What Is A1c Blood Test? Your Diabetes Answer
The A1c blood test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, is a crucial diagnostic tool used to assess the average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months. This test is particularly important for individuals with diabetes, as it provides valuable insights into how well their blood sugar levels are being managed. In essence, the A1c test measures the percentage of glucose that has attached to hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, giving healthcare providers a clear picture of long-term glucose control.
Understanding How the A1c Test Works
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. When glucose is present in the blood, it can bind to hemoglobin, forming a compound called glycated hemoglobin or hemoglobin A1c. The more glucose in the blood, the more hemoglobin gets glycated. Since red blood cells have a lifespan of approximately 120 days, measuring the level of glycated hemoglobin can give an indication of the average blood glucose levels over the preceding 2 to 3 months.
Why is the A1c Test Important?
The A1c test is important for several reasons:
Assessment of Diabetes Control: For individuals with diabetes, the A1c test is a key indicator of how well their diabetes is being managed. It helps in adjusting treatment plans, including medications, diet, and exercise, to achieve better blood sugar control.
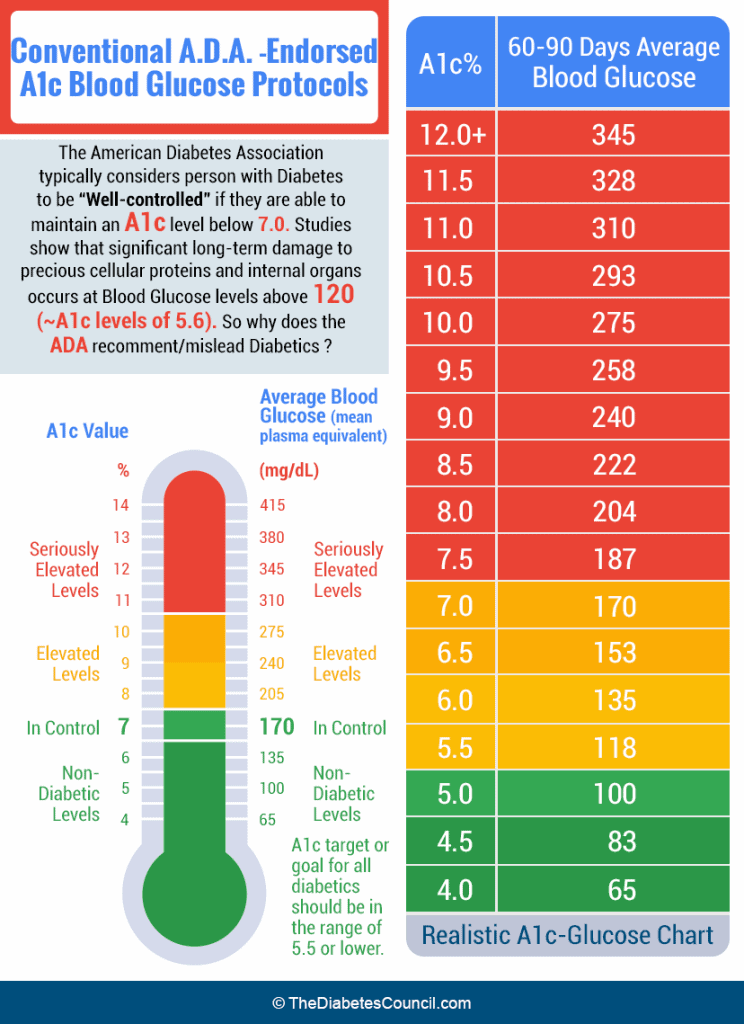
Diagnosis of Diabetes: The A1c test can also be used as a diagnostic tool for diabetes and prediabetes. The American Diabetes Association recommends an A1c level of 6.5% or higher for the diagnosis of diabetes.
Risk Assessment: Elevated A1c levels are associated with an increased risk of complications from diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. Therefore, achieving and maintaining a target A1c level is crucial for preventing these complications.
What Do A1c Results Mean?
- Normal: Less than 5.7% - This range is typically considered normal and suggests that the individual is at low risk for developing diabetes.
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4% - This range indicates an increased risk of developing diabetes and suggests the need for lifestyle changes to prevent the onset of diabetes.
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher - This level confirms the diagnosis of diabetes.
How Often Should the A1c Test be Done?
The frequency of A1c testing depends on the individual’s condition and the stability of their diabetes management plan. Generally, individuals with diabetes are advised to have an A1c test at least twice a year if their diabetes is well-controlled and they are meeting treatment goals. If diabetes control is poor or if changes are made to the treatment plan, the test may be performed more frequently, such as every 3 months.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve A1c Levels
Improving A1c levels involves a combination of dietary changes, increased physical activity, and, if prescribed, adherence to medication regimens. Some key strategies include:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet that is low in sugar, saturated fats, and salt. Increasing the intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage blood glucose levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps the body use insulin more efficiently, reducing blood glucose levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can raise blood glucose levels. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Conclusion
The A1c blood test is a powerful tool for managing diabetes and preventing its complications. By understanding the implications of A1c levels and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals with diabetes can achieve better control over their condition and improve their overall health and quality of life. Regular monitoring and adjustments to treatment plans based on A1c results are crucial for effective diabetes management.
What is the ideal A1c level for someone with diabetes?
+The American Diabetes Association recommends an A1c goal for many adults with diabetes as less than 7%. However, this goal may be adjusted based on individual characteristics, such as duration of diabetes, life expectancy, resources, and support system. For example, a less stringent A1c goal (such as <8%) may be appropriate for patients with a history of severe hypoglycemia, limited life expectancy, advanced microvascular or macrovascular complications, extensive insulin use, or those with a history of inadequate health care.
How can I lower my A1c levels naturally?
+To lower your A1c levels naturally, focus on dietary changes such as reducing carbohydrate intake, increasing fiber consumption, and eating foods with a low glycemic index. Regular physical activity, such as walking or other aerobic exercises, can also significantly improve insulin sensitivity and lower A1c levels. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can contribute to better blood glucose control.
Can A1c levels be affected by factors other than blood glucose?
+Yes, A1c levels can be influenced by factors other than blood glucose. These include red blood cell lifespan, which can be affected by conditions such as anemia or blood disorders, and certain medications. Additionally, conditions like kidney and liver disease can also impact A1c results. It's essential to discuss any potential influences on A1c levels with your healthcare provider to ensure accurate interpretation of test results.
In conclusion, the A1c blood test is a vital tool for assessing and managing diabetes. By understanding the test, its implications, and how lifestyle changes can impact A1c levels, individuals can take proactive steps towards better diabetes control and a healthier life.



