What Is Thoracentesis
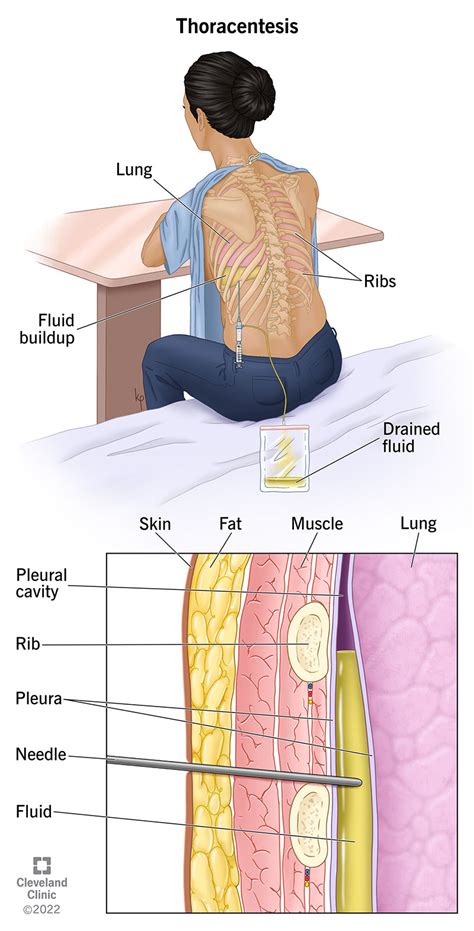
Thoracentesis, also known as pleural fluid aspiration or pleurocentesis, is a medical procedure used to remove fluid or air from the pleural space, which is the area between the lungs and the chest wall. This procedure is often performed to diagnose and treat various conditions affecting the lungs and pleura, such as pleural effusion, pneumonia, and lung cancer.
The pleural space is a thin, fluid-filled gap between the lungs and the chest wall that helps to reduce friction during breathing. Under normal conditions, the pleural space contains a small amount of fluid, known as pleural fluid, which is produced by the pleura, a thin membrane that lines the lungs and chest wall. However, in certain conditions, excess fluid can accumulate in the pleural space, leading to a pleural effusion.
There are two types of thoracentesis: diagnostic and therapeutic. Diagnostic thoracentesis is performed to collect a sample of pleural fluid for laboratory analysis, which can help diagnose the underlying cause of the pleural effusion. Therapeutic thoracentesis, on the other hand, is performed to remove excess fluid from the pleural space, which can help to relieve symptoms such as shortness of breath and chest pain.
The procedure of thoracentesis typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The patient is usually seated or lying on their side, with their arms raised above their head. The skin is cleaned and disinfected, and a local anesthetic is injected to numb the area.
- Insertion of the needle: A needle is inserted into the pleural space, usually between the ribs, and guided by ultrasound or chest X-ray to ensure accurate placement.
- Aspiration of fluid: The needle is connected to a syringe or a drainage system, and the fluid is slowly aspirated from the pleural space.
- Collection of specimen: A sample of the pleural fluid is collected for laboratory analysis, which can include tests such as cytology, microbiology, and biochemistry.
- Removal of the needle: The needle is removed, and the site is covered with a dressing to prevent infection.
Thoracentesis is a relatively safe procedure, but it can be associated with certain risks and complications, such as:
- Pneumothorax: Air can leak into the pleural space, leading to a collapsed lung.
- Hemothorax: Blood can leak into the pleural space, leading to a blood-filled chest cavity.
- Infection: Bacteria can enter the pleural space, leading to an infection.
- Damage to surrounding structures: The needle can accidentally puncture surrounding structures, such as the lung, diaphragm, or blood vessels.
To minimize the risks associated with thoracentesis, it is essential to perform the procedure under the guidance of an experienced healthcare professional, using proper technique and sterile equipment.
In terms of indications, thoracentesis is often performed to diagnose and treat conditions such as:
- Pleural effusion: Excess fluid accumulation in the pleural space, which can be caused by conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, and lung cancer.
- Pneumonia: Infection of the lungs, which can cause fluid accumulation in the pleural space.
- Lung cancer: Cancer of the lungs, which can cause fluid accumulation in the pleural space.
- Pulmonary embolism: Blockage of the blood vessels in the lungs, which can cause fluid accumulation in the pleural space.
Overall, thoracentesis is a valuable medical procedure that can help to diagnose and treat various conditions affecting the lungs and pleura. By understanding the procedure, its indications, and its potential risks and complications, healthcare professionals can provide high-quality care to patients with pleural effusions and other related conditions.
In conclusion, thoracentesis is a safe and effective procedure when performed under the guidance of an experienced healthcare professional. By understanding the procedure, its indications, and its potential risks and complications, healthcare professionals can provide high-quality care to patients with pleural effusions and other related conditions.
What is the purpose of thoracentesis?
+The purpose of thoracentesis is to remove fluid or air from the pleural space, which can help to diagnose and treat conditions such as pleural effusion, pneumonia, and lung cancer.
What are the risks associated with thoracentesis?
+The risks associated with thoracentesis include pneumothorax, hemothorax, infection, and damage to surrounding structures. However, these risks can be minimized by performing the procedure under the guidance of an experienced healthcare professional, using proper technique and sterile equipment.
How is thoracentesis performed?
+Thoracentesis is performed by inserting a needle into the pleural space, guided by ultrasound or chest X-ray, and aspirating fluid for laboratory analysis or therapeutic relief. The procedure typically involves the following steps: preparation, insertion of the needle, aspiration of fluid, collection of specimen, and removal of the needle.


