What Is A Wart
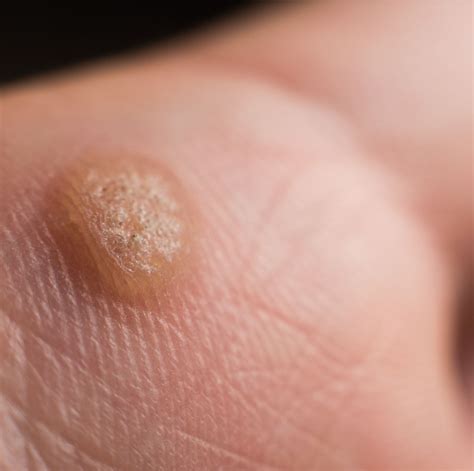
Warts are small, rough growths on the skin that are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can appear anywhere on the body, but are most commonly found on the hands, feet, and face. Warts are highly contagious and can be spread through skin-to-skin contact, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects.
There are several types of warts, including:
- Common warts: These are the most common type of wart and typically appear as small, rough, and rounded growths on the hands or fingers.
- Plantar warts: These warts appear on the soles of the feet and can be painful when walking or standing.
- Flat warts: These warts are small and flat, and can appear in large numbers on the face, hands, or arms.
- Genital warts: These warts appear on the genitals or anus, and are usually spread through sexual contact.
- Filiform warts: These warts are long and thin, and can appear on the face, neck, or armpits.
Warts can be treated with a variety of methods, including:
- Cryotherapy: This involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen, which causes the wart to eventually fall off.
- Salicylic acid: This is a topical treatment that can be applied directly to the wart to help dissolve it.
- Cantharidin: This is a topical treatment that is applied to the wart and causes it to blister and eventually fall off.
- Surgery: In some cases, warts may need to be removed surgically, especially if they are large or in a sensitive area.
- Laser therapy: This involves using a laser to destroy the wart and surrounding tissue.
It’s worth noting that warts can also be treated with home remedies, such as applying duct tape to the wart or using castor oil to help dissolve it. However, these methods are not always effective and may not be recommended by healthcare professionals.
Causes and Risk Factors
Warts are caused by the HPV virus, which is highly contagious and can be spread through:
- Skin-to-skin contact: Touching someone who has a wart can cause the virus to spread.
- Contaminated surfaces: The virus can survive on surfaces for extended periods, making it possible to contract warts through contact with contaminated objects or surfaces.
- Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to contracting warts.
Risk factors for developing warts include:
- Age: Warts are most common in children and young adults.
- Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to contracting warts.
- Skin-to-skin contact: Engaging in activities that involve skin-to-skin contact, such as sports or intimacy, can increase the risk of contracting warts.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing warts typically involves a visual examination by a healthcare professional. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment options for warts vary depending on the type and severity of the wart, as well as the individual’s overall health. Healthcare professionals may recommend a combination of treatments, such as cryotherapy and salicylic acid, to effectively remove the wart.
Complications and Potential Consequences
If left untreated, warts can lead to complications, such as:
- Discomfort or pain: Warts can cause discomfort or pain, especially if they are located on the soles of the feet or in sensitive areas.
- Infection: Warts can become infected, leading to further complications and potentially serious health issues.
- Scarring: Removing warts can cause scarring, especially if the wart is large or in a sensitive area.
- Spread of the virus: Untreated warts can lead to the spread of the HPV virus, which can cause other health issues, such as genital warts or cervical cancer.
How do I know if I have a wart?
+A wart is typically a small, rough growth on the skin that can appear anywhere on the body. If you suspect you have a wart, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Can warts be treated at home?
+While there are home remedies for warts, such as applying duct tape or castor oil, these methods are not always effective and may not be recommended by healthcare professionals. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
How can I prevent the spread of warts?
+To prevent the spread of warts, it's essential to practice good hygiene, avoid sharing personal items, and wear protective footwear in public areas. Additionally, getting vaccinated against HPV can help prevent certain types of warts.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for warts, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent the spread of the virus and effectively manage symptoms. Consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan to ensure the best possible outcome.