What Is Cbc Test
The Complete Blood Count (CBC) test, also known as a full blood count or blood panel, is a comprehensive diagnostic tool used to evaluate various components of the blood. It is one of the most commonly ordered blood tests, providing valuable information about the different types of cells in the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What does a CBC test measure?
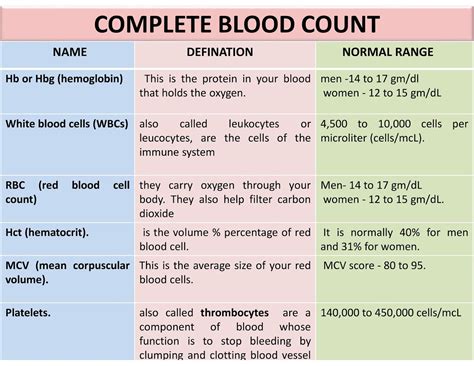
A CBC test measures several parameters, including:
- Red Blood Cell (RBC) count: The number of red blood cells in the blood, which carry oxygen to different parts of the body.
- Hemoglobin (Hb): The amount of hemoglobin in the blood, which is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
- Hematocrit (Hct): The proportion of red blood cells in the blood.
- White Blood Cell (WBC) count: The number of white blood cells in the blood, which help fight infections.
- Platelet count: The number of platelets in the blood, which help the blood to clot.
- Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV): The average size of red blood cells.
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH): The average amount of hemoglobin in red blood cells.
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC): The average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells.
- Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW): The variation in the size of red blood cells.
- White Blood Cell Differential: The proportion of different types of white blood cells, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
Why is a CBC test ordered?
A CBC test is ordered for various reasons, including:
- Routine health check-ups: To monitor overall health and detect potential problems early.
- Diagnosis of anemia: To evaluate the severity of anemia and its underlying cause.
- Infection or inflammation: To detect and monitor infections, such as bacterial or viral infections, or inflammatory conditions, such as autoimmune disorders.
- Blood disorders: To diagnose and monitor blood disorders, such as leukemia, lymphoma, or bleeding disorders.
- Monitoring medication effects: To monitor the effects of medications that can affect blood cells, such as chemotherapy or antibiotics.
How is a CBC test performed?
A CBC test is performed by drawing a blood sample from a vein, usually in the arm, using a needle and syringe. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What are the normal ranges for a CBC test?
The normal ranges for a CBC test vary depending on the laboratory and the individual’s age, sex, and other factors. Here are some general normal ranges:
- RBC count: 4.32-5.72 million cells per microliter (µL)
- Hemoglobin: 13.5-17.5 grams per deciliter (g/dL)
- Hematocrit: 40.7-50.3%
- WBC count: 3,500-10,500 cells per µL
- Platelet count: 150,000-450,000 cells per µL
Abnormal results may indicate various conditions, such as anemia, infection, inflammation, or blood disorders. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to interpret the results and determine the next course of action.
What is the purpose of a CBC test?
+The purpose of a CBC test is to evaluate various components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, to diagnose and monitor a range of conditions, including anemia, infection, inflammation, and blood disorders.
What are the normal ranges for a CBC test?
+The normal ranges for a CBC test vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. However, general normal ranges include: RBC count: 4.32-5.72 million cells per microliter (µL), Hemoglobin: 13.5-17.5 grams per deciliter (g/dL), Hematocrit: 40.7-50.3%, WBC count: 3,500-10,500 cells per µL, and Platelet count: 150,000-450,000 cells per µL.
What does a CBC test measure?
+A CBC test measures several parameters, including red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, white blood cell count, platelet count, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, and red cell distribution width.
In conclusion, a CBC test is a valuable diagnostic tool used to evaluate various components of the blood, providing essential information for diagnosing and monitoring a range of conditions. By understanding what a CBC test measures and its normal ranges, individuals can better comprehend their test results and work with their healthcare providers to make informed decisions about their health.