What Is Metoprolol Er Succinate 50Mg? Dosage Guide
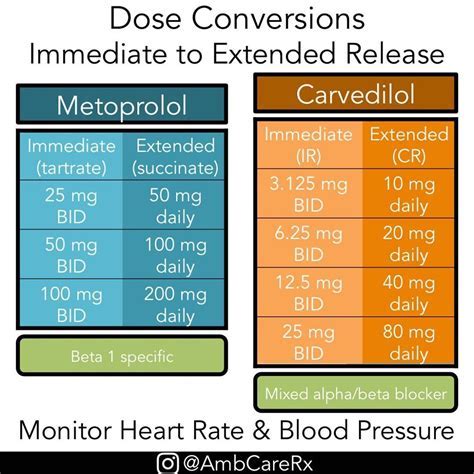
Metoprolol ER succinate 50mg is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as beta-blockers. It is used to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, and heart failure. The “ER” in its name stands for extended-release, indicating that the medication is designed to release the active ingredient, metoprolol succinate, slowly over a period of time, allowing for once-daily dosing.
What is MetoprololUsed For?
Metoprolol succinate is primarily used for the treatment of:
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): To lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
- Angina Pectoris: To reduce the frequency and severity of angina attacks.
- Heart Failure: To improve survival and reduce the risk of hospitalization in patients with heart failure.
- Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack): To reduce the risk of death and reinfarction in patients who have had a heart attack.
Dosage Guide
The dosage of metoprolol ER succinate varies depending on the condition being treated. Here are some general guidelines:
For Hypertension: The usual initial dose is 50mg to 100mg once daily. The dose may be increased at weekly intervals until optimal blood pressure control is achieved. The maximum dose is 400mg once daily.
For Angina Pectoris: The initial dose is typically 100mg once daily. The dose may be increased to 200mg once daily if needed.
For Heart Failure: The dose starts at 25mg once daily for one week, then increases to 50mg once daily. Further increases can be made at weekly intervals, up to 200mg once daily, as tolerated by the patient.
For Myocardial Infarction (Post-MI): Treatment with metoprolol succinate may be initiated as soon as the patient’s condition allows. The dose should be individualized and is typically around 50mg every 6 hours for the first 48 hours, transitioning to a sustained-release form as soon as possible.
Important Considerations
Dose Titration: It’s crucial to titrate the dose of metoprolol succinate gradually to minimize side effects and allow the body to adjust to its effects.
Combination Therapy: Metoprolol succinate can be used in combination with other antihypertensive agents, though careful monitoring is required to avoid excessive blood pressure reduction.
Contraindications: It’s contraindicated in patients with severe bradycardia, heart block greater than first degree, cardiogenic shock, and decompensated heart failure.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Metoprolol should be used with caution in pregnant women and those who are breastfeeding, as it can pose risks to the fetus or baby.
Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, fatigue, shortness of breath, and nausea. More severe side effects may include bronchospasm, cardiac arrhythmias, and severe allergic reactions.
Conclusion
Metoprolol ER succinate 50mg is an effective medication for managing cardiovascular conditions. Its extended-release formulation allows for once-daily dosing, enhancing compliance. However, it’s essential to follow the dosage guide, monitor side effects, and adjust the dose under the guidance of a healthcare provider to maximize benefits while minimizing risks.


