What Is Sulfameth Used For
Sulfamethoxazole, commonly referred to as sulfameth, is an antibiotic that belongs to the sulfonamide class. It is used in combination with trimethoprim (a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor) to form a widely used antibiotic combination known as co-trimoxazole or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX). This combination is effective against a broad spectrum of bacterial infections.
Mechanism of Action
Sulfamethoxazole works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria. It does this by interfering with the production of folic acid, which is essential for the synthesis of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) in bacteria. When used in combination with trimethoprim, the synergistic effect of the two drugs enhances the antimicrobial activity, making it more effective against a wider range of bacteria.
Common Uses
The sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim combination is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including:
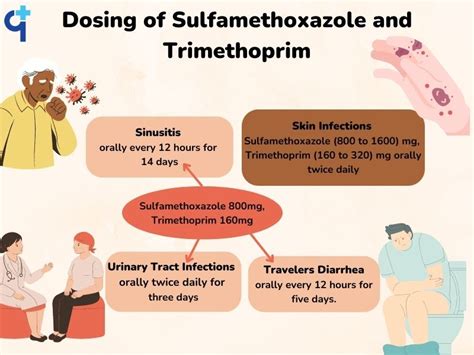
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): It is commonly used to treat UTIs caused by susceptible strains of E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, and other bacteria.
- Respiratory Tract Infections: It is used to treat respiratory infections such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and sinusitis caused by susceptible bacteria.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: It is effective against skin and soft tissue infections, including abscesses, cellulitis, and wound infections.
- Gastrointestinal Infections: It is used to treat gastrointestinal infections, including salmonellosis and shigellosis.
- Prostatitis: It is used to treat prostatitis, an inflammation of the prostate gland.
- Traveler’s Diarrhea: It is used to treat traveler’s diarrhea caused by susceptible bacteria.
- Pneumocystis Jirovecii Pneumonia: It is used to treat and prevent Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) in patients with HIV/AIDS.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim vary depending on the specific infection being treated, the patient’s age, weight, and kidney function. It is usually taken orally in the form of tablets or suspension, and the typical dose is 800-1600 mg of sulfamethoxazole and 160-320 mg of trimethoprim per day, divided into two or three doses.
Side Effects and Contraindications
While sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. It is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to sulfonamides or trimethoprim, as well as in patients with severe kidney or liver impairment.
Interactions with Other Medications
Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim can interact with other medications, including blood thinners, diabetes medications, and certain antidepressants. It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking before starting treatment with sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim.
What is the difference between sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim?
+Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are two different antibiotics that work together to treat bacterial infections. Sulfamethoxazole inhibits the production of folic acid in bacteria, while trimethoprim inhibits the use of folic acid by bacteria.
Can I take sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim if I have a sulfur allergy?
+No, if you have a known allergy to sulfonamides, you should not take sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim. However, a sulfur allergy is not the same as a sulfonamide allergy. If you have a sulfur allergy, consult your healthcare provider before taking sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim.
How long does it take for sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim to start working?
+The length of time it takes for sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim to start working varies depending on the specific infection being treated. In general, you may start to notice improvement within 24-48 hours of starting treatment.
It is essential to use sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim only under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as misuse or overuse can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Additionally, patients should be aware of the potential side effects and interactions with other medications to ensure safe and effective treatment.


