What Is Normal Diabetes Sugar Level Chart? Easy Management
For individuals living with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing complications. A normal diabetes sugar level chart provides a guideline for individuals to understand the target ranges for their blood glucose levels. This chart is typically used in conjunction with a blood glucose meter and a logbook to track and manage diabetes effectively.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
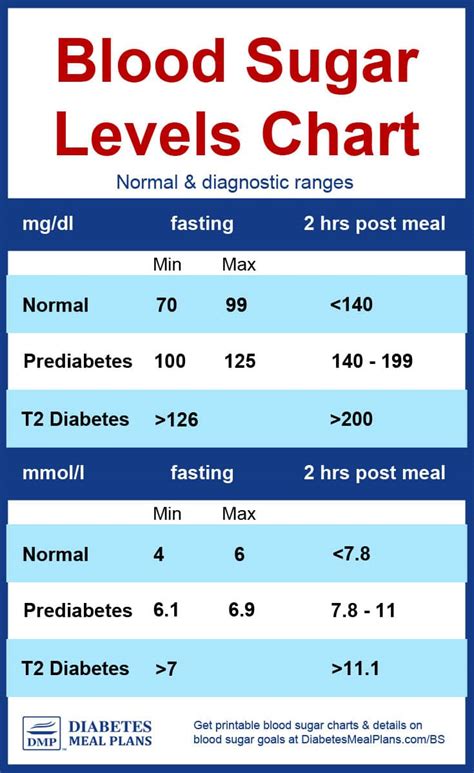
Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following target blood glucose levels for people with diabetes:
- Before meals (preprandial): 80-130 mg/dL (4.4-7.2 mmol/L)
- After meals (postprandial): Less than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L)
- At bedtime: 100-140 mg/dL (5.6-7.8 mmol/L)
- At fasting (not eaten for at least 8 hours): Less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) for people without diabetes, and less than 130 mg/dL (7.2 mmol/L) for those with diabetes.
Creating a Personalized Diabetes Management Plan
While these targets serve as a general guideline, it’s essential to work with a healthcare provider to create a personalized diabetes management plan. This plan should take into account the individual’s lifestyle, medication regimen, dietary preferences, and physical activity level.
Key Components of a Diabetes Management Plan:
- Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels to understand how different factors (such as diet, exercise, and medication) affect levels throughout the day.
- Medication Adherence: Taking diabetes medications as prescribed by the healthcare provider.
- Healthy Eating: Following a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, and low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, to help lower blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Stress Management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, as stress can raise blood glucose levels.
Easy Management Tips
Managing diabetes requires a holistic approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and adherence to a treatment plan. Here are some easy management tips:
- Keep a Logbook: Recording blood glucose levels, meals, physical activity, and medication can help identify patterns and make informed decisions about diabetes care.
- Meal Planning: Working with a dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan that balances carbohydrate intake with insulin sensitivity and physical activity.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water to help the body regulate blood sugar levels and prevent dehydration.
- Regular Check-Ups: Scheduling regular appointments with a healthcare provider to monitor progress, adjust the treatment plan as needed, and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes is a ongoing process that requires dedication, patience, and the right guidance. By understanding normal diabetes sugar level charts, creating a personalized management plan, and incorporating easy management tips into daily life, individuals with diabetes can achieve better control over their blood sugar levels and improve their overall quality of life.
What are the target blood glucose levels for people with diabetes?
+The American Diabetes Association recommends the following target blood glucose levels for people with diabetes: before meals (preprandial) - 80-130 mg/dL, after meals (postprandial) - less than 180 mg/dL, at bedtime - 100-140 mg/dL, and at fasting - less than 130 mg/dL.
How often should I monitor my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of monitoring blood glucose levels depends on the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and individual needs. Generally, people with type 1 diabetes may need to check their levels more frequently than those with type 2 diabetes.
What are the benefits of keeping a logbook for diabetes management?
+Keeping a logbook helps identify patterns in blood glucose levels, allowing for informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication. It also facilitates communication with healthcare providers and can lead to better control over diabetes.
In conclusion, managing diabetes effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes understanding target blood glucose levels, creating a personalized management plan, and incorporating lifestyle changes. By following these guidelines and staying committed to their care, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.



