Several factors can cause blood sugar levels to fluctuate. Understanding these factors is key to managing diabetes and preventing complications. The main factors include:
Diet and Nutrition: The type and amount of food consumed play a significant role in blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates, especially those with a high glycemic index, can cause a rapid increase in blood glucose. Foods high in fiber, protein, and healthy fats can help slow down this process.
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity improves the body’s sensitivity to insulin, helping to lower blood sugar levels. The timing and intensity of exercise can also impact blood glucose levels; for example, intense exercise can cause a temporary increase in blood sugar due to the release of stress hormones like adrenaline.
Stress Levels: Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Chronic stress can lead to prolonged elevated blood sugar levels, posing a challenge for diabetes management.
Medications: Certain medications, including steroids and some psychiatric medications, can raise blood sugar levels. It’s essential for individuals with diabetes to consult with their healthcare provider about any new medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Sleep Patterns: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt the balance of hormones that regulate glucose, leading to higher blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help manage blood sugar.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can affect insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels. Women with diabetes should closely monitor their blood sugar levels during these times and adjust their management plan as needed.
Age: As people age, their risk of developing insulin resistance increases, which can lead to higher blood sugar levels. Regular health check-ups and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate this risk.
Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in the development of diabetes. Individuals with a first-degree relative (parent or sibling) with diabetes are at a higher risk and should prioritize preventive measures.
Expert Advice for Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Given the complexity of factors that can influence blood sugar readings, managing diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Regular Monitoring: Check blood sugar levels as recommended by your healthcare provider to understand how different factors affect your readings.
- Balanced Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Work with a dietitian or diabetes educator to develop a personalized meal plan.
- Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. Include strength-training activities at least twice a week.
- Stress Management: Engage in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Medication Adherence: Take your medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider and consult with them before making any changes.
- Regular Health Check-Ups: Schedule regular appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor your condition and adjust your management plan as necessary.
Conclusion
Managing blood sugar levels is a multifaceted challenge that requires patience, dedication, and a thorough understanding of the factors that influence glucose readings. By acknowledging the impact of diet, physical activity, stress, medications, sleep, hormonal changes, age, and genetics, individuals can develop a personalized approach to maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Remember, the key to successful diabetes management is a proactive and holistic strategy that incorporates expert advice, regular monitoring, and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle.
What are the ideal blood sugar levels for someone with diabetes?
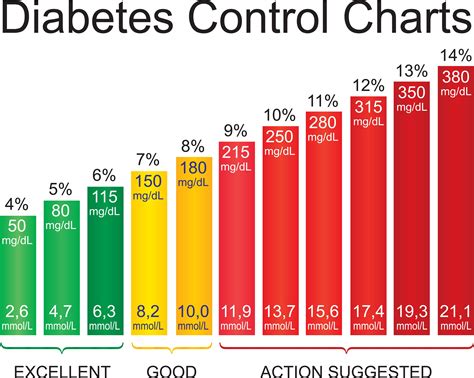
+For individuals with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood sugar targets: before meals, less than 130 mg/dL, and after meals, less than 180 mg/dL. However, these targets can vary based on age, other health conditions, and the type of diabetes. It’s crucial to follow the specific guidelines provided by your healthcare provider.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and how well the condition is managed. For example, individuals with type 1 diabetes may need to check their levels more frequently than those with type 2 diabetes who are managing their condition through diet and exercise alone. Your healthcare provider will recommend a monitoring schedule based on your individual needs.
Can diet and exercise alone control blood sugar levels?
+For some individuals, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise routine can help control blood sugar levels. However, this approach may not be sufficient for everyone, especially those with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes. Medications, including insulin, may be necessary to achieve and maintain target blood sugar levels. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best management plan for your condition.