What Is Methylprednisolone? Effective Relief Guide
Methylprednisolone is a synthetic corticosteroid that belongs to the class of medications known as glucocorticoids. It is widely used to treat various inflammatory conditions, autoimmune diseases, and severe allergic reactions. As a potent anti-inflammatory agent, methylprednisolone works by suppressing the immune system’s response to inflammation, thereby reducing swelling, redness, and pain in the affected areas.
History and Development
Methylprednisolone was first introduced in the 1950s as a more potent and longer-acting alternative to other corticosteroids. Its development marked a significant milestone in the treatment of inflammatory conditions, offering improved efficacy and reduced side effects compared to earlier medications. Today, methylprednisolone is one of the most commonly prescribed corticosteroids, available in various forms, including tablets, injections, and topical creams.
How Methylprednisolone Works
Methylprednisolone exerts its therapeutic effects by binding to specific receptors in the body, which triggers a cascade of events that ultimately lead to the reduction of inflammation. This process involves the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines, the suppression of immune cell activation, and the induction of anti-inflammatory genes. As a result, methylprednisolone effectively reduces the production of inflammatory mediators, such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes, which contribute to the development of inflammation and tissue damage.
Therapeutic Applications
Methylprednisolone has a broad range of therapeutic applications, including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Methylprednisolone is used to reduce joint inflammation and slow disease progression.
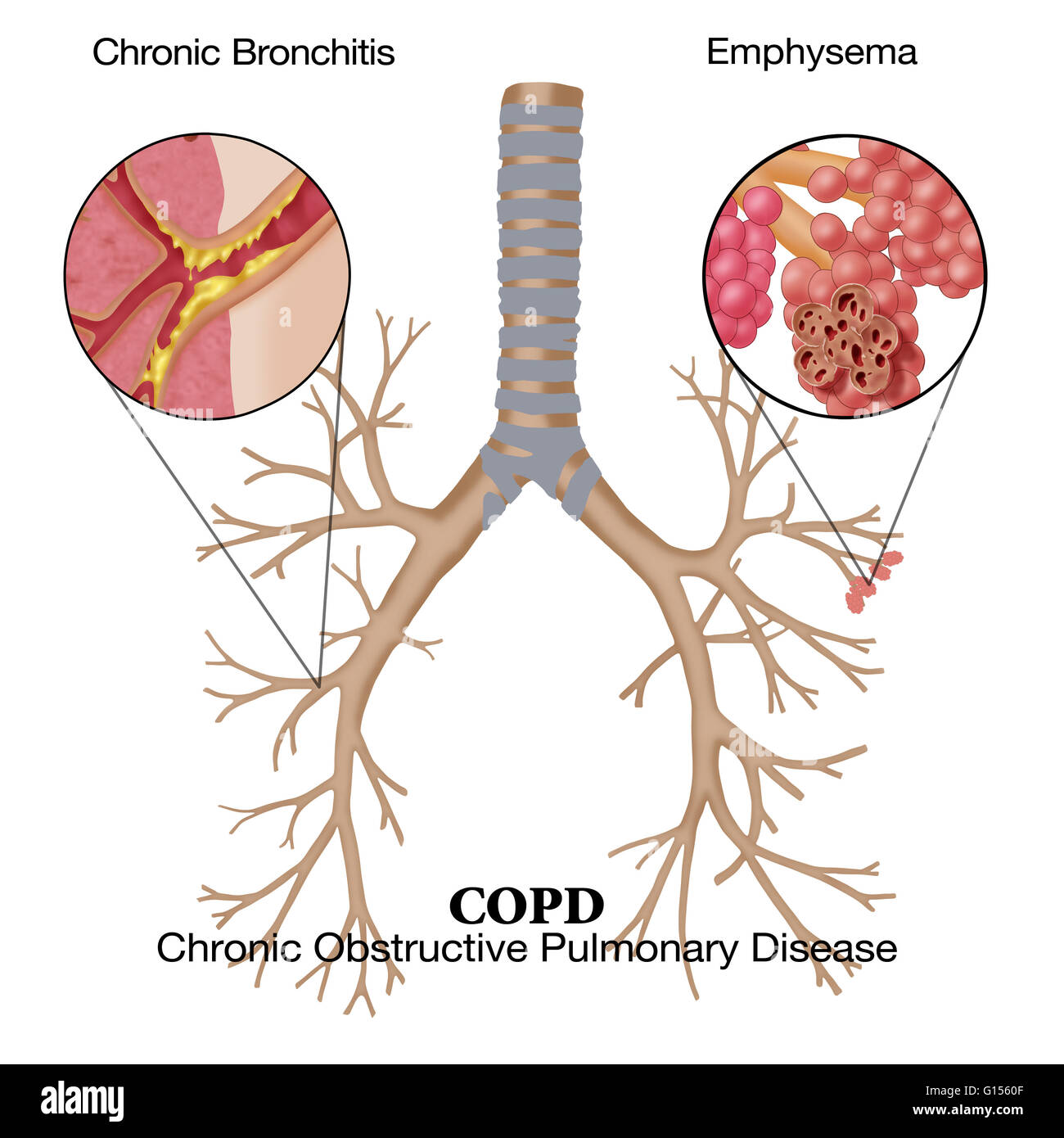
- Asthma: It helps to control asthma symptoms by reducing airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness.
