What Does Dehydration Feel Like
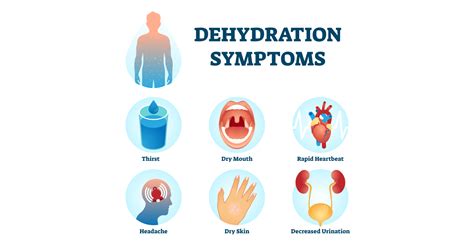
Dehydration is a condition where the body loses more fluids than it takes in, causing an imbalance in the body’s water and electrolyte levels. This can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, that can affect various parts of the body. So, what does dehydration feel like?
Early Signs: In the early stages of dehydration, people may experience a dry mouth, fatigue, and headaches. They may feel a bit lightheaded or dizzy, especially when standing up from a sitting or lying down position. The skin may also start to feel dry and tight, and the urine output may decrease. Some individuals may notice that their urine is darker than usual, which is a sign that the body is concentrating the waste in the urine due to lack of fluids.
Physical Symptoms: As dehydration progresses, the physical symptoms can become more pronounced. The body may start to feel weak and lethargic, making it difficult to perform daily activities. Muscles may cramp, and joints may ache due to the lack of fluids and electrolytes. The heart rate may increase, and blood pressure may drop, leading to dizziness and fainting spells. In severe cases, dehydration can cause seizures, brain damage, and even death.
Emotional and Mental Symptoms: Dehydration can also affect a person’s emotional and mental well-being. They may feel irritable, anxious, and confused, and have difficulty concentrating. Some individuals may experience mood swings, depression, and anxiety attacks. In severe cases, dehydration can cause hallucinations, disorientation, and a loss of consciousness.
Specific Symptoms in Different Parts of the Body: Dehydration can affect various parts of the body in different ways. For example:
- Skin: Dehydration can cause the skin to feel dry, tight, and flaky. It may also lead to skin irritations, such as itching, redness, and rashes.
- Eyes: Dehydration can cause dry, itchy eyes, and blurred vision. In severe cases, it can lead to eye damage and vision loss.
- Mouth and Throat: Dehydration can cause a dry mouth, sore throat, and bad breath. It can also lead to mouth sores, gum recession, and tooth decay.
- Head and Brain: Dehydration can cause headaches, migraines, and brain fog. It can also lead to seizures, brain damage, and coma in severe cases.
- Muscles and Joints: Dehydration can cause muscle cramps, joint pain, and stiffness. It can also lead to muscle weakness, spasms, and paralysis in severe cases.
Who is at Risk: Anyone can experience dehydration, but certain groups are more susceptible. These include:
- Older Adults: Older adults are more prone to dehydration due to age-related changes, such as decreased thirst sensation and reduced ability to regulate body temperature.
- Young Children: Young children are more susceptible to dehydration due to their small body size, high metabolism, and limited ability to communicate their needs.
- Athletes and Individuals with Active Lifestyles: Athletes and individuals with active lifestyles are at risk of dehydration due to excessive sweating and fluid loss.
- People with Chronic Medical Conditions: People with chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and heart failure, are more prone to dehydration due to their underlying health conditions.
Prevention and Treatment: The best way to prevent dehydration is to drink plenty of fluids, especially water, and to eat foods that are rich in water content. It’s also essential to avoid excessive sweating, heat exposure, and strenuous activities, especially in hot weather. If dehydration occurs, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment typically involves replenishing fluids and electrolytes, either orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the condition.
What are the early signs of dehydration?
+The early signs of dehydration include dry mouth, fatigue, headaches, and dark urine. If you experience any of these symptoms, it's essential to drink plenty of fluids and seek medical attention if they persist or worsen.
How can I prevent dehydration?
+To prevent dehydration, drink plenty of fluids, especially water, and eat foods that are rich in water content. Avoid excessive sweating, heat exposure, and strenuous activities, especially in hot weather. It's also essential to monitor your urine output and color, as dark urine can be a sign of dehydration.
What are the consequences of severe dehydration?
+Severe dehydration can lead to seizures, brain damage, and even death. It's essential to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know is experiencing severe dehydration symptoms, such as excessive thirst, dark urine, and decreased urine output.
In conclusion, dehydration is a condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. It’s essential to be aware of the symptoms, risks, and prevention strategies to avoid dehydration and its complications. By drinking plenty of fluids, eating water-rich foods, and monitoring urine output, you can help prevent dehydration and maintain optimal health. If you experience any symptoms of dehydration, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention to ensure prompt treatment and prevent long-term damage.



