What Causes Low Co2 In Blood? Symptoms & Remedies
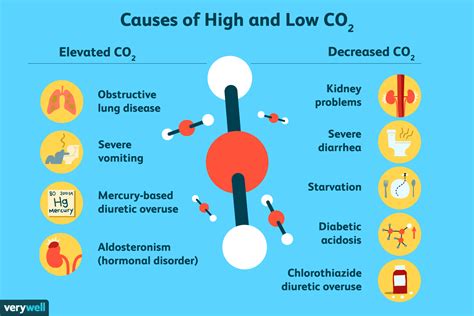
Low CO2 levels in the blood, also known as respiratory alkalosis, occur when the body loses too much carbon dioxide. This condition can be caused by various factors, including hyperventilation, where a person breathes too quickly or deeply, leading to an excessive elimination of CO2 from the bloodstream. Other causes include pneumonia, asthma, and other respiratory diseases that affect the lungs’ ability to regulate gas exchange.
One of the primary mechanisms behind low CO2 levels is the body’s attempt to compensate for an underlying condition. For instance, in the case of an infection or inflammation, the body might hyperventilate in an attempt to increase oxygen delivery to tissues. However, this can lead to an imbalance, where the increase in oxygen is not matched by a corresponding increase in carbon dioxide, resulting in a state of alkalosis.
Symptoms of low CO2 levels can vary but often include dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting due to reduced blood flow to the brain. Muscle cramps, spasms, and tingling sensations are also common, as the altered blood chemistry affects nerve function. Additionally, individuals might experience a numbness or tingling sensation in the fingers and toes, further complicating their condition.
Addressing low CO2 levels typically involves treating the underlying cause. For instance, if the condition is due to hyperventilation caused by anxiety, practicing controlled breathing exercises can help normalize breathing patterns and gradually increase CO2 levels in the blood. In cases of respiratory diseases, medical treatment focuses on managing the disease itself, which in turn helps regulate CO2 levels.
Dietary adjustments can also play a significant role in managing low CO2 levels. Foods with a high acid content can help reduce the body’s alkalinity. Including more protein-rich foods and reducing the intake of alkaline foods like citrus fruits and vegetables can be beneficial. However, these dietary changes should be made under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure they are safe and effective.
In more severe cases, where low CO2 levels lead to significant symptoms, medical intervention may be necessary. This can include administering CO2 directly or using medications that help stabilize breathing patterns. In extreme cases, such as during acute asthma attacks, hospitalization may be required to monitor the condition closely and provide appropriate treatment.
It’s crucial for individuals experiencing persistent or severe symptoms of low CO2 levels to seek medical attention. A healthcare provider can perform the necessary tests, including blood gas analyses, to diagnose the condition accurately and recommend appropriate treatment options.
For those diagnosed with chronic conditions leading to low CO2 levels, managing the condition effectively is key to improving quality of life. This often involves regular follow-ups with healthcare providers, adherence to treatment plans, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments to mitigate the risk of complications.
Steps to Manage Low CO2 Levels:
- Seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause of low CO2 levels.
- Practice controlled breathing exercises to normalize breathing patterns.
- Make dietary adjustments under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Adhere to any prescribed medical treatment.
- Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers to monitor progress and adjust treatment as necessary.
In conclusion, low CO2 levels in the blood can have a significant impact on an individual’s health and quality of life. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing appropriate remedies, individuals can effectively manage this condition and work towards achieving a better balance of CO2 in their blood.
What are the primary symptoms of low CO2 levels in the blood?
+Primary symptoms include dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting, muscle cramps, spasms, and tingling sensations. Individuals might also experience numbness or tingling in the fingers and toes.
How can low CO2 levels be managed?
+Management involves addressing the underlying cause, practicing controlled breathing exercises, making dietary adjustments under professional guidance, and adhering to prescribed medical treatments.
When should an individual seek medical attention for low CO2 levels?
+Individuals should seek medical attention if they experience persistent or severe symptoms, as low CO2 levels can lead to serious health complications if not properly managed.
Ultimately, the key to managing low CO2 levels effectively is a comprehensive approach that includes medical intervention, lifestyle adjustments, and a good understanding of the condition itself. By taking proactive steps and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can mitigate the effects of low CO2 levels and improve their overall health and well-being.