What Is Cardiac Rehab
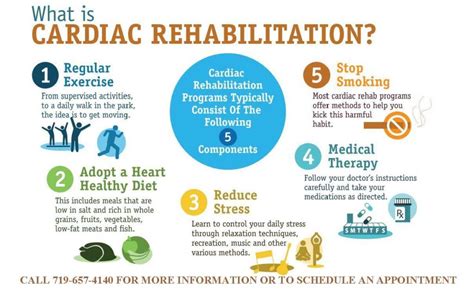
Cardiac rehabilitation, commonly referred to as cardiac rehab, is a comprehensive program designed to help individuals recover from cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks, heart failure, and coronary artery bypass grafting. The primary goal of cardiac rehab is to improve the patient’s overall health, reduce the risk of future heart problems, and enhance their quality of life.
A typical cardiac rehab program consists of three phases, each with specific objectives and interventions. Phase 1 begins in the hospital, immediately after a cardiac event or surgery, and focuses on stabilizing the patient’s condition, managing pain and discomfort, and initiating basic mobilization and education. Phase 2 takes place in an outpatient setting, usually several weeks after discharge, and emphasizes exercise training, education, and lifestyle modification. Phase 3 is a long-term maintenance program that helps patients maintain a healthy lifestyle, manage risk factors, and prevent future cardiac events.
Cardiac rehab programs often include a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, such as cardiologists, nurses, exercise physiologists, dietitians, and psychologists. These team members work together to provide individualized care, guidance, and support to patients and their families. The program’s components may vary depending on the patient’s specific needs, but common elements include:
- Exercise training: Supervised exercise sessions, such as aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises, to improve cardiovascular health and functional capacity.
- Education: Classes, workshops, and one-on-one sessions to teach patients about heart-healthy lifestyle habits, such as nutrition, stress management, and medication management.
- Risk factor modification: Strategies to help patients manage and reduce cardiovascular risk factors, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and smoking.
- Psychological support: Counseling and therapy to address emotional and psychological aspects of cardiac disease, such as anxiety, depression, and coping mechanisms.
- Monitoring and follow-up: Regular check-ups and monitoring to track progress, adjust treatment plans, and prevent complications.
The benefits of cardiac rehab are numerous and well-documented. Participants can expect to:
- Improve cardiovascular health: Enhance heart function, reduce symptoms, and increase functional capacity.
- Reduce mortality risk: Decrease the likelihood of future cardiac events, such as heart attacks and strokes.
- Enhance quality of life: Improve overall well-being, increase energy levels, and reduce disability.
- Improve mental health: Reduce anxiety, depression, and stress, and enhance coping mechanisms.
- Increase adherence to healthy habits: Develop and maintain healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management.
In addition to the traditional components of cardiac rehab, many programs now incorporate innovative and evidence-based approaches, such as:
- Telehealth: Remote monitoring and virtual consultations to increase accessibility and convenience.
- Mobile health apps: Digital tools to track progress, monitor vital signs, and provide personalized feedback.
- Mind-body therapies: Integrative therapies, such as meditation, yoga, and cognitive-behavioral therapy, to address emotional and psychological aspects of cardiac disease.
- Community-based initiatives: Partnerships with local organizations and community centers to promote cardiovascular health and provide support services.
What are the eligibility criteria for cardiac rehab?
+Eligibility criteria for cardiac rehab vary depending on the program and the patient's specific needs. Generally, patients with a history of heart attack, coronary artery bypass grafting, heart failure, or other cardiovascular conditions are eligible. Patients should consult with their healthcare provider to determine if cardiac rehab is right for them.
How long does a typical cardiac rehab program last?
+The duration of a cardiac rehab program can vary, but it typically lasts several weeks to several months. Phase 1 may last a few weeks, while Phase 2 and Phase 3 can last several months to a year or more.
Is cardiac rehab covered by insurance?
+Cardiac rehab is often covered by insurance, including Medicare and Medicaid. However, coverage and reimbursement policies may vary depending on the insurance provider and the specific program. Patients should check with their insurance provider to determine the extent of their coverage.
In conclusion, cardiac rehab is a comprehensive and evidence-based program designed to help individuals recover from cardiovascular diseases and improve their overall health and well-being. By incorporating a multidisciplinary approach, innovative technologies, and community-based initiatives, cardiac rehab programs can provide patients with the tools and support they need to achieve optimal health outcomes and reduce the risk of future cardiac events.