What Are Furosemide 20Mg Side Effects? Safety Guide
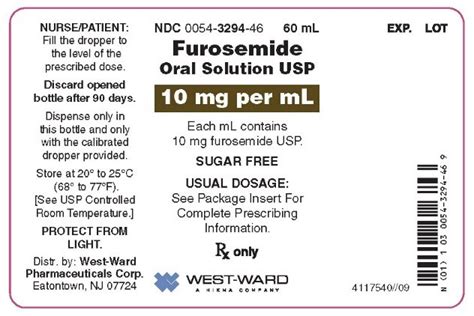
Furosemide, commonly known by its brand name Lasix, is a powerful diuretic medication used to treat fluid build-up (edema) and swelling that is caused by congestive heart failure, liver disease, a severe kidney disorder, or a medical condition called nephrotic syndrome. It belongs to a class of medications known as loop diuretics, which work by causing the kidneys to get rid of more sodium and water in the urine, thereby reducing the amount of fluid in the body.
Given its potency and the significant effects it has on the body’s fluid balance and electrolyte levels, furosemide can cause a range of side effects, some of which can be severe. Understanding these potential side effects is crucial for the safe and effective use of this medication. Here, we’ll delve into the side effects associated with furosemide 20mg, the importance of monitoring while on this medication, and provide guidance on mitigating potential adverse effects.
Common Side Effects
- Increased Urination: This is the most common and expected side effect of furosemide. It’s a sign that the drug is working to remove excess fluid from the body. However, it can sometimes lead to dehydration if not managed properly.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Due to the rapid loss of fluids and changes in blood pressure, patients may experience dizziness, especially when standing up quickly.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired is a common complaint, partly due to changes in electrolyte balances and dehydration.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some patients may experience stomach upset, nausea, or vomiting, which can further exacerbate dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
- Muscle Cramps: Changes in electrolyte levels can cause muscle cramps, weakness, or spasms.
- Thirst: As the body loses more water, feeling thirsty is a natural response.
Serious Side Effects
While less common, some side effects of furosemide can be serious and require immediate medical attention:
- Dehydration: Severe dehydration can lead to serious complications, including low blood volume (hypovolemia), which can cause a drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness, fainting, or even organ failure.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Furosemide can disrupt the balance of electrolytes (such as potassium, sodium, and chloride) in the body, leading to muscle weakness, heart arrhythmias, and other complications.
- Hearing Loss: High doses of furosemide can cause temporary or, in rare cases, permanent hearing loss.
- Allergic Reactions: Though rare, some individuals may experience an allergic reaction, which can range from mild skin rashes to life-threatening anaphylaxis.
- Gout: Increased uric acid levels due to furosemide can precipitate gout attacks in susceptible individuals.
- Glucose Tolerance: Furosemide can impair glucose tolerance, posing a risk for patients with diabetes or those at risk for developing diabetes.
Safety and Monitoring
To ensure the safe use of furosemide, regular monitoring is crucial. This includes:
- Blood Tests: Regular checks of electrolyte levels (such as potassium, sodium), kidney function, and uric acid levels.
- Blood Pressure Checks: Monitoring blood pressure to adjust the dose of furosemide as needed.
- Fluid Status: Assessing the patient’s hydration status and adjusting fluid intake and possibly the medication dose to avoid dehydration.
- Weight Checks: Daily weighing can help monitor fluid retention and guide adjustments in medication or fluid intake.
Mitigating Side Effects
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water is essential, but the amount may need to be balanced to avoid excessive fluid buildup.
- Dietary Adjustments: Monitoring and possibly restricting salt intake can help control fluid retention.
- Electrolyte Replacement: In cases of significant electrolyte imbalances, supplements or dietary changes may be recommended.
- Regular Medical Follow-Up: Adhering to scheduled appointments allows for the timely detection and management of potential side effects.
In conclusion, while furosemide 20mg is an effective medication for managing fluid build-up and related conditions, its use must be carefully monitored due to the potential for significant side effects. By understanding these risks and working closely with healthcare providers, patients can minimize adverse effects and maximize the benefits of this treatment.