What Is Normal Sugar Level Range? Healthy Targets
Understanding the normal sugar level range is crucial for maintaining good health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar levels, measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), indicate the amount of glucose present in the blood. The body’s primary source of energy is glucose, which comes from the food we eat. The hormone insulin, produced by the pancreas, helps to regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the entry of glucose into cells.
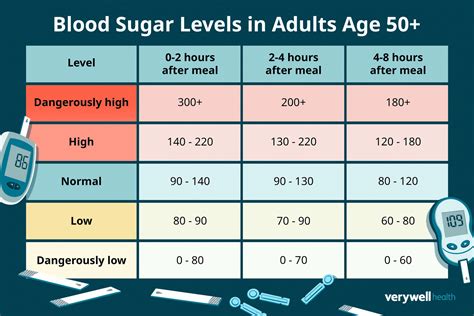
For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels typically fall within specific ranges throughout the day. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) provides guidelines for blood sugar levels:
- Fasting Blood Sugar: 70 mg/dL to 99 mg/dL (less than 100 mg/dL) after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours.
- After Eating (Postprandial): Less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after a meal. This is because after eating, the body absorbs glucose from the food, causing blood sugar levels to rise. The peak usually occurs about 1-2 hours after eating.
For people with diabetes, the target blood sugar ranges are slightly different, as managing diabetes involves keeping levels within a target range to prevent complications:
- Before Meals: 70 mg/dL to 130 mg/dL for many adults, though this can vary.
- After Meals: Less than 180 mg/dL 1 to 2 hours after the start of eating.
- At Bedtime: 100 mg/dL to 140 mg/dL, though this might vary based on individual health goals and the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) during the night.
It’s essential to understand that these are general guidelines. Your healthcare provider might set different targets for you based on factors like age, other health conditions, the risk of low blood sugar, duration of diabetes, and lifestyle. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes may have slightly different targets as well.
Maintaining blood sugar levels within these healthy targets requires a combination of dietary management, regular physical activity, and, if prescribed, medication or insulin therapy. Monitoring blood sugar levels throughout the day helps individuals understand how different factors, such as food choices, physical activity, and stress, can affect their levels, enabling them to make informed decisions about their care.
Moreover, individuals should be aware of the signs of high and low blood sugar to take prompt action when levels are not within the target range. Symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can include shakiness, sweating, hunger, dizziness, palpitations, confusion, or irritability.
Regular health check-ups and discussing any concerns or questions with a healthcare provider are crucial for managing blood sugar levels effectively and preventing the long-term complications associated with diabetes and blood sugar imbalances.
Practical Tips for Healthy Blood Sugar Management
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help the body regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Monitor Carbohydrates: Understanding the carbohydrate content of foods and managing portion sizes can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Include Physical Activity: Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity and can help control blood sugar levels.
- Eat Regular Meals: Skipping meals can lead to Overeating and poor food choices, negatively affecting blood sugar control.
- Reduce Stress: Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
- Get Enough Sleep: Lack of quality sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate hunger and fullness, leading to poor food choices and negatively affecting blood sugar control.
- Choose Whole Foods: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to support blood sugar management and overall health.
By understanding the normal sugar level range, recognizing the importance of maintaining healthy targets, and incorporating practical management strategies into daily life, individuals can better control their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of related health complications.



