What Causes Fibroid Tumor? Effective Uterus Treatment
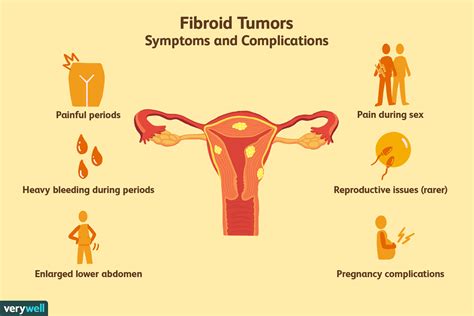
Fibroid tumors, also known as uterine leiomyomas, are benign growths that develop in or around the uterus. These tumors can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain and heavy bleeding. Understanding the causes of fibroid tumors is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies. In this article, we will delve into the potential causes of fibroid tumors and explore the various treatment options available for uterus health.
Hormonal Influence
Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in the development of fibroid tumors. Estrogen and progesterone are two primary hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle and fertility. Fibroid tumors are known to be estrogen-dependent, meaning that they tend to grow in response to estrogen stimulation. This is why fibroids often shrink or disappear after menopause, when estrogen levels decrease. Additionally, genetic predisposition can influence an individual’s sensitivity to hormonal changes, making some women more susceptible to fibroid growth.
Genetic Factors
Research suggests that genetic mutations can contribute to the development of fibroid tumors. Specific genetic alterations can affect the way cells grow and divide, leading to the formation of tumors. Family history also plays a role, as women with a first-degree relative (mother or sister) who has fibroids are more likely to develop them themselves. However, it is essential to note that genetic factors do not guarantee the development of fibroids, and many women without a family history can still be affected.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as diet and lifestyle, may also contribute to the development of fibroid tumors. A diet high in red meat and low in fruits and vegetables has been linked to an increased risk of fibroids. Additionally, exposure to certain environmental toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metals, has been suggested to play a role in the development of fibroids. While the evidence is still limited, maintaining a balanced diet and minimizing exposure to toxins may help reduce the risk of fibroid growth.
Other Potential Causes
Other potential causes of fibroid tumors include:
- Vitamin D deficiency: Research suggests that low levels of vitamin D may contribute to the development of fibroids.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances, which may contribute to fibroid growth.
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase the risk of fibroids, possibly due to the associated hormonal changes.
Effective Uterus Treatment Options
Fortunately, there are various treatment options available for managing fibroid tumors and promoting uterus health. These include:
- Watchful waiting: For small, asymptomatic fibroids, monitoring with regular check-ups and ultrasounds may be sufficient.
- Medications: Hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, can help shrink fibroids or alleviate symptoms.
- Minimally invasive procedures: Options like uterine artery embolization (UAE), magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS), or radiofrequency ablation can reduce fibroid size and alleviate symptoms.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical removal of the fibroid (myomectomy) or the entire uterus (hysterectomy) may be necessary.
FAQ Section
What are the symptoms of fibroid tumors?
+Common symptoms of fibroid tumors include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, and infertility or recurrent miscarriage.
Can fibroid tumors be prevented?
+While there is no guaranteed way to prevent fibroid tumors, maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress may help reduce the risk of development.
Are fibroid tumors cancerous?
+Fibroid tumors are typically benign, meaning they are non-cancerous. However, in rare cases, a type of cancer called uterine leiomyosarcoma can develop, which requires prompt medical attention.
Conclusion
Fibroid tumors are complex growths that can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life. Understanding the potential causes, including hormonal influences, genetic factors, and environmental factors, is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies. By exploring the various treatment options available and consulting with a healthcare provider, women can find relief from fibroid symptoms and promote overall uterus health. Remember, each individual’s experience with fibroids is unique, and a personalized approach to diagnosis and treatment is essential for achieving optimal outcomes.