- Allergic reactions: Methylprednisolone is effective in treating severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis and angioedema.
- Skin conditions: It is used to treat various skin conditions, including psoriasis, eczema, and dermatitis.
- Eye and ear conditions: Methylprednisolone is used to treat inflammatory conditions of the eye, such as uveitis, and ear conditions, such as otitis media.
Administration and Dosage
Methylprednisolone can be administered orally, intravenously, or topically, depending on the specific condition being treated. The dosage and duration of treatment vary widely, ranging from short-term use for acute conditions to long-term use for chronic diseases. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and treatment schedule to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Side Effects and Precautions
While methylprednisolone is generally well-tolerated, it can cause a range of side effects, including:
- Weight gain: Increased appetite and water retention can lead to weight gain.
- Mood changes: Mood swings, anxiety, and insomnia are common side effects.
- Increased blood sugar: Methylprednisolone can cause hyperglycemia, particularly in patients with diabetes.
- Osteoporosis: Long-term use can lead to bone thinning and osteoporosis.
To minimize the risk of side effects, it is crucial to:
- Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly check blood sugar levels, especially in patients with diabetes.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eat a balanced diet to minimize weight gain and maintain bone health.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in regular exercise to maintain bone density and overall health.
- Attend follow-up appointments: Regularly scheduled appointments with your healthcare provider can help monitor treatment efficacy and minimize side effects.
Interactions and Contraindications
Methylprednisolone can interact with various medications, including:
- Anticoagulants: Increased risk of bleeding when combined with anticoagulants.
- Diuretics: Increased risk of hypokalemia (potassium deficiency) when combined with diuretics.
- Insulin: Adjust insulin dosage as needed to maintain blood sugar control.
Methylprednisolone is contraindicated in patients with:
- Active infections: Methylprednisolone can exacerbate infections, such as tuberculosis.
- Peptic ulcers: Increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding when combined with NSAIDs.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Methylprednisolone can pass into breast milk and affect fetal development.
What is the typical dosage of methylprednisolone for rheumatoid arthritis?
+The typical dosage of methylprednisolone for rheumatoid arthritis ranges from 4-16 mg per day, depending on the severity of symptoms and disease activity.
Can I take methylprednisolone with other medications?
+It is essential to consult your healthcare provider before taking methylprednisolone with other medications, as interactions can occur. Your healthcare provider can help you minimize the risk of interactions and ensure safe treatment.
How long does it take for methylprednisolone to start working?
+The onset of action for methylprednisolone varies depending on the condition being treated. In general, improvements in symptoms can be seen within 1-3 days, but it may take several weeks to achieve optimal therapeutic effects.
In conclusion, methylprednisolone is a powerful corticosteroid that offers effective relief for various inflammatory conditions. While it can cause side effects, careful monitoring and adherence to prescribed treatment schedules can minimize risks. By understanding the therapeutic applications, administration, and potential interactions of methylprednisolone, patients can work with their healthcare providers to achieve optimal treatment outcomes and improve their overall quality of life.