What Is A1c Blood Test? Diabetic Control
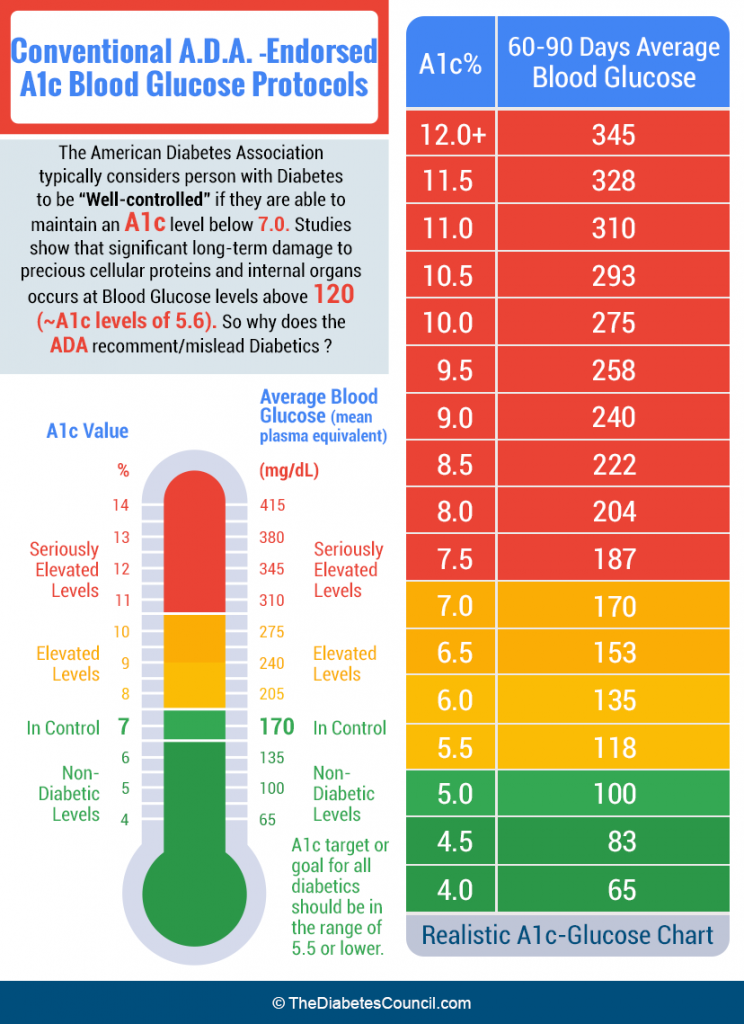
The A1c blood test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, is a crucial diagnostic tool used to measure the average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months. This test is essential for individuals with diabetes, as it helps assess the effectiveness of their treatment plan and provides valuable insights into their blood sugar control.
How Does the A1c Test Work?
The A1c test measures the percentage of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. When glucose enters the bloodstream, it attaches to hemoglobin, forming a compound called glycated hemoglobin. The more glucose in the blood, the more hemoglobin gets glycated. Since red blood cells have a lifespan of approximately 120 days, the A1c test can reflect average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months.
Why is the A1c Test Important for Diabetic Control?
The A1c test is a vital component of diabetes management, as it:
- Assesses blood sugar control: The test helps determine how well an individual’s blood sugar levels have been managed over time.
- Evaluates treatment effectiveness: By monitoring A1c levels, healthcare providers can adjust treatment plans to achieve better blood sugar control.
- Predicts complications risk: Studies have shown that high A1c levels are associated with an increased risk of diabetes-related complications, such as kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
- Identifies potential health issues: The test can detect abnormal blood sugar levels, even if symptoms are not apparent, allowing for early intervention and prevention of long-term damage.
Interpreting A1c Results
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following A1c targets for individuals with diabetes:
- Less than 5.7%: Normal blood sugar control
- 5.7% to 6.4%: Prediabetes or impaired glucose regulation
- 6.5% or higher: Diabetes
For individuals with diabetes, the ADA recommends an A1c goal of:
- Less than 7%: For most adults
- Less than 7.5%: For adults with a history of severe hypoglycemia, limited life expectancy, or extensive insulin use
- Less than 8%: For adults with significant comorbidities or a history of severe hyperglycemia
Factors That Can Affect A1c Results
Several factors can influence A1c results, including:
- Red blood cell lifespan: Conditions that affect red blood cell lifespan, such as anemia or blood transfusions, can impact A1c results.
- Hemoglobin variants: Certain hemoglobin variants, such as sickle cell disease or thalassemia, can affect A1c measurements.
- Kidney or liver disease: These conditions can alter glucose metabolism and affect A1c results.
- Pregnancy: A1c levels can be lower during pregnancy due to changes in red blood cell lifespan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the A1c blood test is a valuable tool for assessing diabetic control and evaluating the effectiveness of treatment plans. By understanding the importance of the A1c test and its results, individuals with diabetes can work with their healthcare providers to achieve better blood sugar control and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the normal range for A1c levels?
+A normal A1c level is less than 5.7%. However, the target A1c level for individuals with diabetes may vary depending on their specific situation and healthcare provider’s recommendations.
How often should I get an A1c test?
+The frequency of A1c testing depends on your individual situation and your healthcare provider’s recommendations. Typically, A1c tests are performed every 3 to 6 months for individuals with diabetes.
Can I use the A1c test to diagnose diabetes?
+The A1c test can be used to diagnose diabetes, but it is not the only diagnostic tool. A diagnosis of diabetes is typically made based on a combination of A1c results, fasting plasma glucose levels, and symptoms.



