Urge incontinence, a condition characterized by a sudden and intense need to urinate, often accompanied by involuntary loss of urine, affects millions of people worldwide. This type of incontinence can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, causing embarrassment, anxiety, and social isolation. Understanding the causes of urge incontinence is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies.
Neurological Factors
Urge incontinence is often linked to neurological disorders or conditions that affect the normal communication between the brain and the bladder. This miscommunication can lead to an overactive bladder, where the bladder muscles contract involuntarily, even when the bladder is not full. Neurological factors that contribute to urge incontinence include:
- Stroke and Spinal Cord Injuries: These conditions can damage the nerves that control the bladder, leading to Problems with bladder control.
- Multiple Sclerosis and Parkinson’s Disease: These neurological diseases can affect the brain’s ability to send signals to the bladder, resulting in incontinence.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, including those that control bladder function.
Muscular Factors
The muscles in the pelvic floor play a critical role in controlling urination. Weakness or overactivity in these muscles can lead to urge incontinence. Factors that contribute to muscular issues include:
- Aging: As people age, the muscles in the pelvic floor can weaken, leading to a decrease in bladder control.
- Childbirth: Vaginal delivery can weaken the pelvic floor muscles, increasing the risk of incontinence.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put additional pressure on the bladder and pelvic floor muscles, leading to incontinence.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can affect bladder control. Decreases in estrogen levels during menopause can lead to thinner, drier, and less elastic tissues in the urethra and vaginal area, increasing the risk of incontinence.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle choices and conditions can exacerbate urge incontinence. These include:
- Caffeine and Alcohol Consumption: Both are bladder irritants that can increase the urgency and frequency of urination.
- Smoking: Smoking can lead to chronic coughing, which puts additional strain on the pelvic floor muscles.
- Constipation: Straining during bowel movements can weaken pelvic floor muscles.
Treatment Options
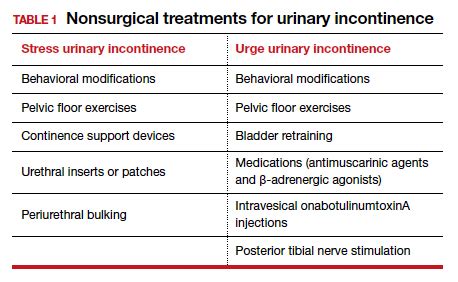
Fortunately, there are several effective treatment options available for urge incontinence. These can be categorized into lifestyle modifications, behavioral techniques, medications, and surgical interventions.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Fluid Management: Limiting fluids or avoiding caffeinated and carbonated beverages can help reduce the urgency and frequency of urination.
- Weight Loss: If obesity is a contributing factor, losing weight can reduce pressure on the bladder and pelvic floor muscles.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can reduce chronic coughing and strain on pelvic muscles.
Behavioral Techniques
- Bladder Training: Gradually increasing the intervals between urinating to train the bladder to hold urine longer.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegel Exercises): Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles through regular exercises can improve bladder control.
- Biofeedback Therapy: Using devices to become aware of physiological responses, such as muscle tension, to learn to control them.
Medications
- Anticholinergics: These medications can help calm an overactive bladder and reduce symptoms of urgency and frequency.
- Mirabegron: A beta-3 adrenergic agonist that helps the bladder muscles to relax, increasing the bladder’s storage capacity.
Surgical Interventions
- Botox Injections: Injecting Botox into the bladder muscle can help reduce muscle spasms and improve bladder control.
- Neuromodulation: Stimulating the nerves that control the bladder can help regulate bladder function.
- Sling Procedures: Surgical placement of a sling to support the urethra and improve bladder control.
Conclusion
Urge incontinence is a treatable condition. By understanding its causes and exploring the various treatment options available, individuals can find relief and improve their quality of life. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan, as what works for one person may not work for another. With the right approach, it is possible to manage urge incontinence effectively and regain control over one’s bladder.
What are the primary causes of urge incontinence?
+Urge incontinence is primarily caused by neurological factors affecting the communication between the brain and the bladder, muscular factors such as weakness in the pelvic floor, hormonal changes, and certain lifestyle factors like caffeine and alcohol consumption.
How can lifestyle modifications help manage urge incontinence?
+Lifestyle modifications such as fluid management, weight loss if necessary, and quitting smoking can significantly help in managing urge incontinence by reducing pressure and strain on the bladder and pelvic floor muscles.
What are the available treatment options for urge incontinence?
+Treatment options for urge incontinence include lifestyle modifications, behavioral techniques like bladder training and pelvic floor exercises, medications such as anticholinergics and mirabegron, and surgical interventions including Botox injections and neuromodulation.